JVM基础 -- 异常处理
抛出异常 + 捕获异常
抛出异常
- 显式抛异常的主体是应用程序,使用throw关键字
- 隐式抛异常的主体是JVM,在JVM执行过程中,碰到无法继续执行的异常状态时,自动抛出异常
- 例如ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
捕获异常
- try代码块
- 标记需要异常监控的代码
- catch代码块
- 定义了针对指定类型的异常处理器
- 多个catch代码块,JVM会从上至下匹配异常处理器
- 前面catch代码块所捕获的异常类型不能覆盖后边的,否则编译器会报错
- finally代码块
- 声明一段必定运行的代码
- 程序正常执行,未抛出异常,try -> finally
- 程序抛出异常未被捕获,try(throw A) -> finally -> throw A
- 程序抛出异常并被捕获,try(throw A) -> catch(A) -> finally
- 程序抛出异常并被捕获,并且catch代码块也抛出异常,try(throw A) -> catch(A, throw B) -> finally -> throw B
- finally代码块抛出异常,中断finally代码块的执行,往外抛出异常
基本概念
继承关系
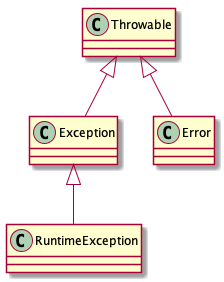
- 所有异常都是Throwable的子类
- Error
- 应用程序不应该捕获的异常
- 当程序触发Error时,已经无法恢复,需要终止线程甚至终止JVM
- Exception
- 应用程序需要捕获的异常(RuntimeException除外)
- RuntimeException和Error属于Java的unchecked exception,其他异常属于checked exception
- 所有checked exception都需要显式捕获或在方法声明中用throws关键词标注
- 通常情况下,程序自定义的异常应该为checked exception,以便于最大化利用Java编译器的编译时检查
- 异常实例的构造是非常昂贵的
- 在构造异常实例时,JVM需要生成该异常的栈轨迹(stack trace)
- 该操作会逐一访问当前线程的Java栈帧,并且记录下各种调试信息
- 栈帧所指向方法的名字,方法所在的类名、文件名,以及在代码中的第几行触发该异常
- 在生成stack trace的时候,JVM会忽略掉异常构造器以及填充栈帧的Java方法(Throwable.fillInStackTrace),直接从新建异常位置开始算起
- JVM还会忽略标记为不可见的方法栈帧
- 即使代价昂贵,依旧不推荐缓存异常实例,容易误导开发人员
捕获异常的机制
Java代码
1 | try { |
字节码
1 | stack=1, locals=3, args_size=1 |
- 编译生成的字节码中,每个方法都附带一个异常表,异常表中的每一个条目代表一个异常处理器
- 条目组成:from指针、to指针、target指针和所捕获的异常类型
- 这里的指针的值指的是字节码索引,用于定位字节码
- from指针和to指针(不含)标示了该异常处理器所监控的范围
- target指针指向异常处理器的起始位置
- 当程序触发异常时,JVM虚拟机会从上而下遍历异常表中的所有条目
- 当触发异常的字节码的索引值在某个异常表条目的监控范围内,JVM会判断所抛出的异常与该条目想要捕获的异常是否匹配
- 如果匹配,JVM会将控制流转移到该条目的target指针指向的字节码
- 如果遍历完所有异常条目,JVM仍未匹配到异常处理器,那么会弹出当前方法所对应的栈帧,并且在调用者中重复上述操作
- 最坏情况:JVM需要遍历当前线程Java栈上所有方法的异常表
finally代码块
- 复制finally代码块的内容,分别放在try-catch代码块的正常执行路径出口以及异常执行路径出口
- 针对异常执行路径,Java编译器会生成一个或多个异常表条目,监控整个try-catch代码块,并且捕获所有种类的异常(any)
- 这些异常表条目的target指针将指向另一份复制的finally代码块
- 在这个代码块最后,Java编译器会重新抛出所捕获的异常
Java代码
1 | public class Foo { |
字节码
1 | stack=2, locals=3, args_size=1 |
- 编译结果包含三份finallyBlock代码块
- 前两份分别位于try代码块和catch代码块的正常执行路径出口
- 最后一份作为异常处理器,监控try代码块和catch代码块,用于捕获两类异常
- try代码块触发的,未被catch代码块捕获的异常
- catch代码块触发的异常
- 如果catch代码块捕获了异常A,并且触发异常B,那么finally捕获并重新抛出的是异常B
- 原本的异常会被忽略掉,对于代码调试非常不方便
Supressed异常+语法糖
- Java 7引入Supressed异常来解决上述问题,允许将一个异常附于另一个异常之上
- 抛出的异常可以附带多个异常的信息
- 语法糖:try-with-resources
- 在字节码层面自动使用Supressed异常
Java代码
1 |
|
输出
1 | Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: Init |
字节码
1 | 103: astore 9 |
同时捕获多个异常
Java代码
1 | public class T { |
字节码
1 | stack=1, locals=3, args_size=1 |
参考资料
All articles on this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless otherwise stated.