实现结构
- HashMap是基于哈希表实现的,继承了AbstractMap并且实现了Map接口
- HashMap根据键的Hash值来决定对应值的存储位置,通过这种索引方式,HashMap获取数据的速度会非常快
- 当发生哈希冲突时,有3种常用的解决方法:开放定址法、再哈希函数法、链地址法
- 开放定址法
- 当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被填满,说明在哈希表中必然还有空位置
- 可以把Key存放到冲突位置后面的空位置上
- 该方法存在很多问题,例如查找、扩容等,不推荐
- 再哈希函数法
- 在同义词产生地址冲突时再计算另一个哈希函数地址,直到不再冲突
- 这种方法不容易产生聚集,但却增加了计算时间
- 链地址法
- HashMap综合考虑了所有因素,采用了链地址法来解决哈希冲突问题
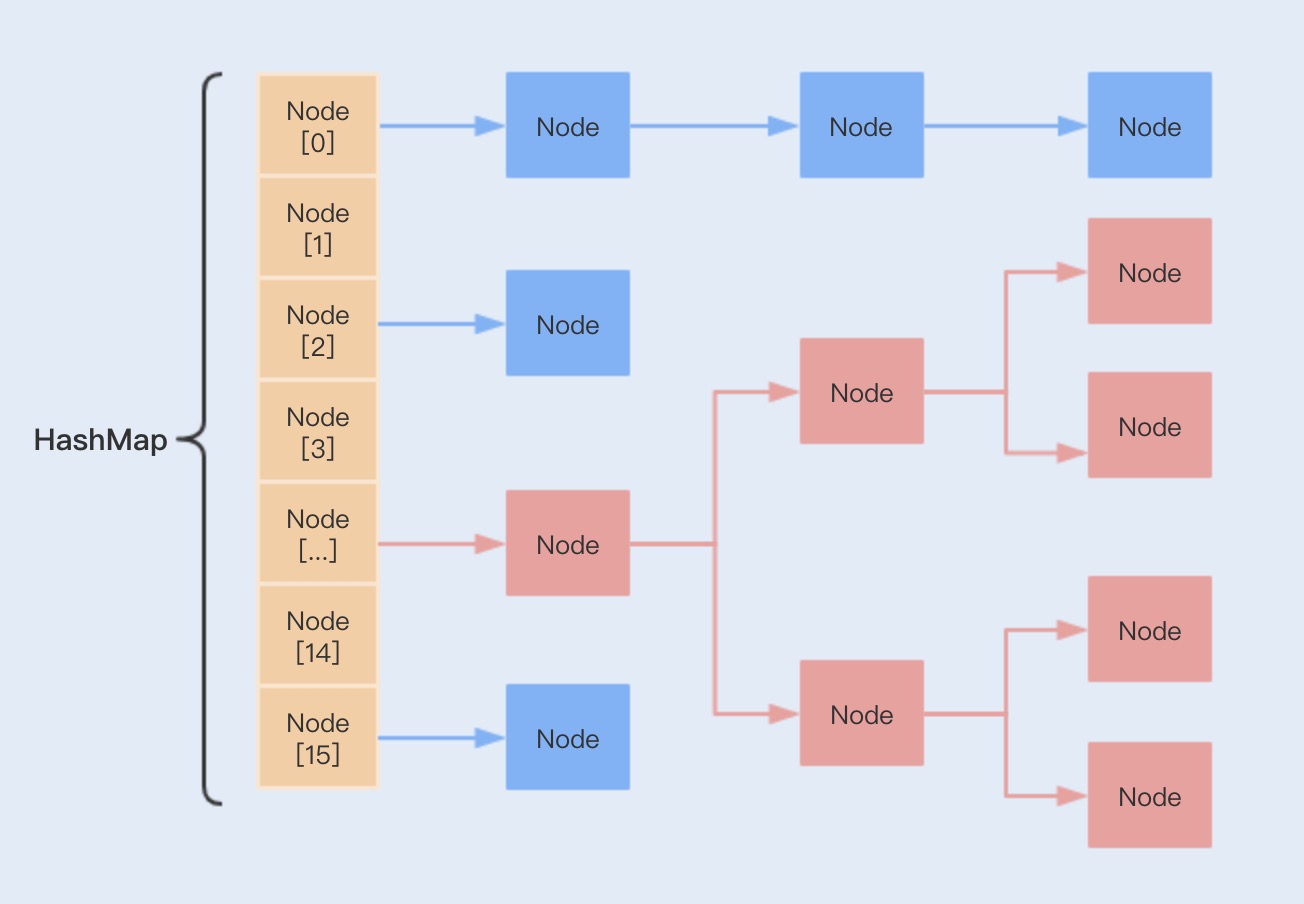
- 该方法采用了数组(哈希表)+链表的数据结构,当发生哈希冲突时,就用一个链表结构存储相同Hash值的数据
重要属性
Node
HashMap是由一个Node数组构成的,每个Node包含一个Key-Value键值对
1
| transient Node<K,V>[] table;
|
Node类是HashMap的一个内部类,定义了一个next指针,指向具有相同hash值的Node对象,构成链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
| static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
}
|
loadFactor + threshold
1
2
| int threshold;
final float loadFactor;
|
- HashMap还有两个重要的属性:加载因子(loadFactor)和边界值(threshold)
- loadFactor用来间接设置Entry数组(哈希表)的内存空间大小,默认值为0.75
- 对于使用链表法的哈希表来说,查找一个元素的平均时间为
O(1+n),n为遍历链表的长度
- 加载因子越大,对空间的利用越充分,链表的长度越长,查找效率越低
- 加载因子太小,哈希表的数据将过于稀疏,对空间造成严重浪费
- Entry数组的threshold是通过初始容量和loadFactor计算所得
优化
添加元素
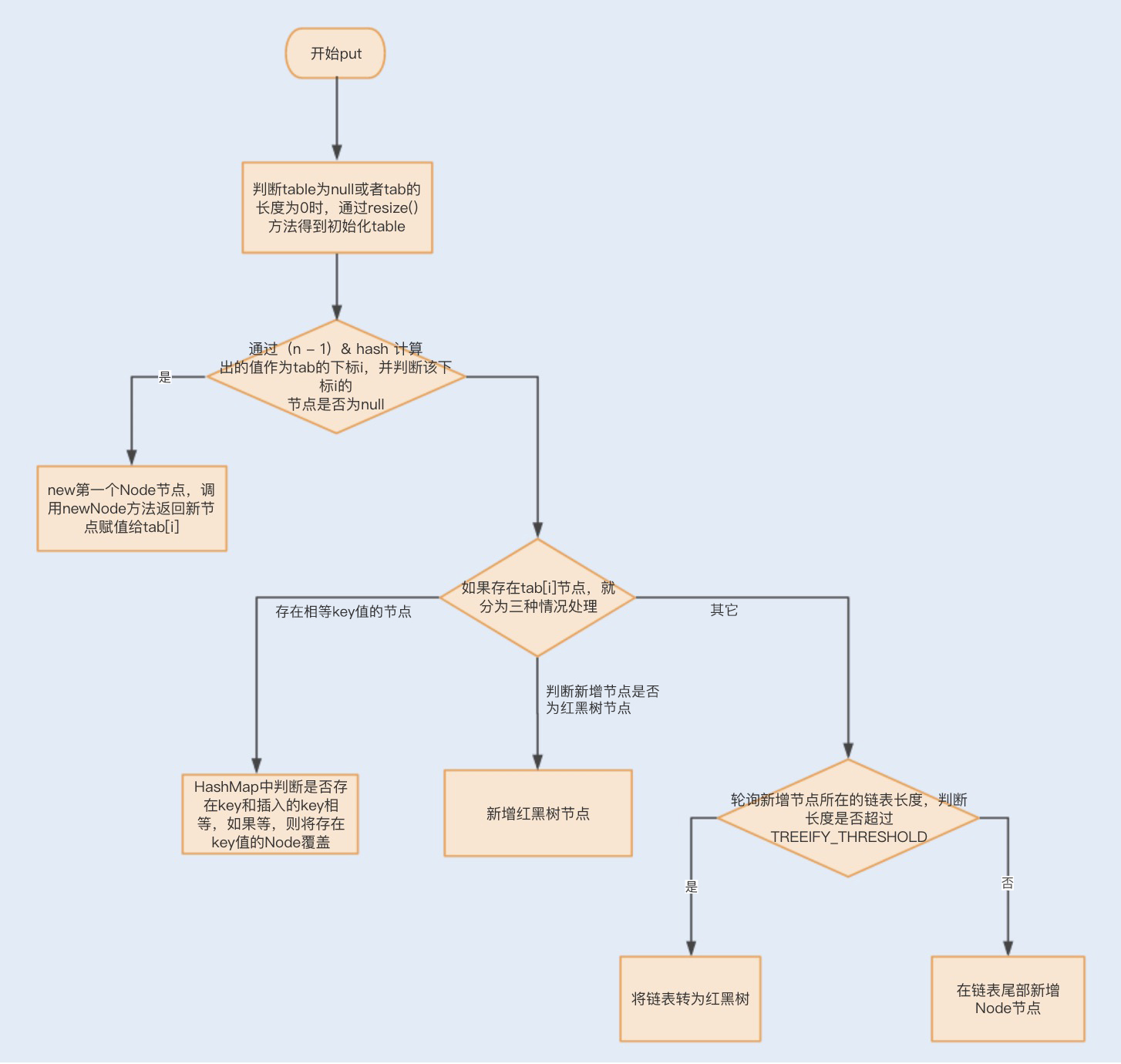
根据key的hashCode()返回值,再通过hash()计算出hash值,再通过(n-1)&hash决定Node的存储位置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
|
流程

putVal
在JDK 1.8中,HashMap引入了红黑树数据结构来提升链表的查询效率(当链表的长度超过8,红黑树的查询效率比链表高)
当链表长度超过8,HashMap会将链表转换为红黑树,此时新增元素会存在左旋和右旋,因此效率会降低
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
|
获取元素
- 当HashMap中只存在数组,而数组中没有Node链表时,是HashMap查询数据性能最好的时候
- 一旦发生大量的哈希冲突,就会产生Node链表,这时每次查询都可能遍历Node链表,从而降低查询性能
- 特别在链表长度过长的情况下,性能将明显降低,而红黑树能很好地解决了这个问题
- 使得查询的平均时间复杂度降低到
O(log(n)),链表越长,使用红黑树替换后的查询效率提升越明显
- 也可以重写Key的hashCode方法,降低哈希冲突,从而减少链表的产生
扩容
- HashMap也是数组类型的数据结构,也一样存在扩容的情况
- JDK 1.7
- 分别取出数组元素,一般该元素是最后一个放入链表的元素
- 然后遍历以该元素为头的单向链表元素,依据每个被遍历元素的hash值计算其在新数组中的下标,然后进行交换
- 将原来哈希冲突的单向链表尾部变成扩容后单向链表的头部
- JDK 1.8
- 扩容数组的长度是2倍的关系,假设初始tableSize=4要扩容到8,就是0100到1000的变化
- 在扩容时,只需要判断原来hash值与oldCap的按位与结果,重新分配索引
hash & oldCap == 0,说明旧有的索引就能覆盖hash & oldCap == 1,说明旧有的索引不能覆盖,索引需要+oldCap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else {
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
|
小结
- HashMap通过哈希表的数据结构来存储键值对,好处:查询效率高
- 如果查询操作比较频繁,可以适当减小loadFactor,如果对内存利用率要求比较高,可以适当增加loadFactor
- 在预知存储数据量的情况下,可以提前设置初始容量(初始容量 = 预知数据量 / 加载因子)
- 可以减少resize()操作,提高HashMap的效率
- HashMap使用数组+链表方式实现链地址法,当有哈希冲突时,将冲突的键值对链成一个链表
- 如果链表过长,查询数据的时间复杂度会增加,HashMap在JDK 1.8中使用红黑树来解决这个问题

参考资料
Java性能调优实战