JVM进阶 -- MAT
概念
Shallow Heap + Retained Heap
Shallow Heap
Shallow heap is the memory consumed by one object. An object needs 32 or 64 bits (depending on the OS architecture) per reference, 4 bytes per Integer, 8 bytes per Long, etc. Depending on the heap dump format the size may be adjusted (e.g. aligned to 8, etc…) to model better the real consumption of the VM.
Retained Set
Retained set of X is the set of objects which would be removed by GC when X is garbage collected.
Retained Heap
Retained heap of X is the sum of shallow sizes of all objects in the retained set of X, i.e. memory kept alive by X.
Generally speaking, shallow heap of an object is its size in the heap and retained size of the same object is the amount of heap memory that will be freed when the object is garbage collected.
 The **Minimum Retained Size** gives a good (under)estimation of the retained size which is calculated ways **faster** than the exact retained size of a set of objects. It only depends on the number of objects in the **inspected set**, not the number of objects in the heap dump.
The **Minimum Retained Size** gives a good (under)estimation of the retained size which is calculated ways **faster** than the exact retained size of a set of objects. It only depends on the number of objects in the **inspected set**, not the number of objects in the heap dump.
Dominator Tree
Memory Analyzer provides a dominator tree of the object graph. The transformation of the object reference graph into a dominator tree allows you to easily identify the biggest chunks of retained memory and the keep-alive dependencies among objects.
Dominate
An object x dominates an object y if every path in the object graph from the start (or the root) node to y must go through x.
Immediate Dominator
The immediate dominator x of some object y is the dominator closest to the object y.
Properties
- The objects belonging to the sub-tree of x (i.e. the objects dominated by x) represent the retained set of x.
- If x is the immediate dominator of y , then the immediate dominator of x also dominates y , and so on.
- The edges in the dominator tree do not directly correspond to object references from the object graph.
 A dominator tree is built out of the object graph. In the dominator tree each object is the **immediate dominator** of its **children**, so dependencies between the objects are easily identified.
A dominator tree is built out of the object graph. In the dominator tree each object is the **immediate dominator** of its **children**, so dependencies between the objects are easily identified.
Overview

Dominator Tree
No Grouping(Objects)

Group By Class

Group By Class Loader
纬度:组件
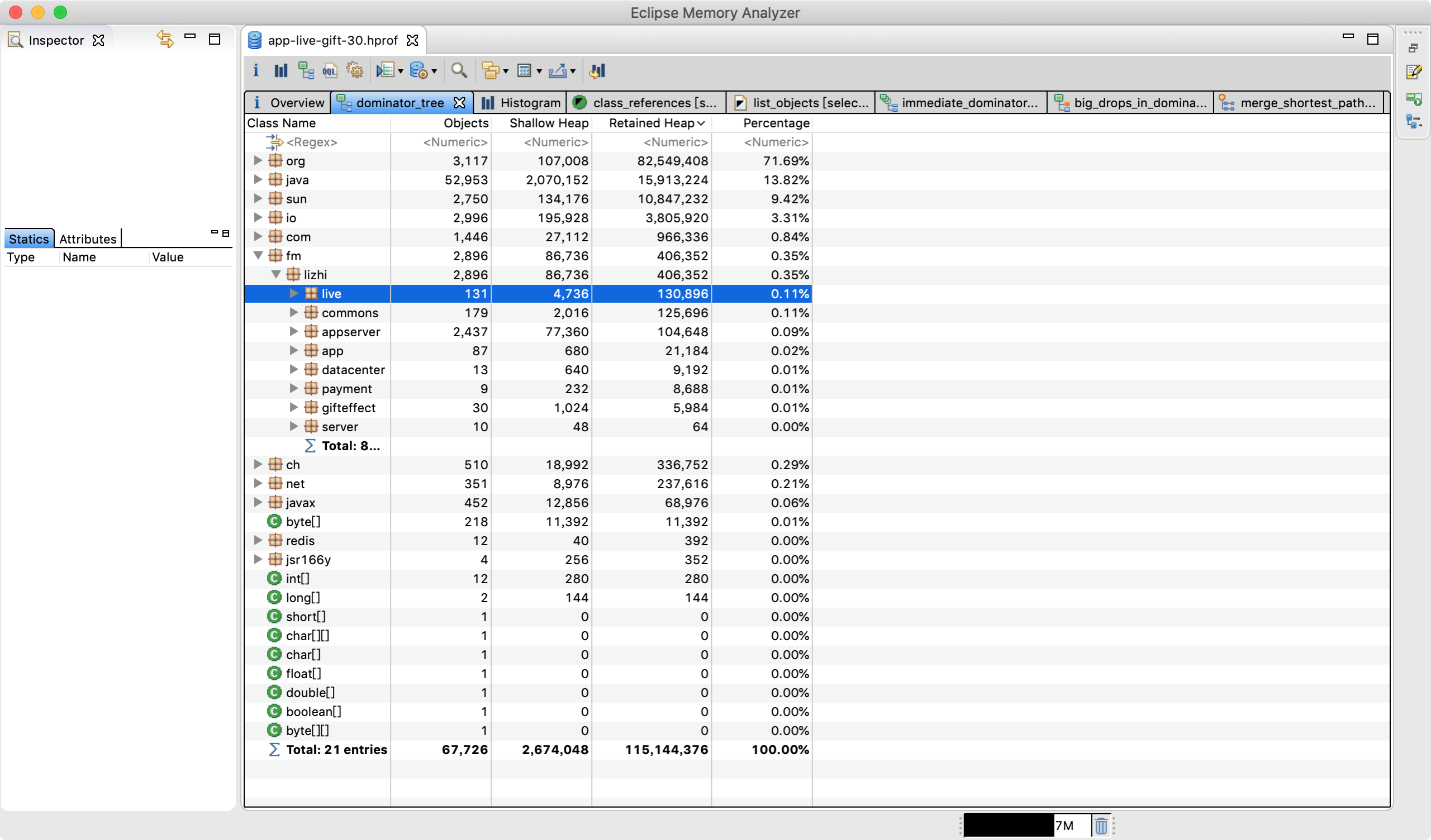
Group By Package
纬度:自身编写的代码
Path To GC Roots


Histogram
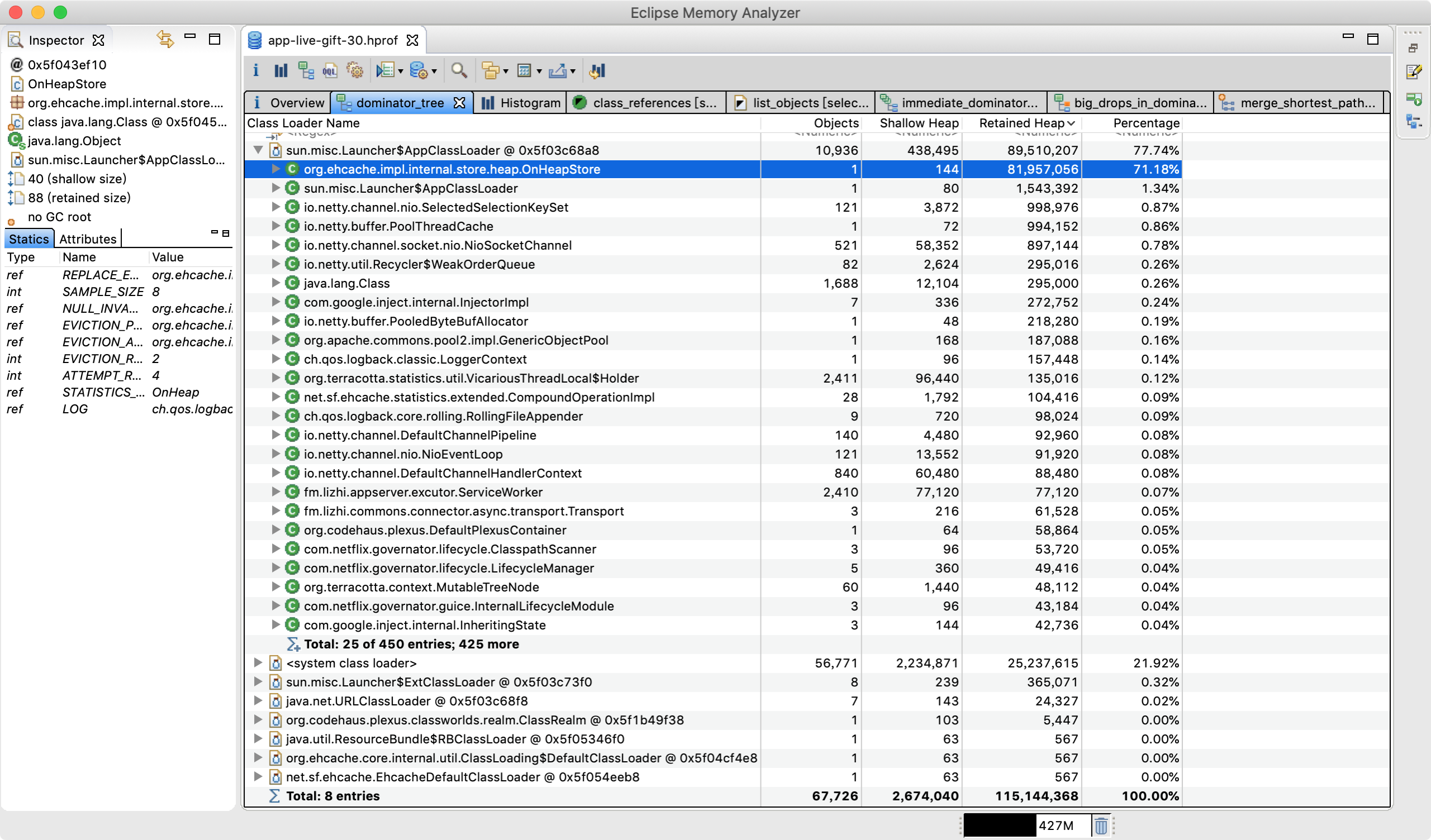
 MAT默认按**Shallow Heap**倒排,手动选择按**Retained Heap**倒排,排第一的是**Ehcache**的**OnHeapStore**类
MAT默认按**Shallow Heap**倒排,手动选择按**Retained Heap**倒排,排第一的是**Ehcache**的**OnHeapStore**类
List objects


Immediate Dominator


Merge Shortest Path To GC Roots