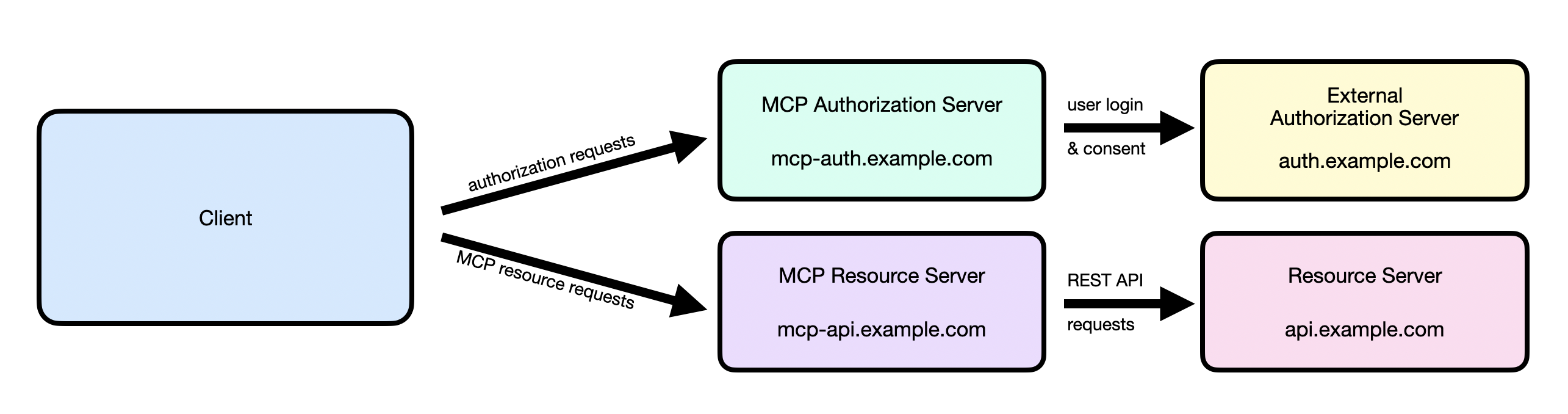
OpenTelemetry vs Prometheus 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 关系概述:互补为主,渐趋融合 OpenTelemetry 和 Prometheus 在指标领域主要是互补关系,而非冲突。两个项目都在积极合作以实现更好的互操作性。 1. 定位差异 Prometheus: - 完整的监控系统(采集、存储、查询、告警) - 专注于指标监控 - 拉模型(Pull-based)为主 - 拥有成熟的时序数据库和查询语言 PromQL OpenTelemetry: - 标准化的遥测数据收集框架 - 支持三大信号:指标、追踪、日志 - 推模型(Push-based)为主 - 不提供存储和查询后端 2. 技术模型对比 | 特性 | Prometheus | OpenTelemetry | |------|---------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------| | 数据模型 | 简单的时序数据模型 | 复杂的三层数据模型 | | 传输协议 | HTTP/文本格式 | OTLP(二进制协议) | | 指标类型 | Counter、Gauge、Histogram、Summary | Counter、Gauge、Histogram、Exponential Histogram | | 命名规范 | 下划线分隔(如 http_requests_total) | 点号分隔(如 http.requests.total) | | 数据收集 | Pull(拉取) | Push(推送) | 3. 兼容性发展历程 过去的挑战(Prometheus 2.0时代) - 命名规范不兼容 - 指标类型映射复杂 - 数据模型转换困难 现状的改善(Prometheus 3.0时代) - Prometheus 3.0 原生支持 OTLP 指标摄入 - UTF-8 标准化:支持点号命名,避免自动转换为下划线 - 双向转换:支持 Prometheus ↔ OpenTelemetry 数据转换 - 标准化规范:官方的互操作性规范 4. 集成模式 模式1:OpenTelemetry → Prometheus 应用程序 → OTel SDK → OTel Collector → Prometheus - 使用 OpenTelemetry Collector 作为桥梁 - 支持多种导出器:Prometheus Remote Write、Prometheus Exporter 模式2:Prometheus → OpenTelemetry 应用程序 → Prometheus Exporter → OTel Collector → 后端存储 - OTel Collector 充当 Prometheus Server 角色 - 抓取 Prometheus 格式指标并转换为 OTLP 模式3:混合部署 ┌─────────────────┐ │ OTel Collector │ └─────────┬───────┘ │ ┌──────────────┼──────────────┐ │ │ │ ┌────▼────┐ ┌─────▼─────┐ ┌───▼───┐ │Prometheus│ │其他OTLP后端│ │Grafana │ └─────────┘ └───────────┘ └───────┘ 5. 实际使用建议 选择 OpenTelemetry 的情况: - 需要统一的三信号观测(指标+追踪+日志) - 希望供应商中立的解决方案 - 需要更丰富的上下文关联 - 计划多云或混合云部署 选择 Prometheus 的情况: - 主要关注基础设施监控 - 已有成熟的 Prometheus 生态 - 需要 PromQL 的强大查询能力 - 团队对 Prometheus 更熟悉 混合使用的情况: - 利用 OpenTelemetry 进行应用观测 - 使用 Prometheus 进行基础设施监控 - 通过 OTel Collector 统一数据流 6. 未来发展趋势 1. 深度融合:Prometheus 3.0+ 将深度集成 OpenTelemetry 2. 标准统一:CNCF 推动统一的可观测性标准 3. 生态互补:两个项目继续发挥各自优势 4. 无缝迁移:提供平滑的迁移路径 总结 OpenTelemetry 和 Prometheus 的关系已经从早期的"冲突"转向"互补和融合"。它们不是竞争关系,而是: - 互补关系:OpenTelemetry 提供标准化的数据收集,Prometheus 提供强大的存储和查询 - 融合趋势:Prometheus 3.0+ 原生支持 OpenTelemetry,两个生态系统正在深度整合 - 最佳实践:根据具体需求选择合适的组合方案 对于新项目,建议采用 OpenTelemetry 进行标准化观测,同时可以选择 Prometheus 作为后端存储之一,实现灵活性和兼容性的平衡。
Getting started
This guide is a “Hello World “-style tutorial which shows how to install , configure , and use a simple Prometheus instance .
You will download and run Prometheus locally
configure it to scrape itself and an example application , then work with queries , rules , and graphs to use collected time series data .
Downloading and running Prometheus Download the latest release of Prometheus for your platform, then extract and run it:
1 2 tar xvfz prometheus-*.tar.gz cd prometheus-*
Before starting Prometheus, let’s configure it.
Configuring Prometheus to monitor itself
Prometheus collects metrics from targets by scraping metrics HTTP endpoints .
Since Prometheus exposes data in the same manner about itself, it can also scrape and monitor its own health .
While a Prometheus server that collects only data about itself is not very useful, it is a good starting example.
Save the following basic Prometheus configuration as a file named prometheus.yml:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 global: scrape_interval: 15s external_labels: monitor: 'codelab-monitor' scrape_configs: - job_name: 'prometheus' scrape_interval: 5s static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:9090' ]
Starting Prometheus To start Prometheus with your newly created configuration file, change to the directory containing the Prometheus binary and run:
1 2 3 # Start Prometheus. # By default, Prometheus stores its database in ./data (flag --storage.tsdb.path). ./prometheus --config.file=prometheus.yml
Prometheus should start up . You should also be able to browse to a status page about itself at localhost:9090 .
Give it a couple of seconds to collect data about itself from its own HTTP metrics endpoint .
You can also verify that Prometheus is serving metrics about itself by navigating to its metrics endpoint: localhost:9090/metrics
Using the expression browser
Let us explore data that Prometheus has collected about itself.
To use Prometheus’s built-in expression browser , navigate to http://localhost:9090/query and choose the “Graph “ tab.
As you can gather from localhost:9090/metrics
one metric that Prometheus exports about itself is named prometheus_target_interval_length_seconds
the actual amount of time between target scrapes
Enter the below into the expression console and then click “Execute “:
1 prometheus_target_interval_length_seconds
This should return a number of different time series (along with the latest value recorded for each)
each with the metric name prometheus_target_interval_length_seconds , but with different labels .
These labels designate different latency percentiles and target group intervals .
If we are interested only in 99th percentile latencies , we could use this query:
1 prometheus_target_interval_length_seconds{quantile="0.99"}
To count the number of returned time series , you could write:
1 count(prometheus_target_interval_length_seconds)
Using the graphing interface
To graph expressions, navigate to http://localhost:9090/query and use the “Graph “ tab.
For example, enter the following expression to graph the per-second rate of chunks being created in the self-scraped Prometheus:
Starting up some sample targets
Let’s add additional targets for Prometheus to scrape.
The Node Exporter is used as an example target
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 tar -xzvf node_exporter-*.*.tar.gz cd node_exporter-*.* # Start 3 example targets in separate terminals: ./node_exporter --web.listen-address 127.0.0.1:8080 ./node_exporter --web.listen-address 127.0.0.1:8081 ./node_exporter --web.listen-address 127.0.0.1:8082
You should now have example targets listening on http://localhost:8080/metrics , http://localhost:8081/metrics , and http://localhost:8082/metrics .
Now we will configure Prometheus to scrape these new targets.
Let’s group all three endpoints into one job called node .
We will imagine that the first two endpoints are production targets, while the third one represents a canary instance.
To model this in Prometheus, we can add several groups of endpoints to a single job , adding extra labels to each group of targets.
In this example, we will add the group=”production” label to the first group of targets, while adding group=”canary” to the second.
To achieve this, add the following job definition to the scrape_configs section in your prometheus.yml and restart your Prometheus instance:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'node' scrape_interval: 5s static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:8080' , 'localhost:8081' ] labels: group: 'production' - targets: ['localhost:8082' ] labels: group: 'canary'
Go to the expression browser and verify that Prometheus now has information about time series that these example endpoints expose, such as node_cpu_seconds_total .
Though not a problem in our example, queries that aggregate over thousands of time series can get slow when computed ad-hoc .
To make this more efficient , Prometheus can prerecord expressions into new persisted time series via configured recording rules .
Let’s say we are interested in recording the per-second rate of cpu time (node_cpu_seconds_total) averaged over all cpus per instance (but preserving the job , instance and mode dimensions) as measured over a window of 5 minutes. We could write this as:
1 avg by (job, instance, mode) (rate(node_cpu_seconds_total[5m]))
To record the time series resulting from this expression into a new metric called job_instance_mode:node_cpu_seconds:avg_rate5m
create a file with the following recording rule and save it as prometheus.rules.yml:
1 2 3 4 5 groups: - name: cpu-node rules: - record: job_instance_mode:node_cpu_seconds:avg_rate5m expr: avg by (job, instance, mode) (rate(node_cpu_seconds_total[5m]))
To make Prometheus pick up this new rule , add a rule_files statement in your prometheus.yml.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 global: scrape_interval: 15s evaluation_interval: 15s external_labels: monitor: "codelab-monitor" rule_files: - "prometheus.rules.yml" scrape_configs: - job_name: "prometheus" scrape_interval: 5s static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090" ] - job_name: "node" scrape_interval: 5s static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:8080" , "localhost:8081" ] labels: group: "production" - targets: ["localhost:8082" ] labels: group: "canary"
Restart Prometheus with the new configuration and verify that a new time series with the metric name job_instance_mode:node_cpu_seconds:avg_rate5m is now available by querying it through the expression browser or graphing it.
Reloading configuration
As mentioned in the configuration documentation
a Prometheus instance can have its configuration reloaded without restarting the process by using the SIGHUP signal.
If you’re running on Linux this can be performed by using kill -s SIGHUP <PID>, replacing <PID> with your Prometheus process ID.
1 2 time=2025-11-08T23:45:43.274+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1502 msg="Loading configuration file" filename=prometheus.yml time=2025-11-08T23:45:44.438+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1542 msg="Completed loading of configuration file" db_storage=2.959µs remote_storage=2.083µs web_handler=1.5µs query_engine=2.041µs scrape=1.163449209s scrape_sd=52.666µs notify=1.375µs notify_sd=792ns rules=340.792µs tracing=3.833µs filename=prometheus.yml totalDuration=1.164344791s
Shutting down your instance gracefully.
While Prometheus does have recovery mechanisms in the case that there is an abrupt process failure
it is recommended to use signals or interrupts for a clean shutdown of a Prometheus instance .
On Linux , this can be done by sending the SIGTERM or SIGINT signals to the Prometheus process .
For example, you can use kill -s <SIGNAL> <PID>, replacing <SIGNAL> with the signal name and <PID> with the Prometheus process ID .
Alternatively, you can press the interrupt character at the controlling terminal , which by default is ^C (Control-C).
SIGTERM
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.337+08:00 level=WARN source=main.go:1080 msg="Received an OS signal, exiting gracefully..." signal=terminated time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.337+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1105 msg="Stopping scrape discovery manager..." time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.337+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1119 msg="Stopping notify discovery manager..." time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.337+08:00 level=INFO source=manager.go:204 msg="Stopping rule manager..." component="rule manager" time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.338+08:00 level=INFO source=manager.go:220 msg="Rule manager stopped" component="rule manager" time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.338+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1156 msg="Stopping scrape manager..." time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.338+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1101 msg="Scrape discovery manager stopped" time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.338+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1148 msg="Scrape manager stopped" time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.338+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1115 msg="Notify discovery manager stopped" time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.348+08:00 level=INFO source=manager.go:559 msg="Stopping notification manager..." component=notifier time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.348+08:00 level=INFO source=manager.go:301 msg="Draining any remaining notifications..." component=notifier time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.348+08:00 level=INFO source=manager.go:307 msg="Remaining notifications drained" component=notifier time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.348+08:00 level=INFO source=manager.go:234 msg="Notification manager stopped" component=notifier time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.348+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1426 msg="Notifier manager stopped" time=2025-11-08T23:49:48.349+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1440 msg="See you next time!"
SIGINT
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.014+08:00 level=WARN source=main.go:1080 msg="Received an OS signal, exiting gracefully..." signal=interrupt time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.014+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1105 msg="Stopping scrape discovery manager..." time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.014+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1119 msg="Stopping notify discovery manager..." time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.014+08:00 level=INFO source=manager.go:204 msg="Stopping rule manager..." component="rule manager" time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.014+08:00 level=INFO source=manager.go:220 msg="Rule manager stopped" component="rule manager" time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.014+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1156 msg="Stopping scrape manager..." time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.014+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1115 msg="Notify discovery manager stopped" time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.014+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1148 msg="Scrape manager stopped" time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.014+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1101 msg="Scrape discovery manager stopped" time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.028+08:00 level=INFO source=manager.go:559 msg="Stopping notification manager..." component=notifier time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.028+08:00 level=INFO source=manager.go:301 msg="Draining any remaining notifications..." component=notifier time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.028+08:00 level=INFO source=manager.go:307 msg="Remaining notifications drained" component=notifier time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.028+08:00 level=INFO source=manager.go:234 msg="Notification manager stopped" component=notifier time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.028+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1426 msg="Notifier manager stopped" time=2025-11-08T23:50:52.028+08:00 level=INFO source=main.go:1440 msg="See you next time!"
Installation Using Docker
All Prometheus services are available as Docker images on Quay.io or Docker Hub
Running Prometheus on Docker is as simple as docker run -p 9090:9090 prom/prometheus .
This starts Prometheus with a sample configuration and exposes it on port 9090 .
The Prometheus image uses a volume to store the actual metrics .
For production deployments it is highly recommended to use a named volume to ease managing the data on Prometheus upgrades .
Setting command line parameters
The Docker image is started with a number of default command line parameters , which can be found in the Dockerfile .
If you want to add extra command line parameters to the docker run command , you will need to re-add these yourself as they will be overwritten .
Volumes & bind-mount
To provide your own configuration, there are several options. Here are two examples.
Bind-mount your prometheus.yml from the host by running:
1 2 3 4 docker run \ -p 9090:9090 \ -v /path/to/prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \ prom/prometheus
Or bind-mount the directory containing prometheus.yml onto /etc/prometheus by running:
1 2 3 4 docker run \ -p 9090:9090 \ -v /path/to/config:/etc/prometheus \ prom/prometheus
Save your Prometheus data
Prometheus data is stored in /prometheus dir inside the container , so the data is cleared every time the container gets restarted .To save your data, you need to set up persistent storage (or bind mounts ) for your container .
Run Prometheus container with persistent storage :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 # Create persistent volume for your data docker volume create prometheus-data # Start Prometheus container docker run \ -p 9090:9090 \ -v /path/to/prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \ -v prometheus-data:/prometheus \ prom/prometheus
Configuration Configuration
Prometheus is configured via command-line flags and a configuration file .
While the command-line flags configure immutable system parameters
such as storage locations , amount of data to keep on disk and in memory, etc.
the configuration file defines everything related to scraping jobs and their instances , as well as which rule files to load .
To view all available command-line flags , run ./prometheus -h .
Prometheus can reload its configuration at runtime .
If the new configuration is not well-formed , the changes will not be applied .
A configuration reload is triggered by sending a SIGHUP to the Prometheus process
or sending a HTTP POST request to the /-/reload endpoint (when the –web.enable-lifecycle flag is enabled).
This will also reload any configured rule files .
Configuration file
To specify which configuration file to load, use the –config.file flag.
The file is written in YAML format, defined by the scheme described below.
Brackets indicate that a parameter is optional .For non-list parameters the value is set to the specified default .
Generic placeholders are defined as follows:
Key
Value
<boolean>a boolean that can take the values true or false
<duration>a duration matching the regular expression `((([0-9]+)y)?(([0-9]+)w)?(([0-9]+)d)?(([0-9]+)h)?(([0-9]+)m)?(([0-9]+)s)?(([0-9]+)ms)?
<filename>a valid path in the current working directory
<float>a floating-point number
<host>a valid string consisting of a hostname or IP followed by an optional port number
<int>an integer value
<labelname>a string matching the regular expression [a-zA-Z_][a-zA-Z0-9_]*.unsupported character in the source label should be converted to an underscore .app.kubernetes.io/name should be written as app_kubernetes_io_name.
<labelvalue>a string of unicode characters
<path>a valid URL path
<scheme>a string that can take the values http or https
<secret>a regular string that is a secret, such as a password
<string>a regular string
<size>a size in bytes, e.g. 512MB. A unit is required. Supported units: B, KB, MB, GB, TB, PB, EB.
<tmpl_string>a string which is template-expanded before usage
The other placeholders are specified separately .
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 🔍 占位符含义 基础数据类型 - <boolean>: 布尔值 - true 或 false - <string>: 普通字符串 - <int>: 整数值 - <float>: 浮点数 - <secret>: 敏感信息(如密码) 时间相关 - <duration>: 持续时间格式 - 支持: 1d, 1h30m, 5m, 10s - 正则: (([0-9]+)y)?(([0-9]+)w)?(([0-9]+)d)?(([0-9]+)h)?(([0-9]+)m)?(([0-9]+)s)?(([0-9]+)ms)? - 示例: 1d30m, 2h, 0 网络相关 - <host>: 主机名或IP + 可选端口 - 示例: localhost:9090, 192.168.1.1, example.com:8080 - <scheme>: 协议 - http 或 https - <path>: URL路径 标签相关 - <labelname>: 标签名称 - 规则: [a-zA-Z_][a-zA-Z0-9_]* - 特殊字符转换: app.kubernetes.io/name → app_kubernetes_io_name - <labelvalue>: 标签值(Unicode字符串) 文件相关 - <filename>: 当前工作目录下的有效路径 - <size>: 大小(字节) - 示例: 512MB, 1GB, 2TB - 单位: B, KB, MB, GB, TB, PB, EB 特殊类型 - <tmpl_string>: 模板字符串(使用前会展开) 📖 为什么需要这些定义? 1. 统一语法规范 # 这些都符合 <duration> 格式 scrape_interval: 1m evaluation_interval: 30s scrape_timeout: 10s 2. 避免歧义 # 明确哪些字段需要哪种格式 port: 9090 # <int> body_size_limit: 100MB # <size> timeout: 30s # <duration> 3. 标签标准化 # Kubernetes 标签转换规则 labels: app_kubernetes_io_name: "my-app" # 正确 app.kubernetes.io/name: "my-app" # 错误,需要转换 🎯 "The other placeholders are specified separately" 这句话的意思是: - 上面列出的是通用占位符 - 特定功能模块的占位符在各自的章节中定义 例如: # 在 <relabel_config> 章节会定义 <relabel_action>: replace | keep | drop | ... # 在 <kubernetes_sd_config> 章节会定义 <kubernetes_role>: node | service | pod | endpoints | ... 💡 实际应用 理解这些占位符能帮助你: 1. 正确编写配置文件 2. 快速理解配置文档 3. 避免常见的配置错误 比如看到配置文档中的: [ scrape_interval: <duration> | default = 1m ] 你就知道这里可以填入:30s, 5m, 1h 等时间格式。
The global configuration specifies parameters that are valid in all other configuration contexts .defaults for other configuration sections.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 global: [ scrape_interval: <duration> | default = 1m ] [ scrape_timeout: <duration> | default = 10s ] [ scrape_protocols: [<string> , ... ] | default = [ OpenMetricsText1.0.0 , OpenMetricsText0.0.1 , PrometheusText0.0.4 ] ] [ evaluation_interval: <duration> | default = 1m ] [ rule_query_offset: <duration> | default = 0s ] external_labels: [ <labelname>: <labelvalue> ... ] [ query_log_file: <string> ] [ scrape_failure_log_file: <string> ] [ body_size_limit: <size> | default = 0 ] [ sample_limit: <int> | default = 0 ] [ label_limit: <int> | default = 0 ] [ label_name_length_limit: <int> | default = 0 ] [ label_value_length_limit: <int> | default = 0 ] [ target_limit: <int> | default = 0 ] [ keep_dropped_targets: <int> | default = 0 ] [ metric_name_validation_scheme: <string> | default "utf8" ] [ convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: <bool> | default = false ] [ always_scrape_classic_histograms: <boolean> | default = false ] runtime: [ gogc: <int> | default = 75 ] rule_files: [ - <filepath_glob> ... ] scrape_config_files: [ - <filepath_glob> ... ] scrape_configs: [ - <scrape_config> ... ] alerting: alert_relabel_configs: [ - <relabel_config> ... ] alertmanagers: [ - <alertmanager_config> ... ] remote_write: [ - <remote_write> ... ] otlp: [ promote_resource_attributes: [<string> , ... ] | default = [ ] ] [ promote_all_resource_attributes: <boolean> | default = false ] [ ignore_resource_attributes: [<string> , ... ] | default = [] ] [ translation_strategy: <string> | default = "UnderscoreEscapingWithSuffixes" ] [ keep_identifying_resource_attributes: <boolean> | default = false ] [ convert_histograms_to_nhcb: <boolean> | default = false ] [ promote_scope_metadata: <boolean> | default = false ] remote_read: [ - <remote_read> ... ] storage: [ tsdb: <tsdb> ] [ exemplars: <exemplars> ] tracing: [ <tracing_config> ]
scrape_protocols
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 📖 参数含义 scrape_protocols - 抓取协议协商 - 作用: 定义 Prometheus 与目标服务通信时支持的协议格式 - 类型: [<string>, ...] (字符串列表) - 大小写敏感: 必须严格按照示例的大小写 🔄 支持的协议 1. PrometheusProto - 格式: Protocol Buffers 二进制格式 - 特点: 高效、紧凑、性能最好 - 适用: 现代化的指标导出器 2. OpenMetricsText1.0.0 - 格式: OpenMetrics 1.0.0 标准文本格式 - 特点: 标准化、兼容性好 - 适用: 遵循 OpenMetrics 标准的服务 3. OpenMetricsText0.0.1 - 格式: OpenMetrics 0.0.1 旧版文本格式 - 特点: 向后兼容 - 适用: 较老的 OpenMetrics 实现 4. PrometheusText0.0.4 - 格式: Prometheus 经典文本格式 - 特点: 最常用、兼容性最强 - 适用: 大部分现有的 Prometheus exporters 🎯 协议协商机制 Prometheus 会按照列表顺序与目标协商使用哪种协议: scrape_protocols: [ PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0, PrometheusText0.0.4 ] # 协商过程: # 1. Prometheus: "支持 PrometheusProto 吗?" # 2. 如果目标支持 → 使用 PrometheusProto # 3. 如果不支持 → "支持 OpenMetricsText1.0.0 吗?" # 4. 如果目标支持 → 使用 OpenMetricsText1.0.0 # 5. 如果不支持 → 继续尝试下一个... 🔄 默认值变化 默认情况: # 默认协议顺序 [ OpenMetricsText1.0.0, OpenMetricsText0.0.1, PrometheusText0.0.4 ] 启用原生直方图时: # 当 --enable-feature=native-histogram 时 [ PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0, OpenMetricsText0.0.1, PrometheusText0.0.4 ] 注意: 启用原生直方图时,PrometheusProto 会排在第一位,因为它对原生直方图支持最好。 🔧 实际配置示例 1. 默认配置 (你的情况) global: # 没有设置 scrape_protocols,使用默认值 scrape_interval: 15s # 实际效果: # scrape_protocols: [ OpenMetricsText1.0.0, OpenMetricsText0.0.1, PrometheusText0.0.4 ] 2. 优化性能配置 global: scrape_protocols: [ PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0 ] # 优先使用二进制协议,性能更好 3. 兼容性优先配置 global: scrape_protocols: [ PrometheusText0.0.4, OpenMetricsText0.0.1 ] # 确保与老版本 exporters 兼容 4. 启用原生直方图配置 # 命令行启动时 ./prometheus --enable-feature=native-histograms # 配置文件 global: # 会自动使用: # [ PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0, OpenMetricsText0.0.1, PrometheusText0.0.4 ] 📊 协议选择建议 推荐配置 (生产环境): global: scrape_protocols: [ PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0, PrometheusText0.0.4 ] 优势: - 优先使用高效的二进制协议 - 保持向后兼容性 - 覆盖大部分使用场景 保守配置 (兼容性优先): global: scrape_protocols: [ PrometheusText0.0.4, OpenMetricsText0.0.1 ] 适用: 需要与老版本或非标准实现兼容的环境 ⚠️ 注意事项 1. 大小写敏感 # ✅ 正确 scrape_protocols: [ PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0 ] # ❌ 错误 scrape_protocols: [ prometheusproto, OpenMetricstext1.0.0 ] 2. 协议顺序重要 # 不同的顺序会有不同的协商结果 [ PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0 ] # 优先二进制 [ OpenMetricsText1.0.0, PrometheusProto ] # 优先文本 3. 与目标服务匹配 确保你的监控目标支持配置的协议,否则协商可能失败。 你的配置使用默认值是一个安全的选择,适合大多数使用场景。
PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0, OpenMetricsText0.0.1, PrometheusText0.0.4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 🎯 概览对比表 | 协议 | 类型 | 标准化 | 性能 | 兼容性 | 主要用途 | |----------------------|-----|------------|-----|-----|-------| | PrometheusProto | 二进制 | Prometheus | 最高 | 中等 | 高性能场景 | | OpenMetricsText1.0.0 | 文本 | CNCF 标准 | 中等 | 高 | 标准化监控 | | OpenMetricsText0.0.1 | 文本 | 旧版标准 | 中等 | 高 | 向后兼容 | | PrometheusText0.0.4 | 文本 | Prometheus | 中等 | 最高 | 最广泛兼容 | 🔧 PrometheusProto (Protocol Buffers) 格式特征: // 二进制格式示例(简化) message WriteRequest { repeated TimeSeries timeseries = 1; repeated MetricMetadata metadata = 2; } message TimeSeries { repeated Label labels = 1; repeated Sample samples = 2; } 优势: - ⚡ 性能最佳: 二进制压缩,解析速度快 - 📦 传输高效: 网络传输量更小 - 🔒 类型安全: 强类型定义,减少解析错误 - 🎯 原生直方图: 对原生直方图支持最好 劣势: - 🔍 调试困难: 二进制格式不易人工查看 - 🔧 工具限制: 需要专门工具解析 - 📊 生态支持: 并非所有工具都支持 适用场景: # 高性能环境 scrape_protocols: [ PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0 ] 📝 OpenMetricsText1.0.0 (CNCF 标准) 格式特征: # 标准化的 OpenMetrics 格式 # HELP http_requests_total The total number of HTTP requests. # TYPE http_requests_total counter # UNIT http_requests_total requests http_requests_total{method="GET",code="200"} 1027 # 明确的直方图格式 # TYPE latency_seconds histogram # UNIT latency_seconds seconds latency_seconds_bucket{le="0.1"} 24054 latency_seconds_bucket{le="0.5"} 33444 latency_seconds_bucket{le="+Inf"} 10000 latency_seconds_sum 1.7560473e+07 latency_seconds_count 2633 # EOF 必须存在 优势: - 🎯 官方标准: CNCF 认证标准 - 🔗 跨工具兼容: 多个监控工具支持 - 📋 元数据丰富: 明确的单位、类型定义 - 📊 结构清晰: 人类可读,机器易解析 新增特性: # 单位信息 (UNIT) # UNIT cpu_usage_percent percent # UNIT memory_bytes bytes # 信息指标 (Info) # TYPE node_info info node_info{version="1.0",os="linux"} 1 # 状态集合 (StateSet) # TYPE feature_flags stateset feature_flags{feature="beta"} 1 feature_flags{feature="alpha"} 0 📚 OpenMetricsText0.0.1 (旧版标准) 格式特征: # 与 1.0.0 基本相同,但缺少一些新特性 # HELP http_requests_total The total number of HTTP requests. # TYPE http_requests_total counter http_requests_total{method="GET",code="200"} 1027 # 没有 EOF 标记要求 主要差异: - 📝 元数据较少: 缺少 UNIT 等新字段 - 🔄 向后兼容: 与 Prometheus 格式更接近 - 📊 功能有限: 不支持最新特性 🏛️ PrometheusText0.0.4 (经典格式) 格式特征: # Prometheus 原始格式 # HELP http_requests_total The total number of HTTP requests. # TYPE http_requests_total counter http_requests_total{method="GET",code="200"} 1027 # 直方图格式略有不同 # HELP http_request_duration_seconds A histogram of the request duration. # TYPE http_request_duration_seconds histogram http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="0.05"} 24054 http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="+Inf"} 10000 http_request_duration_seconds_sum 1.7560473e+07 http_request_duration_seconds_count 2633 特点: - 🔧 最成熟: 经过长期验证的格式 - 🌐 最广泛支持: 几乎所有 Prometheus 兼容工具都支持 - 📊 简单直接: 易于理解和实现 - 🎯 生态标准: Prometheus 生态系统的事实标准 🔄 协议协商过程 scrape_protocols: [ PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0, OpenMetricsText0.0.1, PrometheusText0.0.4 ] 协商流程: Prometheus → Target: "支持 PrometheusProto 吗?" ├─ ✅ 支持 → 使用 PrometheusProto (最快) └─ ❌ 不支持 → "支持 OpenMetricsText1.0.0 吗?" ├─ ✅ 支持 → 使用 OpenMetricsText1.0.0 (标准化) └─ ❌ 不支持 → "支持 OpenMetricsText0.0.1 吗?" ├─ ✅ 支持 → 使用 OpenMetricsText0.0.1 (兼容) └─ ❌ 不支持 → 使用 PrometheusText0.0.4 (最兼容) 📈 性能对比 | 操作 | PrometheusProto | OpenMetricsText1.0.0 | PrometheusText0.0.4 | |--------|-----------------|----------------------|---------------------| | 序列化 | 快 | 中等 | 中等 | | 反序列化 | 快 | 中等 | 中等 | | 网络传输 | 小 | 大 | 大 | | 内存占用 | 低 | 高 | 高 | | CPU 使用 | 低 | 中等 | 中等 | 🎯 选择建议 生产环境推荐配置: # 平衡性能和兼容性 scrape_protocols: [ PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0, PrometheusText0.0.4 ] 兼容性优先配置: # 确保最大兼容性 scrape_protocols: [ OpenMetricsText1.0.0, PrometheusText0.0.4 ] 性能优先配置: # 追求最高性能 scrape_protocols: [ PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0 ] 💡 你的配置分析 你的配置使用默认协议顺序: # 默认情况下 scrape_protocols: [ OpenMetricsText1.0.0, OpenMetricsText0.0.1, PrometheusText0.0.4 ] 这是一个很好的选择: - 🎯 优先使用标准化格式 - 🔄 自动回退到兼容格式 - 🛡️ 确保与各种目标都能通信 - 📊 平衡了标准性和兼容性 如果启用原生直方图功能,会自动调整为: # --enable-feature=native-histograms 时 scrape_protocols: [ PrometheusProto, OpenMetricsText1.0.0, OpenMetricsText0.0.1, PrometheusText0.0.4 ] 这样会优先使用性能更好的二进制协议来处理原生直方图。
evaluation_interval
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 🔍 独立运行的任务 抓取数据 和 评估规则 是两个独立的调度任务,它们各自按照自己的间隔运行,不会互相阻塞。 ✅ 正确的时间线 你的配置: global: scrape_interval: 15s # 抓取调度器 evaluation_interval: 1m # 规则评估调度器 实际运行情况: 时间线: 00:00 - 规则评估 (使用当前已有数据) 00:15 - 抓取数据 00:30 - 抓取数据 00:45 - 抓取数据 01:00 - 规则评估 (使用最新抓取的数据) + 同时可能也在抓取数据 01:15 - 抓取数据 01:30 - 抓取数据 01:45 - 抓取数据 02:00 - 规则评估 + 同时可能也在抓取数据 ⚙️ 并发执行机制 两个独立的调度器: // 伪代码展示并发执行 func main() { // 抓取调度器 - 每15秒运行 go func() { for { scrapeTargets() // 抓取数据 time.Sleep(15s) } }() // 规则评估调度器 - 每1分钟运行 go func() { for { evaluateRules() // 评估规则 time.Sleep(1m) } }() } 01:00 时刻的情况: 在 01:00 这一时刻: ├─ 规则评估调度器触发 │ └─ 评估所有告警规则 │ └─ 使用 TSDB 中最新的数据 │ └─ 抓取调度器可能也同时触发 └─ 抓取目标的指标数据 └─ 将新数据写入 TSDB 🎯 关键点 1. 不会互相等待: - 规则评估不会等待数据抓取完成 - 数据抓取也不会等待规则评估完成 - 两者完全独立运行 2. 数据一致性: # 规则评估时使用的是 TSDB 中已有的数据 # 不一定是最新抓取的数据 expr: cpu_usage > 80 # 在 01:00 评估时,可能使用的是 00:45 抓取的数据 # 01:00 抓取的新数据要等到 02:00 评估时才会用到 3. 时间重叠处理: 01:00 时刻: ├─ 规则评估开始 (使用 00:45 的数据) ├─ 数据抓取开始 (获取新数据) ├─ 规则评估完成 (生成告警状态) └─ 数据抓取完成 (新数据写入TSDB,下次评估使用) 📊 实际影响 最大数据延迟: # 最坏情况下的数据延迟 问题发生时刻: 00:46 下次抓取: 01:00 (但可能稍晚几毫秒) 下次评估: 01:00 (使用00:45的数据,还没看到问题) 再次评估: 02:00 (使用01:00的数据,此时才看到问题) # 实际最大延迟 ≈ 15s (抓取间隔) + 60s (评估间隔) = 75秒 为什么这样设计: - ✅ 性能优化: 避免评估等待抓取 - ✅ 资源隔离: 两个任务互不干扰 - ✅ 简化调度: 各自独立,逻辑清晰 - ✅ 容错性: 一个任务失败不影响另一个
rule_query_offset
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 ⏺ 📖 参数含义 rule_query_offset - 规则查询时间偏移 - 作用: 将规则评估的时间点向后偏移指定时间,确保底层数据已经到达 - 类型: <duration> (持续时间) - 默认值: 0s (无偏移) - 用途: 解决数据延迟问题 🎯 解决的问题 数据延迟场景: 正常情况: 时间: 09:00:00 指标时间: 09:00:00 (实时数据) 评估: 立即使用 ✅ 延迟情况: 时间: 09:00:00 指标时间: 08:59:30 (延迟30秒) 评估: 使用了不完整的数据 ❌ 具体延迟场景: 1. 远程写入场景: # 架构: Exporter → Prometheus → Remote Storage → Prometheus # 数据流向: # 09:00:00 - Exporter 暴露指标 # 09:00:05 - Prometheus 抓取并写入远程存储 # 09:00:15 - 远程存储持久化完成 # 09:00:30 - Prometheus 从远程存储读取 # 09:01:00 - 规则评估 (此时数据已完整) 2. 网络延迟: # 跨数据中心或云环境 # Exporter 在 A 地区 # Prometheus 在 B 地区 # 网络延迟可能导致数据传输慢 3. 抓取异常: # 目标服务偶尔响应慢 # 或网络抖动导致抓取失败重试 # 数据到达时间不规律 ⏰ 工作原理 无偏移 (默认): global: evaluation_interval: 1m rule_query_offset: 0s # 默认值 # 评估时间点: # 09:00:00 - 评估 09:00:00 的数据 # 09:01:00 - 评估 09:01:00 的数据 # 09:02:00 - 评估 09:02:00 的数据 有偏移: global: evaluation_interval: 1m rule_query_offset: 30s # 偏移30秒 # 评估时间点: # 09:00:00 - 评估 08:59:30 的数据 (向前推30秒) # 09:01:00 - 评估 09:00:30 的数据 (向前推30秒) # 09:02:00 - 评估 09:01:30 的数据 (向前推30秒) 🔧 配置示例 1. 远程写入环境: global: evaluation_interval: 1m rule_query_offset: 2m # 给远程写入2分钟缓冲时间 # 确保从远程存储读取时数据已完整 2. 网络不稳定环境: global: evaluation_interval: 30s rule_query_offset: 45s # 45秒偏移应对网络延迟 # 适合跨云或跨地域部署 3. 大规模抓取: global: scrape_interval: 15s evaluation_interval: 1m rule_query_offset: 1m # 1分钟偏移确保所有数据到达 # 当抓取目标很多时,完成一轮需要时间 📊 实际影响分析 延迟计算: # 你的配置 (假设添加了偏移) global: scrape_interval: 15s evaluation_interval: 1m rule_query_offset: 30s # 告警响应时间: # 问题发生 → 最多15秒被抓取 → 最多30秒偏移缓冲 → 1分钟评估 → 5分钟for时间 # 总延迟 ≈ 15s + 30s + 1m + 5m = 6分45秒 数据新鲜度: # 无偏移: 使用最新数据,但可能不完整 rule_query_offset: 0s # 查询时间: 09:00:00 → 数据范围: 09:00:00 ± 5m # 有偏移: 使用稍旧数据,但更可靠 rule_query_offset: 30s # 查询时间: 09:00:00 → 数据范围: 08:59:30 ± 5m 🎯 使用建议 何时需要设置: - ✅ 远程写入架构: Prometheus 作为远程写入目标 - ✅ 跨地域部署: 网络延迟较高 - ✅ 大规模抓取: 大量目标导致抓取时间长 - ✅ 数据延迟敏感: 需要确保数据完整性 何时不需要设置: - ❌ 本地部署: 数据路径短,延迟低 - ❌ 简单架构: 单一 Prometheus 实例 - ❌ 实时要求高: 需要立即响应变化 - ❌ 资源充足: 可以接受偶发的数据不完整 推荐设置: # 根据架构复杂度调整 rule_query_offset: 30s # 轻微延迟 rule_query_offset: 1m # 中等延迟 rule_query_offset: 2m # 较重延迟 💡 与你的配置关系 你的当前配置: global: scrape_interval: 15s evaluation_interval: 1m # rule_query_offset: 0s (默认,无偏移) 这是合理的: - ✅ 本地部署: 假设是本地或同网络环境 - ✅ 数据及时: 无额外延迟,告警响应快 - ✅ 简单架构: 适合大多数标准部署 如果遇到以下情况,可以考虑添加偏移: - 发现告警总是延迟触发 - 确认存在数据传输延迟 - 使用了远程存储或远程写入架构 总的来说,这个参数是一个保险机制,在数据延迟不可控时提供可靠性保障。
external_labels
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 ⏺ 📖 参数含义 external_labels - 外部标签 - 作用: 为所有时间序列和告警添加全局标签,用于与外部系统通信 - 用途: 联邦、远程存储、Alertmanager 通信 - 环境变量: 支持环境变量引用 ${var} 或 $var 🏷️ 标签添加范围 影响的外部系统: 1. Federation (联邦): 其他 Prometheus 实例抓取时 2. Remote Storage (远程存储): 发送到远程存储系统时 3. Alertmanager: 发送告警到 Alertmanager 时 不影响的范围: - ❌ 本地查询和规则评估 - ❌ 本地 API 响应 - ❌ 直接查看的指标 🔧 基础配置示例 你的配置: global: external_labels: monitor: "codelab-monitor" 实际效果: # 原始指标 http_requests_total{instance="localhost:9090", job="prometheus"} 100 # 添加外部标签后 (发送到外部系统时) http_requests_total{instance="localhost:9090", job="prometheus", monitor="codelab-monitor"} 100 🌍 环境变量支持 基本语法: external_labels: # 两种环境变量语法 cluster: "${CLUSTER_NAME}" # 推荐语法 region: "$REGION" # 简化语法 datacenter: "${DATACENTER:-default}" # 默认值语法 version: "v1.2.3-${BUILD_ID}" # 与静态值组合 转义处理: external_labels: # 转义 $ 字符 literal_dollar: "$$escaped_value" # 结果: $escaped_value money_sign: "$${CURRENCY}" # 如果CURRENCY=USD,结果: $USD 环境变量处理规则: - ✅ 存在变量: 替换为实际值 - ❌ 不存在变量: 替换为空字符串 "" - 💡 转义: $$ 转义为单个 $ 🎯 实际应用场景 1. 联邦场景 (Federation): # 主 Prometheus 配置 global: external_labels: prometheus: "main" region: "us-west" cluster: "production" # 子 Prometheus 抓取 # /federate?prometheus=main®ion=us-west&cluster=production 2. 远程存储场景: global: external_labels: source: "prometheus-main" env: "${ENVIRONMENT}" datacenter: "${DATACENTER}" # 所有发送到远程存储的指标都包含这些标签 # 用于区分不同 Prometheus 实例的数据 3. Alertmanager 场景: global: external_labels: cluster: "${CLUSTER_NAME}" region: "${AWS_REGION}" team: "platform" # 告警发送时会自动添加这些标签 # Alertmanager 路由规则可以使用这些标签 🏢 复杂配置示例 生产环境配置: global: external_labels: # 环境信息 environment: "${ENV:-production}" region: "${AWS_REGION:-us-west-2}" availability_zone: "${AZ:-us-west-2a}" # 实例标识 cluster: "${CLUSTER_NAME}" prometheus_instance: "${HOSTNAME}" team: "${TEAM:-platform}" # 版本信息 prometheus_version: "v3.7.3" config_version: "2024.11.09" # 业务标识 business_unit: "infrastructure" cost_center: "IT-OPS" 动态环境变量: # 设置环境变量 export CLUSTER_NAME="prod-k8s-cluster" export AWS_REGION="us-west-2" export TEAM="observability" export DATACENTER="datacenter-1" # Prometheus 启动时会读取这些环境变量 ./prometheus --config.file=prometheus.yml 📊 标签传播机制 告警标签传播: # 规则文件中的告警 - alert: HighCPUUsage expr: cpu_usage > 80 labels: severity: critical annotations: summary: "High CPU usage detected" # 发送到 Alertmanager 时自动添加外部标签: { "labels": { "alertname": "HighCPUUsage", "severity": "critical", "monitor": "codelab-monitor" # ← external_labels 添加 } } 联邦查询标签: # 源 Prometheus global: external_labels: source: "main-prometheus" region: "us-west" # 目标 Prometheus 联邦查询 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'federate' honor_labels: true metrics_path: /federate params: 'match[]': - '{__name__=~".+"}' static_configs: - targets: ['source-prometheus:9090'] # 获取到的指标包含源的外部标签 up{job="federate", instance="source-prometheus:9090", source="main-prometheus", region="us-west"} ⚠️ 注意事项 1. 标签名称规范: # ✅ 正确的标签名 external_labels: cluster: "production" # 符合规范 region: "us-west-2" # 符合规范 # ❌ 错误的标签名 external_labels: app.kubernetes.io/name: "app" # 需要转换为: app_kubernetes_io_name invalid-name: "value" # 包含连字符,需要转换 2. 环境变量处理: # 安全的环境变量引用 external_labels: # 使用默认值避免空值 cluster: "${CLUSTER_NAME:-unknown}" # 确保变量存在或提供默认值 environment: "${ENVIRONMENT:-production}" 3. 标签数量控制: # 避免添加过多标签 external_labels: # ✅ 必要标签 cluster: "prod-cluster" region: "us-west-2" # ❌ 避免添加过多详细信息 # pod_name: "${POD_NAME}" # 变化太频繁 # container_id: "${CONTAINER_ID}" # 无关信息 💡 你的配置分析 你的配置: global: external_labels: monitor: "codelab-monitor" 这是一个很好的实践: - ✅ 标识明确: 清楚标识数据来源 - ✅ 简洁有效: 只添加必要的标识信息 - ✅ 便于管理: 在多 Prometheus 环境中容易区分 - ✅ 告警有用: Alertmanager 可以基于此标签路由 建议可以根据需要逐步扩展,添加更多环境或业务相关的标签。
query_log_file + scrape_failure_log_file
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 ⏺ 📖 日志配置参数解释 1. query_log_file - PromQL 查询日志 含义: - 记录所有执行的 PromQL 查询 - 包括来自 API、Web UI、规则评估的查询 - 配置重载时会重新打开文件 用途: - 🔍 审计查询活动 - 🐛 调试性能问题 - 📊 分析查询模式 - 🛡️ 安全审计 配置示例: global: query_log_file: "/var/log/prometheus/queries.log" 日志格式: 2024-11-09T10:15:30.123Z http://localhost:9090/api/v1/query?query=up&time=1731135330.123 2024-11-09T10:15:35.456Z http://localhost:9090/api/v1/query_range?query=rate(http_requests_total[5m])&start=1731 135300&end=1731135330&step=15 2024-11-09T10:16:00.789Z rule=HighCPUUsage query=cpu_usage > 80 2. scrape_failure_log_file - 抓取失败日志 含义: - 记录所有抓取失败的详细信息 - 包括超时、连接错误、HTTP错误等 - 配置重载时会重新打开文件 用途: - 🔧 监控抓取问题 - 🐛 排查目标服务问题 - 📊 统计失败率 - 🚨 及时发现服务异常 配置示例: global: scrape_failure_log_file: "/var/log/prometheus/scrape_failures.log" 日志格式: 2024-11-09T10:15:30.123Z scrape_failed job="node" instance="localhost:9100" error="context deadline exceeded" 2024-11-09T10:15:45.456Z scrape_failed job="api" instance="api.example.com:8080" error="connection refused" 2024-11-09T10:16:00.789Z scrape_failed job="web" instance="web.example.com:80" error="HTTP 500 Internal Server Error" 🎯 实际应用场景 查询日志 (query_log_file) 1. 性能调试: # 发现慢查询 grep "rate(http_requests_total[1h])" /var/log/prometheus/queries.log # 分析查询频率 cat /var/log/prometheus/queries.log | awk '{print $1}' | sort | uniq -c 2. 安全审计: # 查看谁在查询敏感指标 grep "secrets" /var/log/prometheus/queries.log # 分析查询模式 grep "http://.*:3000" /var/log/prometheus/queries.log # Grafana 查询 3. 调试规则: # 查看规则评估查询 grep "rule=" /var/log/prometheus/queries.log 抓取失败日志 (scrape_failure_log_file) 1. 监控目标健康: # 统计失败目标 cat /var/log/prometheus/scrape_failures.log | grep -o 'instance="[^"]*"' | sort | uniq -c # 分析失败类型 cat /var/log/prometheus/scrape_failures.log | grep -o 'error="[^"]*"' | sort | uniq -c 2. 网络问题排查: # 查看网络相关错误 grep -E "(timeout|refused|connection)" /var/log/prometheus/scrape_failures.log 3. 配置验证: # 检查哪些 job 经常失败 grep -o 'job="[^"]*"' /var/log/prometheus/scrape_failures.log | sort | uniq -c | sort -nr ⚙️ 配置建议 生产环境配置: global: # 启用查询日志用于审计 query_log_file: "/var/log/prometheus/queries.log" # 启用抓取失败日志用于监控 scrape_failure_log_file: "/var/log/prometheus/scrape_failures.log" 开发环境配置: global: # 开发环境可以启用详细日志 query_log_file: "/tmp/prometheus-queries.log" scrape_failure_log_file: "/tmp/prometheus-scrape-failures.log" 调试时临时启用: global: # 临时开启用于调试 query_log_file: "/var/log/prometheus/debug-queries.log" 🔧 文件管理 日志轮转 (logrotate 配置): # /etc/logrotate.d/prometheus-logs /var/log/prometheus/*.log { daily rotate 7 compress delaycompress missingok notifempty create 644 prometheus prometheus postrotate kill -USR1 $(cat /var/run/prometheus.pid) endscript } 监控日志大小: # 监控日志文件大小 du -sh /var/log/prometheus/*.log # 实时监控日志 tail -f /var/log/prometheus/scrape_failures.log ⚠️ 注意事项 性能影响: - ✅ 查询日志: 轻微性能开销 - ⚠️ 抓取失败日志: 失败较多时可能影响性能 - 💾 磁盘空间: 需要监控日志文件大小 敏感信息: - 🔒 查询日志: 可能包含敏感的查询信息 - 🛡️ 访问控制: 限制日志文件的访问权限 文件权限: # 设置合适的文件权限 chown prometheus:prometheus /var/log/prometheus/*.log chmod 640 /var/log/prometheus/*.log 💡 最佳实践 1. 渐进式启用: # 先启用抓取失败日志 scrape_failure_log_file: "/var/log/prometheus/scrape_failures.log" # 后续根据需要启用查询日志 query_log_file: "/var/log/prometheus/queries.log" 2. 定期分析: # 设置定期分析脚本 # 每天分析失败率,每周分析查询模式 3. 与监控集成: # 在日志中提取指标用于监控 # 例如: prometheus_scrape_failures_total{job="node"} 这两个日志功能是 Prometheus 运维的重要工具,建议在生产环境中启用抓取失败日志,根据需要启用查询日志。
body_size_limit + sample_limit + label_limit + label_name_length_limit + label_value_length_limit + target_limit
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 这些参数用于控制 Prometheus 抓取过程中的资源使用和稳定性保护。 🎯 1. body_size_limit - 响应体大小限制 含义: - 限制目标服务返回的未压缩响应体大小 - 超过限制时整个抓取失败 - 0 表示无限制 配置示例: global: body_size_limit: 100MB # 限制100MB # 或者 body_size_limit: 50MB # 限制50MB body_size_limit: 0 # 无限制 (默认) 适用场景: - ✅ 防止目标服务返回过多数据 - ✅ 避免内存溢出 - ✅ 保护 Prometheus 稳定性 - ⚠️ 实验性功能,可能变化 🔢 2. sample_limit - 样本数量限制 含义: - 限制每次抓取接受的样本数量 - 在指标重标签后计算 - 超过限制时整个抓取失败 配置示例: global: sample_limit: 1000000 # 限制100万个样本 # 或者针对特定job scrape_configs: - job_name: "heavy_metrics" sample_limit: 500000 # 该job限制50万样本 实际影响: # 正常情况: 10,000 个样本 ✅ # 超过限制: 1,500,000 个样本 ❌ (如果 limit=1,000,000) 🏷️ 3. label_limit - 标签数量限制 含义: - 限制每个样本的标签数量 - 在指标重标签后检查 - 任何样本超过限制都导致整个抓取失败 配置示例: global: label_limit: 50 # 每个样本最多50个标签 scrape_configs: - job_name: "labeled_metrics" label_limit: 30 # 该job每个样本最多30个标签 标签示例: # 正常样本: ~10-20个标签 ✅ metric{job="api",instance="1.2.3.4",method="GET",status="200",...} 100 # 标签过多: 可能100+个标签 ❌ metric{label1="value1",label2="value2",...,label100="value100"} 100 📏 4. label_name_length_limit - 标签名长度限制 含义: - 限制每个标签名的字节长度 - UTF-8编码,字符可能占1-4字节 - 任何标签名超长都导致抓取失败 配置示例: global: label_name_length_limit: 512 # 标签名最多512字节 # 或者更严格 label_name_length_limit: 256 # 标签名最多256字节 UTF-8 字符计算: # ASCII字符: 1字节 "job" = 3字节 ✅ # 中文字符: 3字节 "中文标签" = 12字节 ✅ # Emoji: 4字节 "🏷️label" = 8字节 ✅ 📝 5. label_value_length_limit - 标签值长度限制 含义: - 限制每个标签值的字节长度 - UTF-8编码,字符可能占1-4字节 - 任何标签值超长都导致抓取失败 配置示例: global: label_value_length_limit: 2048 # 标签值最多2048字节 # 或者针对不同job scrape_configs: - job_name: "api_metrics" label_value_length_limit: 1024 实际示例: # 正常值 version: "1.2.3" # 7字节 ✅ build_id: "abc123" # 6字节 ✅ # 可能过长的值 trace_id: "550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000" # 36字节 ✅ long_description: "这是一个很长的描述文本..." # 可能超长 ❌ 🎯 6. target_limit - 目标数量限制 含义: - 限制每个抓取配置的唯一目标数量 - 在目标重标签后计算 - 超过限制时目标被标记为失败,不进行抓取 - 实验性功能 配置示例: global: target_limit: 10000 # 全局限制1万个目标 scrape_configs: - job_name: "kubernetes_pods" target_limit: 5000 # 该job限制5000个目标 实际效果: # Kubernetes服务发现可能返回数千个pod # 限制后只抓取前5000个,其余标记为失败 🔧 综合配置示例 生产环境配置: global: # 响应体大小限制 body_size_limit: 100MB # 样本数量限制 sample_limit: 5000000 # 标签相关限制 label_limit: 100 label_name_length_limit: 512 label_value_length_limit: 4096 # 目标数量限制 target_limit: 10000 资源受限环境: global: # 更严格的限制 body_size_limit: 50MB sample_limit: 1000000 label_limit: 50 label_name_length_limit: 256 label_value_length_limit: 1024 target_limit: 5000 Job级别配置: scrape_configs: - job_name: "light_metrics" # 轻量级服务,较少限制 sample_limit: 10000 label_limit: 20 - job_name: "heavy_metrics" # 重型服务,严格限制 body_size_limit: 200MB sample_limit: 100000 label_limit: 30 📊 监控这些限制 Prometheus 指标: # 检查抓取失败 prometheus_scrape_samples_scraped_total prometheus_scrape_samples_failed_total # 检查目标状态 up{job="heavy_metrics"} # 0表示抓取失败 日志监控: # 查看抓取失败日志 grep "scrape_failed" /var/log/prometheus/scrape_failures.log | grep "limit" ⚠️ 注意事项 1. 实验性功能: - ⚠️ body_size_limit 和 target_limit 是实验性的 - 🔄 未来版本可能变化 - 📋 生产环境谨慎使用 2. 性能权衡: - ✅ 限制严格: 保护资源,稳定运行 - ❌ 限制过严: 可能丢失重要数据 - ⚖️ 需要根据实际情况调整 3. 配置优先级: # Job级别配置覆盖全局配置 global: sample_limit: 1000000 scrape_configs: - job_name: "special_job" sample_limit: 500000 # 覆盖全局设置 4. 渐进式调整: # 建议从宽松限制开始,根据实际使用情况逐步收紧 sample_limit: 0 # 先无限制运行 sample_limit: 10000000 # 然后设置较宽松限制 sample_limit: 5000000 # 最后调整到合适值 这些限制是保护 Prometheus 稳定运行的重要机制,建议根据实际环境和监控需求合理配置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 📊 Prometheus Global 限制参数表 | 参数 | 默认值 | 限制对象 | 计算时机 | 超限后果 | 实验性 | 配置格式 | |--------------------------|-----|-----------|--------------------|-------|-----|--------| | body_size_limit | 0 | HTTP响应体大小 | 接收响应时 | 抓取失败 | ✅ | 100MB | | target_limit | 0 | 抓取目标数量 | target_relabeling后 | 目标不抓取 | ✅ | 10000 | | sample_limit | 0 | 样本数量 | metric_relabeling后 | 抓取失败 | ❌ | 500000 | | label_limit | 0 | 每个样本的标签数 | metric_relabeling后 | 抓取失败 | ❌ | 100 | | label_name_length_limit | 0 | 标签名长度 | metric_relabeling后 | 抓取失败 | ❌ | 512 | | label_value_length_limit | 0 | 标签值长度 | metric_relabeling后 | 抓取失败 | ❌ | 2048 | 🎯 快速配置参考 生产环境推荐: global: body_size_limit: 100MB target_limit: 10000 sample_limit: 5000000 label_limit: 100 label_name_length_limit: 512 label_value_length_limit: 2048 资源受限环境: global: body_size_limit: 50MB target_limit: 5000 sample_limit: 1000000 label_limit: 50 label_name_length_limit: 256 label_value_length_limit: 1024 💡 关键要点 - 0 = 无限制 - 所有参数默认无限制 - 字节计算 - UTF-8编码,中文字符占3字节 - 实验性 - body_size_limit 和 target_limit 可能变化 - 渐进调整 - 建议从宽松到严格逐步收紧
keep_dropped_targets
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 keep_dropped_targets - 保留丢弃目标的内存限制 - 作用: 限制被 relabeling 丢弃但仍在内存中保留的目标数量 - 类型: <int> (整数) - 默认值: 0 (无限制) - 适用: 每个 scrape 配置 🎯 工作原理 Relabeling 过程: scrape_configs: - job_name: "kubernetes-pods" kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod relabel_configs: # 丢弃某些目标 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] regex: "true" action: keep # 只保留有该注解的pod 内存保留机制: 原始发现: 1000个pod targets Relabeling后: 200个有效targets (保留) 丢弃的: 800个targets keep_dropped_targets 控制这800个丢弃目标在内存中的保留数量 💾 内存管理 无限制 (默认): global: keep_dropped_targets: 0 # 默认值,无限制 # 所有被丢弃的目标都保留在内存中 # 优点: relabeling规则变更时目标能快速恢复 # 缺点: 内存占用可能很高 有限制: scrape_configs: - job_name: "kubernetes-pods" keep_dropped_targets: 1000 # 最多保留1000个丢弃目标 # 超过限制的丢弃目标会从内存中清理 # 优点: 节省内存 # 缺点: 目标恢复需要重新发现 🔧 实际应用场景 1. Kubernetes 环境: scrape_configs: - job_name: "kubernetes-pods" kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod relabel_configs: # 只监控带有特定注解的pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] regex: "true" action: keep keep_dropped_targets: 5000 # 保留5000个被丢弃的pod信息 # 场景: 集群中有大量pod,只有少数需要监控 # 保留被丢弃的pod信息,当注解变更时能快速恢复监控 2. 大规模服务发现: scrape_configs: - job_name: "consul-services" consul_sd_configs: - server: consul:8500 relabel_configs: # 过滤不需要监控的服务 - source_labels: [__meta_consul_tags] regex: ".*,monitoring,.*" action: keep keep_dropped_targets: 2000 # 场景: Consul中有几千个服务,只有带monitoring标签的才监控 3. 动态环境: scrape_configs: - job_name: "dynamic-targets" file_sd_configs: - files: ["/etc/prometheus/targets/*.yml"] relabel_configs: # 根据环境变量过滤 - source_labels: [__meta_filesd_env] regex: "${ENVIRONMENT}" action: keep keep_dropped_targets: 1000 # 场景: 目标经常变更,需要保留历史信息 📊 内存使用对比 配置示例: # 场景: 发现10000个目标,relabeling后保留1000个 # 被丢弃: 9000个目标 # 配置1: 无限制 (默认) keep_dropped_targets: 0 # 内存占用: ~9000个目标的元数据 # 配置2: 有限制 keep_dropped_targets: 1000 # 内存占用: ~1000个目标的元数据 (节省90%内存) 内存估算: # 每个丢弃目标的内存开销 # 标签信息: ~200-500字节 # 元数据: ~100-300字节 # 总计: ~300-800字节/目标 # 10000个丢弃目标 ≈ 3-8MB 内存 # 1000个丢弃目标 ≈ 0.3-0.8MB 内存 ⚙️ 配置建议 根据环境选择: 🏭 生产环境: scrape_configs: - job_name: "production-pods" keep_dropped_targets: 5000 # 平衡内存和恢复速度 💾 资源受限环境: scrape_configs: - job_name: "edge-devices" keep_dropped_targets: 500 # 严格限制内存使用 🔬 开发环境: scrape_configs: - job_name: "dev-services" keep_dropped_targets: 0 # 开发环境无限制 根据目标类型选择: 稳定目标: # 目标很少变更,可以设置较低限制 keep_dropped_targets: 100 动态目标: # 目标频繁变更,设置较高限制便于快速恢复 keep_dropped_targets: 5000 🔍 监控和调试 监控内存使用: # 查看 Prometheus 内存使用 curl http://localhost:9090/api/v1/series?match[]=process_resident_memory_bytes # 查看目标数量 curl http://localhost:9090/api/v1/series?match[]=prometheus_sd_discovered_targets 调整建议: # 1. 先运行观察内存使用 keep_dropped_targets: 0 # 2. 根据实际使用情况设置限制 keep_dropped_targets: 2000 # 3. 监控内存变化,继续调整 ⚠️ 注意事项 1. 性能影响: - ✅ 限制较多: 节省内存,但目标恢复慢 - ❌ 无限制: 内存占用高,但目标恢复快 - ⚖️ 需要根据实际情况权衡 2. 配置层级: # 这个参数通常在 scrape_config 级别设置 scrape_configs: - job_name: "example" keep_dropped_targets: 1000 # 在这里设置 # 而不是在 global 级别 global: # keep_dropped_targets: 1000 # ❌ 这样设置无效 3. 与其他限制配合: scrape_configs: - job_name: "kubernetes-pods" # 综合配置 target_limit: 5000 # 限制总目标数 sample_limit: 1000000 # 限制样本数 keep_dropped_targets: 2000 # 限制丢弃目标内存 💡 最佳实践 1. 渐进式调整: # 步骤1: 无限制运行观察 keep_dropped_targets: 0 # 步骤2: 根据内存使用设置限制 keep_dropped_targets: 5000 # 步骤3: 继续优化到合适值 keep_dropped_targets: 2000 2. 分级配置: # 根据job重要性分级 scrape_configs: - job_name: "critical-services" keep_dropped_targets: 5000 # 重要服务,保留更多 - job_name: "debug-metrics" keep_dropped_targets: 100 # 调试指标,严格限制 这个参数主要用于大规模服务发现环境中控制内存使用,特别是在 Kubernetes 或 Consul 等环境中,当发现的目标数量远大于实际监控的目标数量时非常有用。
metric_name_validation_scheme
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 ⏺ 📖 参数含义 metric_name_validation_scheme - 指标名称验证方案 - 作用: 定义指标和标签名称的字符验证规则 - 默认值: "utf8" - 选项: "" (空白)、"utf8"、"legacy" 🎯 三种验证方案对比 | 验证方案 | 默认值 | 支持字符 | Unicode支持 | 向后兼容 | 适用场景 | |----------|-----|--------------|-----------|--------|-------| | "utf8" | ✅ | 所有UTF-8字符 | ✅ 完全支持 | ❌ 新标准 | 现代化环境 | | "legacy" | ❌ | 字母、数字、冒号、下划线 | ❌ 仅ASCII | ✅ 兼容旧版 | 保守环境 | | "" (空白) | ❌ | 同"utf8" | ✅ 完全支持 | ❌ 新标准 | 同utf8 | 🔤 字符支持详解 UTF-8 方案 ("utf8"): # ✅ 支持所有这些指标名 cpu_usage_核心 # 中文 + 下划线 métrique_française # 法语字符 метрика_русская # 俄语字符 メトリックス日本語 # 日语字符 📊_system_metrics # Emoji字符 namespace/service:metric # 斜杠、冒号组合 Legacy 方案 ("legacy"): # ✅ 只支持这些 cpu_usage_total # 字母 + 下划线 http_requests_total # 字母 + 下划线 node_memory_available # 字母 + 下划线 prometheus_sd_discovered # 字母 + 下划线 duration:seconds_bucket # 字母 + 冒号 + 下划线 # ❌ 不支持 cpu_usage_核心 # 中文字符 métrique_française # 非ASCII字符 namespace/metric # 斜杠 📊_system_metrics # Emoji 🔧 配置示例 现代环境 (推荐): global: metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" # 允许丰富的指标命名 # 支持国际化、特殊符号等 兼容环境: global: metric_name_validation_scheme: "legacy" # 严格的字符限制 # 确保与旧版本兼容 默认行为: global: # 不设置,使用默认值 # 等同于: metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" 🌍 国际化支持示例 中文指标名: # UTF-8 模式下 # 指标导出 服务器_cpu使用率{instance="host1"} 75.5 数据库连接池大小{instance="db1"} 10 # 查询 rate(服务器_cpu使用率[5m]) 多语言混合: # 混合语言的指标 api_request_total # 英文 métrique_latence_ms # 法语 応答時間ミリ秒 # 日语 продолжительность_запроса # 俄语 特殊字符: # 支持各种特殊字符 http://server:8080/metrics_rate # URL风格 service:instance:cpu_usage # 层次结构 🚀_system_startup_time_seconds # Emoji ⚠️ 兼容性考虑 PromQL 查询兼容性: # UTF-8 指标在 PromQL 中的使用 # ✅ 正确 rate(服务器_cpu使用率[5m]) # 可能需要转义的特殊字符 rate(http://server:8080/metrics_rate[5m]) # 或者使用标签过滤 rate(metrics_rate{url="http://server:8080"}[5m]) 系统集成影响: # 影响的组件: # 1. Prometheus Server (存储和查询) # 2. Alertmanager (告警规则) # 3. Grafana (可视化) # 4. Remote Storage (远程存储) # 5. Federated Prometheus (联邦) 🔄 迁移指南 从 Legacy 迁移到 UTF-8: # 步骤1: 检查现有指标 # 运行 Prometheus 查看是否有不合规的指标 # 步骤2: 评估影响 # 检查下游系统是否支持 UTF-8 指标名 # 步骤3: 逐步迁移 global: metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" # 步骤4: 更新查询和仪表板 # 使用新的 UTF-8 指标名 从 UTF-8 回退到 Legacy: # 如果遇到兼容性问题 global: metric_name_validation_scheme: "legacy" # 需要修改指标导出器 # 使用 ASCII 字符重命名指标 📊 实际应用场景 1. 国际化团队: global: metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" # 团队可以使用母语命名指标 # 便于理解和维护 2. 微服务架构: global: metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" # 使用层次化的指标命名 service:user:api:request_total service:payment:db:connection_pool service:notification:email:queue_size 3. 云原生环境: global: metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" # 支持 Kubernetes 风格的标签 app.kubernetes.io/name: "myapp" app.kubernetes.io/version: "v1.2.3" 🎯 选择建议 选择 UTF-8 当: - ✅ 团队国际化,需要多语言支持 - ✅ 现代化监控系统 - ✅ 需要丰富的指标命名 - ✅ 下游系统支持 UTF-8 选择 Legacy 当: - ✅ 需要与旧版本 Prometheus 兼容 - ✅ 下游系统不支持 UTF-8 - ✅ 保守的生产环境 - ✅ 只需要基础的 ASCII 字符 💡 你的配置分析 你的配置使用默认值: global: # metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" (默认) 这是很好的选择: - ✅ 现代化: 支持完整的 UTF-8 字符集 - ✅ 国际化: 支持多语言指标命名 - ✅ 灵活性: 允许丰富的命名约定 - ✅ 未来兼容: 符合云原生监控的发展趋势 如果将来遇到兼容性问题,可以随时切换到 legacy 模式。
convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb + always_scrape_classic_histograms
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 ⏺ 📊 Prometheus 直方图配置参数详解 这两个参数都与 Prometheus 的原生直方图功能相关。 🎯 1. convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb - 经典直方图转换 含义: - 将所有抓取的经典直方图转换为原生直方图 - NHCB = Native Histograms with Custom Buckets - 需要启用原生直方图功能: --enable-feature=native-histograms 配置示例: global: convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true # 启用转换 # convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: false # 默认值,不转换 转换效果: # 经典直方图 (抓取前) http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="0.1"} 100 http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="0.5"} 300 http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="1.0"} 450 http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="+Inf"} 500 http_request_duration_seconds_sum 123.45 http_request_duration_seconds_count 500 # 转换为原生直方图 (存储后) http_request_duration_seconds{n="500",s="123.45",b="0.1,0.5,1.0"} 500 # 其中 b 是自定义桶边界 🔄 2. always_scrape_classic_histograms - 经典直方图抓取控制 含义: - 控制是否同时抓取经典直方图和原生直方图 - 只有启用原生直方图功能时才有效 - 默认情况下,如果原生直方图可用,就不会抓取经典版本 配置示例: global: always_scrape_classic_histograms: true # 同时抓取两种格式 # always_scrape_classic_histograms: false # 默认值 🔧 配置组合效果 场景1: 默认配置 global: # 默认值 convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: false always_scrape_classic_histograms: false # 启动命令 ./prometheus --enable-feature=native-histograms # 行为: # - 优先抓取原生直方图 # - 如果没有原生直方图,抓取经典直方图 # - 不进行转换 场景2: 启用转换 global: convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true always_scrape_classic_histograms: false # 启动命令 ./prometheus --enable-feature=native-histograms # 行为: # - 抓取经典直方图 # - 自动转换为原生直方图存储 # - 不保留原始经典格式 场景3: 同时抓取两种格式 global: convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: false always_scrape_classic_histograms: true # 启动命令 ./prometheus --enable-feature=native-histograms # 行为: # - 同时抓取原生直方图和经典直方图 # - 两种格式都存储 # - 占用更多存储空间 场景4: 完整兼容模式 global: convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true always_scrape_classic_histograms: true # 启动命令 ./prometheus --enable-feature=native-histograms # 行为: # - 同时抓取两种格式 # - 经典格式转换为原生格式存储 # - 最大兼容性,但存储开销最大 📊 直方图格式对比 | 特性 | 经典直方图 | 原生直方图 | |------|--------|--------| | 存储格式 | 多个时间序列 | 单一时间序列 | | 桶边界 | 预定义 | 动态自适应 | | 精度 | 受限于桶数量 | 更高精度 | | 存储效率 | 较低 | 更高 | | 查询性能 | 一般 | 更好 | | 兼容性 | 广泛支持 | 较新功能 | 🎯 实际应用场景 1. 渐进式迁移: # 步骤1: 启用原生直方图,保持经典兼容 global: convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true always_scrape_classic_histograms: false # 步骤2: 逐步迁移到原生直方图 # 更新 exporters 支持原生直方图 # 步骤3: 完全使用原生直方图 global: convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: false always_scrape_classic_histograms: false 2. 高精度监控: global: convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true # 将现有的经典直方图转换为高精度的原生直方图 # 适用于需要精确延迟分析的场景 3. 兼容性优先: global: always_scrape_classic_histograms: true # 确保下游工具能继续使用经典格式 # 适用于 Grafana 仪表板和告警规则依赖经典格式的情况 ⚠️ 重要注意事项 功能启用: # 必须启用原生直方图功能 ./prometheus --enable-feature=native-histograms # 否则这些配置无效 存储影响: # 存储空间需求 # 经典直方图: 基准 # 原生直方图: 通常更节省空间 # 两种格式: 约双倍空间 查询兼容性: # 查询语句可能需要调整 # 经典: histogram_quantile(0.95, rate(http_request_duration_seconds_bucket[5m])) # 原生: histogram_quantile(0.95, rate(http_request_duration_seconds[5m])) 💡 配置建议 对于你的环境: 如果刚开始使用原生直方图: global: convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true always_scrape_classic_histograms: false # 启用转换,享受原生直方图的好处 如果需要最大兼容性: global: convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: false always_scrape_classic_histograms: true # 同时支持两种格式,确保兼容性 如果追求最佳性能: global: convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: false always_scrape_classic_histograms: false # 完全使用原生直方图,获得最佳性能 🚀 启用示例 # 1. 启动 Prometheus 时启用原生直方图 ./prometheus \ --config.file=prometheus.yml \ --enable-feature=native-histograms \ --storage.tsdb.path=data/ # 2. 配置文件中设置转换策略 global: convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true always_scrape_classic_histograms: false 这些参数主要用于从经典直方图向原生直方图迁移的过渡期,帮助用户平滑升级到新的直方图格式。
gogc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 gogc - Go 垃圾回收器参数 - 作用: 配置 Go 运行时的垃圾回收器 GOGC 参数 - 默认值: 75 - 类型: <int> (整数) - 影响: 内存使用与 CPU 使用的平衡 🎯 工作原理 GOGC 参数含义: GOGC=75 表示:当新分配的内存达到上次回收后存活内存的 75% 时触发垃圾回收 计算公式: // 触发条件 新分配内存 >= (上次GC后存活内存 * GOGC / 100) // 示例计算 上次GC后存活内存 = 100MB GOGC = 75 触发阈值 = 100MB * 75 / 100 = 75MB // 当新分配75MB内存时,触发下一次GC 📊 不同设置的影响 默认值 (75): runtime: gogc: 75 # 默认值 # 特点: # - 平衡的内存和CPU使用 # - 适合大多数工作负载 # - Go 语言的推荐默认值 较低值 (更频繁GC): runtime: gogc: 50 # 更频繁回收 # 影响: # ✅ 内存占用更低 # ✅ 内存压力更小 # ❌ CPU 使用更高 # ❌ GC 暂停更频繁 较高值 (较少GC): runtime: gogc: 100 # 较少回收 # 影响: # ✅ CPU 使用更低 # ✅ GC 暂停更少 # ❌ 内存占用更高 # ❌ 可能出现内存峰值 🔧 实际配置示例 1. 内存敏感环境: runtime: gogc: 50 # 更积极的GC,减少内存使用 # 适用场景: # - 容器环境内存限制严格 # - 内存成本较高的环境 # - 需要稳定内存占用的应用 2. CPU敏感环境: runtime: gogc: 100 # 减少GC频率,节省CPU # 适用场景: # - CPU资源受限 # - 需要低延迟的处理 # - 内存充足的环境 3. 高负载监控: runtime: gogc: 25 # 非常积极的GC # 适用场景: # - 大量指标处理 # - 需要严格控制内存 # - 可以接受更高CPU使用 4. 稳定性优先: runtime: gogc: 200 # 非常保守的GC # 适用场景: # - 追求最低延迟 # - 内存资源充足 # - 对GC暂停敏感 📈 性能对比表 | GOGC 值 | 内存使用 | CPU 使用 | GC 频率 | 延迟 | 适用场景 | |--------|------|--------|-------|-----|--------| | 25 | 很低 | 很高 | 很高 | 较低 | 内存受限 | | 50 | 低 | 高 | 高 | 低 | 平衡偏内存 | | 75 | 中等 | 中等 | 中等 | 中等 | 默认推荐 | | 100 | 高 | 低 | 低 | 高 | 平衡偏CPU | | 200 | 很高 | 很低 | 很低 | 很高 | CPU受限 | 🎯 Prometheus 特定考虑 工作负载特征: # Prometheus 的内存使用模式: # 1. 大量时间序列数据 # 2. 频繁的数据写入 # 3. 查询时的临时内存分配 # 4. 规则评估的内存需求 推荐配置: # 根据部署规模调整 # 小规模 ( < 100万时间序列) runtime: gogc: 75 # 默认值即可 # 中规模 (100万-1000万时间序列) runtime: gogc: 50 # 稍微积极一些 # 大规模 ( > 1000万时间序列) runtime: gogc: 25 # 更积极的GC控制 🔍 监控和调优 监控 GC 指标: # 查看 Prometheus 自身的 GC 指标 curl http://localhost:9090/metrics | grep gc # 相关指标: # go_gc_duration_seconds - GC 耗时 # go_memstats_heap_alloc_bytes - 堆内存分配 # go_memstats_next_gc_bytes - 下次GC触发阈值 调优流程: # 步骤1: 监控当前GC行为 # 观察 go_gc_duration_seconds 和内存使用模式 # 步骤2: 设置初始值 runtime: gogc: 50 # 步骤3: 监控效果 # 观察CPU和内存使用变化 # 步骤4: 根据结果调整 # 根据实际需求微调 gogc 值 ⚠️ 注意事项 1. 平衡权衡: # 没有完美的值,需要权衡: # - 内存使用 vs CPU 使用 # - GC频率 vs 暂停时间 # - 稳定性 vs 性能 2. 环境差异: # 不同环境可能需要不同设置 # - 物理机 vs 容器 # - 内存充足 vs 内存受限 # - 高负载 vs 低负载 3. 监控影响: # 调整后需要监控: # - 内存使用模式 # - CPU 使用率 # - GC 暂停时间 # - 查询性能 💡 配置建议 生产环境: runtime: gogc: 50 # 稍微保守一些,控制内存使用 开发环境: runtime: gogc: 100 # 可以更宽松,减少GC干扰 容器环境: runtime: gogc: 25 # 容器内存限制通常较严格 资源充足环境: runtime: gogc: 100 # 内存充足时优先考虑性能 🎯 实际应用 你的配置使用默认值: # runtime 部分通常不显式配置 # 使用默认的 gogc: 75 这是一个合理的默认设置: - ✅ 平衡性好: 适合大多数场景 - ✅ 稳定可靠: Go 官方推荐的默认值 - ✅ 易于维护: 不需要特殊调优 如果遇到内存压力或性能问题,可以考虑调整这个参数。通常建议先从 50 开始尝试,然后根据实际效果进一步调整。
rule_files
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 rule_files - 规则文件配置 - 作用: 指定包含告警规则和录制规则的文件路径 - 格式: 文件路径列表,支持 glob 模式匹配 - 内容: 从所有匹配的文件中读取规则和告警 🔧 基础配置 简单配置: rule_files: - "prometheus.rules.yml" - "alerts.yml" 你的配置: rule_files: - "prometheus.rules.yml" Glob 模式匹配: rule_files: - "rules/*.yml" # rules目录下所有.yml文件 - "alerts/**/*.yaml" # alerts目录及子目录下所有.yaml文件 - "/etc/prometheus/rules.d/*.rules" # 系统配置目录 📋 规则文件内容 录制规则 (Recording Rules): # prometheus.rules.yml groups: - name: recording_rules interval: 30s # 评估间隔,可选 rules: - record: job:http_requests:rate5m expr: rate(http_requests_total[5m]) - record: job:http_requests:rate5m:sum expr: sum(rate(http_requests_total[5m])) 告警规则 (Alerting Rules): # prometheus.rules.yml groups: - name: alert_rules rules: - alert: HighCPUUsage expr: cpu_usage > 80 for: 5m labels: severity: warning annotations: summary: "CPU usage is above 80%" description: "CPU usage has been above 80% for more than 5 minutes" 🎯 完整规则文件示例 综合规则文件: # prometheus.rules.yml groups: # 录制规则组 - name: performance_metrics interval: 15s rules: - record: instance:cpu_usage:rate5m expr: 100 - (avg by(instance) (rate(node_cpu_seconds_total{mode="idle"}[5m])) * 100) - record: instance:memory_usage:rate5m expr: (1 - (node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes / node_memory_MemTotal_bytes)) * 100 # 告警规则组 - name: system_alerts rules: - alert: InstanceDown expr: up == 0 for: 1m labels: severity: critical annotations: summary: "Instance {{ $labels.instance }} is down" description: "Instance {{ $labels.instance }} has been down for more than 1 minute" - alert: HighCPUUsage expr: instance:cpu_usage:rate5m > 80 for: 5m labels: severity: warning annotations: summary: "High CPU usage on {{ $labels.instance }}" description: "CPU usage is {{ $value }}% on instance {{ $labels.instance }}" 📁 文件组织策略 按功能分类: rule_files: - "rules/system.yml" # 系统监控规则 - "rules/application.yml" # 应用监控规则 - "rules/network.yml" # 网络监控规则 - "alerts/critical.yml" # 严重告警 - "alerts/warning.yml" # 警告告警 按环境分类: rule_files: - "rules/common.yml" # 通用规则 - "rules/production.yml" # 生产环境规则 - "rules/staging.yml" # 测试环境规则 - "rules/development.yml" # 开发环境规则 按团队分类: rule_files: - "rules/platform.yml" # 平台团队 - "rules/application.yml" # 应用团队 - "rules/security.yml" # 安全团队 - "rules/network.yml" # 网络团队 🔍 Glob 模式详解 常用模式: rule_files: # 基础模式 - "rules.yml" # 单个文件 - "rules/*.yml" # rules目录下所有.yml文件 - "rules/**/*.yml" # rules目录及子目录下所有.yml文件 # 高级模式 - "/etc/prometheus/rules/*.yml" # 绝对路径 - "rules/*-rules.yml" # 匹配特定命名模式 - "rules/[a-z]*.yml" # 正则表达式模式 多文件合并: rule_files: - "rules/base.yml" # 基础规则 - "rules/custom/*.yml" # 自定义规则 - "rules/overrides/*.yml" # 覆盖规则 # Prometheus 会按顺序加载所有文件 # 后加载的规则会覆盖同名的录制规则 ⚙️ 实际配置示例 小型环境: rule_files: - "prometheus.rules.yml" 中型环境: rule_files: - "rules/system.yml" - "rules/application.yml" - "alerts/common.yml" 大型环境: rule_files: - "rules/infrastructure/*.yml" - "rules/applications/*.yml" - "rules/security/*.yml" - "alerts/critical/*.yml" - "alerts/warning/*.yml" - "overrides/production/*.yml" 🔧 文件热重载 重载触发: # 发送 SIGHUP 信号重载配置 kill -HUP $(pidof prometheus) # 或者使用 HTTP API curl -X POST http://localhost:9090/-/reload 重载行为: # 重载时会: # 1. 重新解析所有规则文件 # 2. 验证规则语法 # 3. 更新内存中的规则 # 4. 不影响正在运行的抓取 ⚠️ 注意事项 1. 文件路径: # ✅ 相对路径 (相对于配置文件目录) rule_files: - "rules/*.yml" # ✅ 绝对路径 rule_files: - "/etc/prometheus/rules/*.yml" # ❌ 不存在的文件会导致启动失败 rule_files: - "nonexistent.yml" 2. 文件格式: # 支持 YAML 和 YAML 格式 rule_files: - "rules.yml" # ✅ - "rules.yaml" # ✅ - "rules.json" # ❌ 不支持 3. 规则验证: # 使用 promtool 验证规则文件 promtool check rules prometheus.rules.yml # 验证多个文件 promtool check rules rules/*.yml 4. 性能考虑: # 避免过多的小文件 # ❌ 不推荐 rule_files: - "rules/001.yml" - "rules/002.yml" - ... - "rules/100.yml" # ✅ 推荐 rule_files: - "rules/system.yml" - "rules/application.yml" 💡 最佳实践 1. 文件命名规范: # 推荐的命名方式 rules-system.yml rules-application.yml alerts-critical.yml overrides-production.yml 2. 规则组织: # 按逻辑分组,不要把所有规则放在一个文件中 # 每个文件专注一个领域 # 定期清理不使用的规则 3. 版本控制: # 将规则文件纳入版本控制 git add rules/ git commit -m "Add new alert rules" 4. 测试验证: # 在部署前测试规则 promtool check rules rules/*.yml # 测试告警表达式 promtool query instant 'up == 0' 🎯 你的配置分析 你的配置: rule_files: - "prometheus.rules.yml" 这是一个简洁的配置: - ✅ 简单明了: 单个文件包含所有规则 - ✅ 易于管理: 规则集中在一个文件中 - ✅ 适合小规模: 对于中小型部署很合适 如果将来规则增多,可以考虑拆分为多个文件按功能分类管理。
scrape_config_files + scrape_configs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 1. scrape_config_files - 抓取配置文件 含义: - 指定包含抓取配置的外部文件路径 - 支持 glob 模式匹配 - 从匹配文件中读取抓取配置并追加到主配置中 用途: - 🔧 模块化配置管理 - 🔄 动态配置更新 - 🏗️ 配置文件分离 2. scrape_configs - 抓取配置列表 含义: - 直接在主配置文件中定义抓取配置 - 包含所有监控目标的抓取设置 - 主要的监控配置部分 🔧 配置方式对比 直接配置 (scrape_configs): # prometheus.yml - 传统方式 scrape_configs: - job_name: "prometheus" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090"] - job_name: "node" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9100"] 外部文件配置 (scrape_config_files): # prometheus.yml - 主配置文件 scrape_config_files: - "configs/*.yml" - "/etc/prometheus/scrape-configs.d/*.yaml" # configs/prometheus.yml - 外部文件 - job_name: "prometheus" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090"] # configs/node.yml - 外部文件 - job_name: "node" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9100"] 🎯 混合使用示例 主配置 + 外部文件: # prometheus.yml global: scrape_interval: 15s evaluation_interval: 1m # 核心配置在主文件中 scrape_configs: - job_name: "prometheus" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090"] # 其他配置从外部文件加载 scrape_config_files: - "configs/services/*.yml" - "configs/infrastructure/*.yml" 📁 文件组织策略 按环境分类: # prometheus.yml scrape_config_files: - "configs/common/*.yml" # 通用配置 - "configs/production/*.yml" # 生产环境 - "configs/staging/*.yml" # 测试环境 按业务分类: scrape_config_files: - "configs/infrastructure/*.yml" # 基础设施 - "configs/applications/*.yml" # 应用服务 - "configs/monitoring/*.yml" # 监控系统 - "configs/security/*.yml" # 安全监控 按团队分类: scrape_config_files: - "configs/platform/*.yml" # 平台团队 - "configs/backend/*.yml" # 后端团队 - "configs/frontend/*.yml" # 前端团队 - "configs/data/*.yml" # 数据团队 🔧 实际配置示例 1. 基础示例: # prometheus.yml scrape_configs: - job_name: "prometheus" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090"] scrape_config_files: - "node-exporter.yml" - "app-metrics.yml" 2. Kubernetes 环境: # prometheus.yml scrape_config_files: - "configs/kubernetes/*.yml" - "configs/services/*.yml" - "configs/infrastructure/*.yml" # configs/kubernetes/pods.yml - job_name: "kubernetes-pods" kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: true 3. 动态配置管理: # prometheus.yml scrape_config_files: - "configs/active/*.yml" # 当前激活的配置 - "configs/templates/*.yml" # 配置模板 # 可以通过脚本动态更新配置文件 # 然后重载 Prometheus 🔄 配置更新机制 文件内容合并: # prometheus.yml scrape_configs: - job_name: "core" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090"] scrape_config_files: - "configs/services/*.yml" # configs/services/web.yml - job_name: "web" static_configs: - targets: ["web1:8080", "web2:8080"] # 最终效果等同于: scrape_configs: - job_name: "core" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090"] - job_name: "web" static_configs: - targets: ["web1:8080", "web2:8080"] 热重载支持: # 重载配置 (包括外部文件) curl -X POST http://localhost:9090/-/reload # 或者发送信号 kill -HUP $(pidof prometheus) 🎯 使用场景 1. 配置分离: # 将配置按模块分离,便于管理 # 不同团队负责各自的配置文件 # 减少主配置文件的复杂度 2. 动态配置: # 通过自动化脚本动态生成配置 # 支持基于服务发现的配置生成 # 便于 CI/CD 集成 3. 环境隔离: # 不同环境使用不同的配置文件 # 主配置保持一致,只替换特定部分 # 支持配置模板化 📊 文件结构示例 /etc/prometheus/ ├── prometheus.yml # 主配置文件 ├── configs/ │ ├── infrastructure/ │ │ ├── node-exporter.yml │ │ ├── cadvisor.yml │ │ └── blackbox-exporter.yml │ ├── applications/ │ │ ├── web-servers.yml │ │ ├── api-servers.yml │ │ └── databases.yml │ └── monitoring/ │ ├── alertmanager.yml │ └── prometheus.yml └── templates/ ├── job-template.yml └── service-template.yml ⚠️ 注意事项 1. 文件格式: # 外部文件只包含抓取配置,不是完整的 Prometheus 配置 # ✅ 正确格式 - job_name: "example" static_configs: - targets: ["host:port"] # ❌ 错误格式 global: scrape_interval: 15s scrape_configs: - job_name: "example" static_configs: - targets: ["host:port"] 2. 文件路径: # 支持相对路径和绝对路径 scrape_config_files: - "configs/*.yml" # 相对路径 - "/etc/prometheus/configs/*.yml" # 绝对路径 3. 重复配置: # 如果出现重复的 job_name,后加载的会覆盖先加载的 # 建议确保 job_name 的唯一性 💡 最佳实践 1. 配置管理: # 使用版本控制管理所有配置文件 # 建立配置文件的命名规范 # 定期清理不使用的配置 2. 文件验证: # 验证配置文件语法 promtool check config prometheus.yml # 测试配置文件 promtool config check prometheus.yml 3. 自动化: # 使用脚本自动生成配置 # 结合服务发现动态更新 # 集成到 CI/CD 流程 🎯 选择建议 使用 scrape_configs 当: - ✅ 配置简单且固定 - ✅ 小规模部署 - ✅ 不需要频繁变更 使用 scrape_config_files 当: - ✅ 配置需要模块化管理 - ✅ 大规模部署 - ✅ 需要动态更新配置 - ✅ 多团队协作 这种配置方式让 Prometheus 的配置管理更加灵活和可扩展,特别适合复杂的生产环境。
alerting
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 alerting - 告警配置 用于配置 Prometheus 如何与 Alertmanager 通信,包括告警重标签和 Alertmanager 实例设置。 🎯 配置结构解析 完整配置示例: alerting: # 告警重标签配置 alert_relabel_configs: - source_labels: [alertname] regex: "HighMemoryUsage" target_label: severity replacement: "warning" # Alertmanager 实例配置 alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9093"] 🏷️ alert_relabel_configs - 告警重标签 作用: 在发送告警到 Alertmanager 之前,对告警标签进行重写 常用重标签操作: 1. 添加/修改标签: alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 添加环境标签 - target_label: environment replacement: "production" # 修改严重级别 - source_labels: [alertname] regex: "High.*" target_label: severity replacement: "warning" 2. 过滤告警: alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 只发送特定告警 - source_labels: [alertname] regex: "CriticalError|ServiceDown" action: keep # 丢弃某些告警 - source_labels: [alertname] regex: "Debug.*" action: drop 3. 标签标准化: alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 标准化集群名称 - source_labels: [cluster] regex: "prod-(.*)" target_label: cluster replacement: "$1" # 添加统一标签 - source_labels: [job] target_label: service replacement: "$1" 📡 alertmanagers - Alertmanager 配置 静态配置: alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: - "alertmanager1:9093" - "alertmanager2:9093" labels: dc: "us-west" 服务发现配置: alerting: alertmanagers: # Kubernetes 服务发现 - kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints namespaces: names: - monitoring relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] regex: "alertmanager" action: keep - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name] regex: "web" action: keep # Consul 服务发现 - consul_sd_configs: - server: consul:8500 services: ["alertmanager"] 🔧 完整配置示例 1. 基础配置: alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9093"] 2. 高可用配置: alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: - "alertmanager-1:9093" - "alertmanager-2:9093" - "alertmanager-3:9093" labels: cluster: "production" alert_relabel_configs: # 添加集群信息 - target_label: cluster replacement: "prod-cluster" # 标准化告警名称 - source_labels: [alertname] regex: "(.*)Alert" target_label: alertname replacement: "$1" 3. 环境分离配置: alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 添加环境标签 - target_label: environment replacement: "${ENVIRONMENT}" # 添加源标签 - target_label: prometheus_source replacement: "${HOSTNAME}" # 过滤调试告警 - source_labels: [alertname] regex: "Debug.*" action: drop alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ["alertmanager-${ENVIRONMENT}:9093"] 4. Kubernetes 集群配置: alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 添加命名空间标签 - source_labels: [namespace] target_label: k8s_namespace # 添加集群标签 - target_label: k8s_cluster replacement: "${CLUSTER_NAME}" # 标准化服务标签 - source_labels: [pod] regex: "(.*)-[0-9a-z]+-[0-9a-z]+" target_label: service replacement: "$1" alertmanagers: - kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints namespaces: names: - monitoring relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] regex: "alertmanager" action: keep - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name] regex: "web" action: keep - source_labels: [__address__] target_label: __address__ replacement: "alertmanager.monitoring.svc:9093" 🎯 实际应用场景 1. 多集群告警聚合: alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 添加集群标识 - target_label: cluster replacement: "${CLUSTER_NAME}" # 统一告警名称 - source_labels: [alertname] regex: "(.*)_.*" target_label: unified_alert replacement: "$1" alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ["central-alertmanager:9093"] 2. 环境隔离: alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 环境标签 - target_label: environment replacement: "production" # 修改告警路由 - source_labels: [severity] regex: "critical" target_label: route replacement: "oncall" alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ["prod-alertmanager:9093"] - static_configs: - targets: ["oncall-alertmanager:9093"] relabel_configs: - source_labels: [route] regex: "oncall" action: keep 🔄 重标签操作详解 常用 action 类型: alert_relabel_configs: # replace: 替换标签值 (默认) - source_labels: [severity] regex: "warning" target_label: level replacement: "warning" # keep: 保留匹配的告警 - source_labels: [team] regex: "backend" action: keep # drop: 丢弃匹配的告警 - source_labels: [environment] regex: "test" action: drop # hashmod: 哈希分片 - source_labels: [alertname] target_label: shard modulus: 3 action: hashmod 高级操作: alert_relabel_configs: # 标签映射 - labelmap: regex: "__meta_(.+)" replacement: "$1" # 多标签组合 - source_labels: [service, instance] separator: "-" target_label: endpoint replacement: "$1-$2" # 条件标签添加 - source_labels: [environment] regex: "production" target_label: urgency replacement: "high" ⚠️ 注意事项 1. 顺序重要: # 重标签按顺序执行 # 后续操作可以基于前面的结果 alert_relabel_configs: - step_1_operation - step_2_operation - step_3_operation 2. 告警丢失风险: # 谨慎使用 drop 操作 # 确保不会意外丢弃重要告警 - source_labels: [alertname] regex: "Important.*" action: drop # 危险操作! 3. 性能影响: # 复杂的重标签规则可能影响性能 # 保持规则简单高效 💡 最佳实践 1. 标签规范化: # 统一标签命名规范 # 添加必要的上下文信息 # 避免标签值过于复杂 2. 高可用配置: # 配置多个 Alertmanager 实例 # 使用负载均衡和故障转移 # 监控 Alertmanager 健康状态 3. 环境一致性: # 使用环境变量统一配置 # 保持不同环境的一致性 # 建立配置模板 这个配置是 Prometheus 告警系统的核心部分,负责将告警正确路由到 Alertmanager 并进行必要的标签处理。
remote_write
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 remote_write - 远程写入配置 - 作用: 将 Prometheus 抓取的指标数据发送到远程存储系统 - 用途: 长期存储、数据分析、多集群数据聚合 - 支持: 多个远程写入端点 🎯 基本配置结构 简单配置: remote_write: - url: "http://remote-storage:9201/api/v1/write" 完整配置: remote_write: - url: "https://remote-storage.example.com/api/v1/write" name: "primary-storage" remote_timeout: 30s headers: X-Custom-Header: "value" write_relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__name__] regex: "go_.*" action: drop queue_config: max_samples_per_send: 1000 capacity: 2500 🔧 详细配置参数 1. 基础连接配置: remote_write: - url: "https://remote-storage.example.com/api/v1/write" # 必需,远程存储URL name: "main-storage" # 可选,配置名称 remote_timeout: 30s # 可选,写入超时时间 headers: # 可选,自定义HTTP头 Authorization: "Bearer token123" X-Tenant-ID: "my-tenant" 2. 认证配置: remote_write: - url: "https://remote-storage.example.com/api/v1/write" # Basic Auth basic_auth: username: "admin" password: "secret" # Bearer Token authorization: type: "Bearer" credentials: "your-token" # OAuth 2.0 oauth2: client_id: "client123" client_secret: "secret123" token_url: "https://auth.example.com/token" # TLS 配置 tls_config: insecure_skip_verify: false ca_file: "/etc/ssl/certs/ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/ssl/certs/client.crt" key_file: "/etc/ssl/certs/client.key" 3. 数据过滤配置: remote_write: - url: "https://remote-storage.example.com/api/v1/write" # 写入前重标签 (过滤/修改数据) write_relabel_configs: # 只发送特定指标 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: "http_requests_total|cpu_usage" action: keep # 排除不需要的指标 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: "go_.*|prometheus_.*" action: drop # 添加额外标签 - target_label: source_prometheus replacement: "${HOSTNAME}" # 修改标签值 - source_labels: [environment] regex: "prod" target_label: env replacement: "production" 4. 队列配置: remote_write: - url: "https://remote-storage.example.com/api/v1/write" queue_config: max_samples_per_send: 1000 # 每次发送最大样本数 max_shards: 50 # 最大分片数 capacity: 2500 # 队列容量 min_shards: 1 # 最小分片数 max_retries: 3 # 最大重试次数 min_backoff: 30ms # 最小退避时间 max_backoff: 100ms # 最大退避时间 batch_send_deadline: 5s # 批次发送超时 🎯 实际配置示例 1. 基础远程存储: remote_write: - url: "http://influxdb:8086/api/v1/prom/write?db=prometheus" write_relabel_configs: # 排除 Prometheus 自身指标 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: "prometheus_.*|go_.*" action: drop 2. Thanos 配置: remote_write: - url: "http://thanos-receive:19291/api/v1/receive" headers: THANOSE-TENANT-ID: "tenant-1" send_exemplars: true send_native_histograms: true queue_config: max_samples_per_send: 2000 capacity: 10000 3. Cortex 配置: remote_write: - url: "http://cortex:9009/api/v1/push" headers: X-Scope-OrgID: "my-org" basic_auth: username: "cortex-user" password: "cortex-password" write_relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__name__] regex: ".*" target_label: __tmp_write replacement: "yes" - source_labels: [__tmp_write] regex: "yes" action: keep 4. 多目标写入: remote_write: # 主存储 - url: "https://primary-storage.example.com/api/v1/write" name: "primary" write_relabel_configs: - source_labels: [environment] regex: "production" action: keep # 备份存储 - url: "https://backup-storage.example.com/api/v1/write" name: "backup" write_relabel_configs: - source_labels: [environment] regex: "production" action: keep 🔄 数据流程 抓取数据 → 重标签过滤 → 队列缓冲 → 批次发送 → 远程存储 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 原始指标 write_relabel queue_config HTTP请求 持久化 队列机制: # 数据流向 1. 指标进入队列 2. 按分片分组 3. 批次发送 4. 失败重试 5. 成功确认 📊 性能调优 1. 队列优化: remote_write: - url: "https://remote-storage.example.com/api/v1/write" queue_config: # 高吞吐量配置 max_samples_per_send: 5000 # 增大批次大小 capacity: 25000 # 增大队列容量 max_shards: 200 # 增加并发 # 网络优化 batch_send_deadline: 10s # 延长批次超时 max_backoff: 1s # 增加重试间隔 2. 数据过滤优化: remote_write: - url: "https://remote-storage.example.com/api/v1/write" write_relabel_configs: # 只发送必要的指标 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: "(http_requests_total|error_rate|latency).*" action: keep # 移除高基数标签 - source_labels: [request_id] action: drop 3. 网络优化: remote_write: - url: "https://remote-storage.example.com/api/v1/write" remote_timeout: 10s # 设置合理超时 headers: Connection: "keep-alive" # 保持连接 queue_config: min_backoff: 10ms # 快速重试 max_retries: 5 # 增加重试次数 ⚠️ 注意事项 1. 资源消耗: # 远程写入会增加: # - CPU 使用 (数据序列化) # - 内存使用 (队列缓冲) # - 网络带宽 # - 磁盘I/O (WAL写入) 2. 数据一致性: # 网络问题可能导致: # - 数据延迟 # - 数据丢失 # - 乱序写入 3. 存储成本: # 远程存储通常按量计费 # 需要控制数据量 # 定期清理过期数据 💡 最佳实践 1. 数据过滤: # 只发送必要的业务指标 # 排除高基数的调试指标 # 定期审查发送的指标列表 2. 监控远程写入: # 监控关键指标 # - prometheus_remote_storage_samples_total # - prometheus_remote_storage_samples_failed_total # - prometheus_remote_storage_queue_highest_sent_timestamp_seconds 3. 容错设计: # 配置多个远程写入端点 # 设置合理的重试策略 # 监控写入健康状态 4. 安全考虑: # 使用HTTPS加密传输 # 配置适当的认证 # 定期轮换密钥和令牌 远程写入是 Prometheus 实现长期存储和水平扩展的重要功能,但需要仔细配置和监控以确保性能和可靠性。
otlp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 ⏺ 这是一个 Prometheus OTLP (OpenTelemetry Protocol) 接收器的配置说明。让我解释各个配置项的作用: 核心功能配置 资源属性处理 - promote_resource_attributes: 将指定的资源属性提升为标签,不能与 promote_all_resource_attributes 同时使用 - promote_all_resource_attributes: 将所有资源属性提升为标签(除了 ignore_resource_attributes 指定的) - ignore_resource_attributes: 当启用 promote_all_resource_attributes 时,忽略指定的资源属性 ⚠️ 注意: 启用 promote_all_resource_attributes 可能导致时间序列抖动和高内存使用 指标名称转换策略 translation_strategy 决定如何处理 OTLP 指标名称: 1. UnderscoreEscapingWithSuffixes (默认): 使用下划线转义特殊字符,添加后缀 2. NoUTF8EscapingWithSuffixes: 保留特殊字符,添加后缀 3. UnderscoreEscapingWithoutSuffixes: 下划线转义但不添加后缀 4. NoTranslation (实验性): 不转换,保留原始名称 ⚠️ 警告: NoTranslation 有显著风险,包括系列冲突和用户体验问题 其他功能 - keep_identifying_resource_attributes: 将服务相关属性添加到 target_info 指标 - convert_histograms_to_nhcb: 将 OTLP 直方图转换为带自定义桶的原生直方图 - promote_scope_metadata: 将 OTel 作用域元数据提升为指标标签 使用建议 根据 OpenTelemetry 最佳实践,推荐使用默认配置以平衡功能性和性能。
remote_read
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 配置结构 remote_read: [ - <remote_read> ... ] # 远程读取配置列表,可以配置多个远程读取端点 主要用途 远程读取允许 Prometheus 从其他 Prometheus 服务器或兼容的存储系统(如 Thanos、Cortex、Mimir)查询数据,而无需本地存储这些数据。 常见配置参数 每个 <remote_read> 配置通常包含: 基本连接 - url: <string> # 远程端点的 URL read_recent: <boolean> # 是否只读取近期数据(默认 false) 认证配置 basic_auth: username: <string> password: <string> bearer_token: <string> bearer_token_file: <string> TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: <string> cert_file: <string> key_file: <string> insecure_skip_verify: <boolean> 高级选项 timeout: <duration> # 请求超时时间 proxy_url: <string> # HTTP 代理 URL headers: # 自定义请求头 [ <string>: <string> ... ] required_matchers: # 必须匹配的标签选择器 [ <labelname>: <labelvalue> ... ] 使用场景 1. 数据联邦: 从多个 Prometheus 实例查询数据 2. 长期存储: 查询存储在 Thanos 等系统的历史数据 3. 数据聚合: 跨多个 Prometheus 实例进行数据聚合 4. 灾难恢复: 从备份系统读取数据 注意事项 - 远程读取会增加查询延迟 - 网络问题可能影响查询性能 - 需要确保远程端点的数据格式兼容性
storage
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 配置结构 storage: [ tsdb: <tsdb> ] # TSDB 时序数据库配置 [ exemplars: <exemplars> ] # 示例数据配置 TSDB 配置 (tsdb) 时间序列数据库的核心配置: 基本存储设置 tsdb: path: /prometheus # 数据存储路径 retention.time: 15d # 数据保留时间 retention.size: 500GB # 基于大小的保留策略 # WAL (Write-Ahead Log) 配置 wal: dir: /prometheus/wal # WAL 目录 segment_size: 100MB # WAL 段大小 性能优化 # 压缩配置 compression: zstd # 压缩算法 (snappy, zstd) # 内存映射 m-lock: false # 是否锁定内存防止交换 # 索引配置 index: max-series-per-metric: 1000000 # 每个指标最大系列数 # 块配置 blocks: max-duration: 2h # 最大块持续时间 min-duration: 2h # 最小块持续时间 运行时可重载参数 - retention.time - 数据保留时间 - retention.size - 基于大小的保留 - compression - 压缩算法 - 部分性能调优参数 Exemplars 配置 (exemplars) 示例数据存储配置,用于存储具体的指标样本: exemplars: path: /prometheus/exemplars # 示例数据存储路径 max_exemplars: 100000 # 最大示例数据数量 # 示例数据保留策略 retention: time: 7d # 保留时间 # 存储后端 storage: tsdb # 存储后端类型 运行时重载特性 ✅ 支持热重载: 可以通过 --web.enable-lifecycle API 或 SIGHUP 信号重新加载配置,无需重启 Prometheus 使用建议 1. 存储路径: 使用高性能存储设备(SSD) 2. 保留策略: 根据磁盘空间和查询需求调整 3. 内存设置: 适当调整 WAL 和缓存大小 4. 监控: 监控存储使用率和性能指标 示例配置 storage: tsdb: path: /data/prometheus retention.time: 30d retention.size: 1TB compression: zstd exemplars: path: /data/prometheus/exemplars max_exemplars: 50000
tracing
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 配置结构 tracing: [ <tracing_config> ] # 链路追踪配置 主要配置选项 追踪类型配置 tracing: # 追踪后端类型 type: jaeger # 或 "otlp", "zipkin", "datadog" # 采样率配置 sampling_fraction: 0.1 # 10% 采样率 Jaeger 配置 tracing: type: jaeger jaeger: # gRPC 端点配置 endpoint: "jaeger:14250" tls: enabled: true cert_file: /path/to/cert key_file: /path/to/key ca_file: /path/to/ca # HTTP 端点配置 collector_endpoint: "http://jaeger:14268/api/traces" OTLP (OpenTelemetry Protocol) 配置 tracing: type: otlp otlp: # gRPC 端点 endpoint: "otel-collector:4317" headers: authorization: "Bearer <token>" # 协议选择 protocol: grpc # 或 "http/protobuf" # TLS 配置 tls: enabled: false Zipkin 配置 tracing: type: zipkin zipkin: endpoint: "http://zipkin:9411/api/v2/spans" # TLS 配置 tls: enabled: true cert_file: /path/to/cert 使用场景 1. 性能监控 - 监控 Prometheus 内部操作性能 - 识别查询和存储瓶颈 - 优化配置和架构 2. 故障排查 - 追踪请求链路 - 定位性能问题根源 - 分析系统行为 3. 可观测性集成 - 与现有 APM 系统集成 - 统一监控视图 - 分布式追踪 追踪内容 Prometheus 会追踪以下操作: - HTTP 请求处理 - 查询执行 - 规则评估 - 远程读写操作 - 存储操作 完整示例 tracing: type: otlp sampling_fraction: 0.05 otlp: endpoint: "otel-collector:4317" protocol: grpc headers: x-api-key: "your-api-key" tls: enabled: true ca_file: /path/to/ca.pem 注意事项 - 追踪会带来一定性能开销 - 采样率建议设置为 1-10% - 确保追踪后端容量充足 - 监控追踪数据量避免存储爆炸
scrape_config
A scrape_config section specifies a set of targets and parameters describing how to scrape them .
In the general case, one scrape configuration specifies a single job . In advanced configurations, this may change.
Targets may be statically configured via the static_configs parameter
or dynamically discovered using one of the supported service-discovery mechanisms .
Additionally, relabel_configs allow advanced modifications to any target and its labels before scraping .
scrape_protocols + fallback_scrape_protocol
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 ⏺ 这两个配置项控制 Prometheus 抓取指标时使用的协议协商和降级策略: scrape_protocols 定义与目标服务协商支持的协议列表,按优先级排序: 支持的协议: - PrometheusProto - Protocol Buffers 二进制格式,最高效 - OpenMetricsText0.0.1 - OpenMetrics 文本格式 0.0.1 版本 - OpenMetricsText1.0.0 - OpenMetrics 文本格式 1.0.0 版本 - PrometheusText0.0.4 - Prometheus 文本格式 0.0.4 版本 - PrometheusText1.0.0 - Prometheus 文本格式 1.0.0 版本 使用示例: scrape_protocols: ["PrometheusProto", "OpenMetricsText1.0.0", "PrometheusText1.0.0"] fallback_scrape_protocol 当主要协议失败时的降级协议: 失败场景: - 返回空白响应 - 无法解析的内容 - 无效的 Content-Type - 协商失败 使用示例: # 优先使用二进制协议,失败时降级到文本格式 scrape_protocols: ["PrometheusProto", "OpenMetricsText1.0.0"] fallback_scrape_protocol: "PrometheusText1.0.0" 协议选择策略 1. 效率优先:PrometheusProto > OpenMetricsText > PrometheusText 2. 版本优先:1.0.0 > 0.0.4 > 0.0.1 3. 兼容性考虑:老旧服务可能只支持文本格式 这种设计确保了与不同版本和格式的 Prometheus 兼容性,同时提供了最优的性能体验。
honor_labels + honor_timestamps
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 ⏺ 这两个配置项控制 Prometheus 如何处理抓取数据中的标签和时间戳: honor_labels (默认: false) 处理标签冲突的策略,当抓取的数据中已包含 Prometheus 服务器端会自动添加的标签时: 冲突的标签包括: - job - 任务名称 - instance - 实例标识 - 手动配置的目标标签 - 服务发现生成的标签 设置为 false (默认): 抓取数据: job="my-app", instance="host1:8080" 服务器端: job="scrape-job", instance="192.168.1.100:8080" 结果: job="scrape-job" (服务器端) instance="192.168.1.100:8080" (服务器端) exported_job="my-app" (重命名后的抓取标签) exported_instance="host1:8080" (重命名后的抓取标签) 设置为 true: 抓取数据: job="my-app", instance="host1:8080" 服务器端: job="scrape-job", instance="192.168.1.100:8080" 结果: job="my-app" (保留抓取数据中的标签) instance="host1:8080" (保留抓取数据中的标签) 使用场景: - Federation:保留原始标签链路 - Pushgateway:保留推送时的所有标签 - 多级聚合:保持标签语义完整性 honor_timestamps (默认: true) 控制是否使用抓取数据中的时间戳: 设置为 true (默认): - 使用目标服务提供的原始时间戳 - 适用于目标服务有精确时间戳的场景 - 保持时间线的准确性 设置为 false: - 忽略目标时间戳,使用抓取时间作为时间戳 - 适用于目标服务时间不可靠的场景 - 确保数据的时间一致性 典型配置组合: # 联邦场景:保留原始标签和时间戳 honor_labels: true honor_timestamps: true # 普通监控:使用服务器标签,忽略目标时间戳 honor_labels: false honor_timestamps: false # Pushgateway:保留标签,使用抓取时间 honor_labels: true honor_timestamps: false 这些设置确保了在不同监控架构下的数据一致性和标签语义的准确性。
track_timestamps_staleness
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 ⏺ track_timestamps_staleness 控制 Prometheus 是否跟踪带有明确时间戳的指标的陈旧性。 默认行为 (false) 当设置为 false 时: - Prometheus 不会明确标记指标变为陈旧 - 指标在目标不可见时会自然过期 - 依赖默认的抓取间隔和超时机制来判断指标健康状态 启用陈旧性跟踪 (true) 当设置为 true 时: 触发条件: 1. 目标下线:目标服务不可访问 2. 指标消失:之前存在的指标在最新抓取中不再出现 3. 抓取失败:连续抓取失败超过阈值 处理方式: 时间线: T1: metric_cpu_usage{instance="host1"} 50.0 (正常) T2: metric_cpu_usage{instance="host1"} 55.0 (正常) T3: 目标下线 T4: 插入陈旧标记 metric_cpu_usage{instance="host1"} (stale marker) T5: 目标恢复,metric_cpu_usage{instance="host1"} 48.0 (恢复) 在 TSDB 中的表现: - 插入特殊的数据点标记指标为陈旧 - 查询时该指标会被过滤掉 - 图表显示中断而非延长到零值 使用场景 启用的优势: # 适用于需要精确状态跟踪的场景 track_timestamps_staleness: true 1. 服务发现环境:快速识别服务上下线 2. 告警准确性:避免基于陈旧数据的误报 3. 数据质量:确保查询结果的时效性 4. 容量规划:准确掌握资源使用状态 性能考虑: - 增加存储开销(陈旧标记) - 增加计算开销(跟踪状态变化) - 对于大规模部署需要评估影响 典型配置: # 核心服务监控 - 启用陈旧性跟踪 - job_name: 'critical-services' track_timestamps_staleness: true scrape_interval: 30s # 批量任务监控 - 可以关闭 - job_name: 'batch-jobs' track_timestamps_staleness: false scrape_interval: 5m 这个功能特别适用于微服务环境和动态基础设施,能够更准确地反映系统的实时状态。
kubernetes_sd_configs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 ⏺ kubernetes_sd_configs 是 Prometheus 用于 Kubernetes 服务发现的核心配置,允许 Prometheus 自动发现和监控 Kubernetes 集群中的各种资源。 基本结构 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: <role> api_server: <string> namespaces: names: [<string>, ...] selectors: - role: <role> label: <string> field: <string> attach_metadata: node: <boolean> 支持的角色 (role) 1. node 发现 Kubernetes 节点 - role: node selectors: - role: node field: metadata.name=node-1 # 选择特定节点 2. pod 发现运行中的 Pod - role: pod namespaces: names: - default - monitoring selectors: - role: pod label: app=nginx # 选择带特定标签的 pod 3. service 发现 Kubernetes 服务 - role: service namespaces: names: - default selectors: - role: service label: monitor=true 4. endpoint 发现服务端点(最常用) - role: endpoints namespaces: names: ["default", "kube-system"] 5. endpointslice 发现 EndpointSlice(大集群优化) - role: endpointslice selectors: - role: endpointslice label: kubernetes.io/service-name=my-service 6. ingress 发现 Ingress 资源 - role: ingress namespaces: names: ["default"] 完整配置示例 1. 基础 Pod 监控 - job_name: 'kubernetes-pods' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod namespaces: names: - default - monitoring relabel_configs: # 只监控带有指定注解的 Pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: true # 设置 metrics 路径 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) # 设置抓取端口 - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port] action: replace regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+) replacement: $1:$2 target_label: __address__ 2. Service 监控 - job_name: 'kubernetes-services' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: service namespaces: names: ["default"] relabel_configs: # 只监控带特定标签的服务 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_label_monitor] action: keep regex: enabled # 添加服务元数据 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: service_name - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_namespace] target_label: service_namespace 3. 节点监控 - job_name: 'kubernetes-nodes' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node relabel_configs: # 添加节点标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name] target_label: node_name - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_label_kubernetes_io_arch] target_label: arch 高级配置选项 API Server 配置 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod api_server: https://kubernetes.default.svc:443 tls_config: ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token 选择器配置 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod selectors: - role: pod label: app: nginx tier: frontend - role: pod field: status.phase: Running spec.restartPolicy: Always 元数据附加 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod attach_metadata: node: true # 附加节点元数据 常用标签 自动生成的标签包括: - __meta_kubernetes_namespace - __meta_kubernetes_pod_name - __meta_kubernetes_pod_ip - __meta_kubernetes_service_name - __meta_kubernetes_node_name - __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_* - __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_* 最佳实践 1. 使用注解控制抓取: # Pod 注解示例 metadata: annotations: prometheus.io/scrape: "true" prometheus.io/port: "8080" prometheus.io/path: "/metrics" 2. 合理命名空间过滤: namespaces: names: ["monitoring", "kube-system"] # 只监控特定命名空间 3. 使用 relabel_configs 优化: relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: true Kubernetes 服务发现为 Prometheus 提供了强大的动态监控能力,能够自动适应集群中的资源变化。
relabel_configs + metric_relabel_configs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 relabel_configs - 目标重标记 在抓取前对目标进行重标记,影响是否抓取以及如何抓取。 基本语法 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [<label>, ...] # 源标签列表 separator: ; # 标签分隔符 (默认;) target_label: <label> # 目标标签 regex: <regex> # 正则表达式 replacement: <string> # 替换字符串 action: <action> # 动作类型 常用动作 (action) 1. replace (默认) - 替换标签值 relabel_configs: # 从实例名提取服务名 - source_labels: [__address__] regex: '([^:]+)(:.*)?' replacement: '$1' target_label: instance_name # 添加环境标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: environment replacement: 'production' 2. keep - 保留匹配的目标 relabel_configs: # 只抓取带有特定注解的 Pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: "true" # 只监控特定命名空间 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] action: keep regex: "(default|monitoring|kube-system)" 3. drop - 丢弃匹配的目标 relabel_configs: # 排除测试环境 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_environment] action: drop regex: "test" # 排除特定的实例 - source_labels: [__address__] action: drop regex: ".*:9091" # 排除 9091 端口 4. hashmod - 哈希分片 relabel_configs: # 将目标分片到不同 Prometheus 实例 - source_labels: [__address__] target_label: __tmp_hash modulus: 3 action: hashmod - source_labels: [__tmp_hash] regex: "^0$" # 只处理第一个分片 action: keep 5. labelmap - 标签映射 relabel_configs: # 将所有 Kubernetes 标签添加为监控标签 - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+) replacement: k8s_pod_label_$1 6. labeldrop / labelkeep - 标签过滤 relabel_configs: # 删除特定标签 - action: labeldrop regex: "__meta_.*" # 只保留特定标签 - action: labelkeep regex: "(instance|job|__address__)" metric_relabel_configs - 指标重标记 在抓取后对指标进行重标记,影响存储哪些指标以及指标格式。 主要用途 1. 删除不需要的指标 metric_relabel_configs: # 删除高基数指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: "(go_.*|process_.*|prometheus_.*|http_.*|grpc_.*|container_.*|machine_.*|cadvisor_*)" # 删除特定前缀的指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: "debug_.*" 2. 重命名指标 metric_relabel_configs: # 统一指标名称 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: "custom_metric_(.+)" replacement: "standardized_metric_$1" action: replace # 删除指标前缀 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: "application_(.+)" replacement: "$1" action: replace 3. 添加或修改标签 metric_relabel_configs: # 添加环境标签 - source_labels: [instance] target_label: environment replacement: "production" action: replace # 提取服务名 - source_labels: [job] regex: "kubernetes-(.+)-endpoints" replacement: "$1" target_label: service action: replace 4. 指标聚合和降采样 metric_relabel_configs: # 降采样:只保留特定标签组合 - source_labels: [__name__, method, status_code] regex: "http_requests_total;(GET|POST);(200|400|500)" action: keep # 聚合:移除细粒度标签 - source_labels: [pod, container] action: labeldrop 完整示例 复杂的 Kubernetes 监控配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'kubernetes-pods' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod relabel_configs: # 1. 只抓取带特定注解的 Pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: "true" # 2. 设置抓取端口 - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port] action: replace regex: '([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)' replacement: '$1:$2' target_label: __address__ # 3. 设置 metrics 路径 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) # 4. 添加 Kubernetes 元数据标签 - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+) replacement: k8s_label_$1 # 5. 清理不需要的元数据 - action: labeldrop regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_.+ metric_relabel_configs: # 1. 删除不需要的指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: "go_.*|process_.*|prometheus_.*" # 2. 重命名指标 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: "custom_(.+)" replacement: "app_$1" action: replace # 3. 添加通用标签 - target_label: cluster replacement: "production" action: replace 性能考虑 1. relabing 在抓取前:减少不必要的网络请求 2. metric relabeling 在抓取后:减少存储和计算开销 3. 正则表达式性能:复杂正则会影响抓取延迟 4. 标签数量控制:过多标签会增加内存使用 这些配置为 Prometheus 提供了强大的灵活性,能够适应各种复杂的监控需求和环境。
body_size_limit + sample_limit + label_limit + label_name_length_limit + label_value_length_limit + target_limit
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 body_size_limit - 响应体大小限制 控制目标服务返回的未压缩响应体的最大字节数。 配置示例 # 限制响应体为 10MB body_size_limit: 10MB # 限制响应体为 100MB body_size_limit: 100MB # 无限制 body_size_limit: 0 使用场景 # 大型应用可能返回大量指标,需要限制 - job_name: 'large-app' static_configs: - targets: ['big-app:8080'] body_size_limit: 50MB # 小型服务可以使用默认值 - job_name: 'small-app' static_configs: - targets: ['small-app:8080'] body_size_limit: 0 # 无限制 sample_limit - 样本数量限制 限制每次抓取接受的样本数量,超过后整个抓取失败。 配置示例 # 限制每个目标最多 10,000 个样本 - job_name: 'high-metrics' sample_limit: 10000 static_configs: - targets: ['metrics-heavy:8080'] # 无限制 - job_name: 'normal-app' sample_limit: 0 static_configs: - targets: ['normal-app:8080'] 实际应用 # 对于已知高基数的服务 - job_name: 'cassandra' sample_limit: 50000 static_configs: - targets: ['cassandra:8080'] # 对于 Web 应用 - job_name: 'web-app' sample_limit: 10000 static_configs: - targets: ['web-app:8080'] label_limit - 标签数量限制 限制每个样本的标签数量。 配置示例 # 每个样本最多 30 个标签 - job_name: 'tag-heavy-app' label_limit: 30 static_configs: - targets: ['app:8080'] # 严格限制 - job_name: 'simple-app' label_limit: 10 static_configs: - targets: ['simple:8080'] 高基数警告 # 防止标签爆炸 - job_name: 'user-metrics' label_limit: 20 metric_relabel_configs: # 删除可能导致高基数的标签 - source_labels: [user_id, session_id] action: labeldrop label_name_length_limit - 标签名长度限制 限制标签名的字节长度(UTF-8 编码)。 配置示例 # 限制标签名最多 100 字节 - job_name: 'custom-app' label_name_length_limit: 100 static_configs: - targets: ['app:8080'] # 严格限制(约 25 个字符) - job_name: 'strict-app' label_name_length_limit: 100 static_configs: - targets: ['strict:8080'] label_value_length_limit - 标签值长度限制 限制标签值的字节长度(UTF-8 编码)。 配置示例 # 限制标签值最多 200 字节 - job_name: 'app-with-long-values' label_value_length_limit: 200 static_configs: - targets: ['app:8080'] # 防止过长的请求ID等 - job_name: 'api-gateway' label_value_length_limit: 500 static_configs: - targets: ['gateway:8080'] target_limit - 目标数量限制 限制每个抓取配置接受的唯一目标数量。 配置示例 # 最多 1000 个目标 - job_name: 'kubernetes-pods' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod target_limit: 1000 # 大集群的严格限制 - job_name: 'large-cluster' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints target_limit: 5000 综合配置示例 生产环境配置 scrape_configs: # 核心 Web 应用 - 严格限制 - job_name: 'web-production' static_configs: - targets: ['web1:8080', 'web2:8080', 'web3:8080'] body_size_limit: 20MB sample_limit: 5000 label_limit: 15 label_name_length_limit: 100 label_value_length_limit: 200 target_limit: 100 # 数据库服务 - 宽松限制 - job_name: 'database-metrics' static_configs: - targets: ['postgres:9187', 'redis:9121'] body_size_limit: 50MB sample_limit: 10000 label_limit: 25 label_name_length_limit: 150 label_value_length_limit: 500 # 大规模微服务 - 中等限制 - job_name: 'microservices' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod namespaces: names: ['microservices'] target_limit: 500 sample_limit: 8000 label_limit: 20 body_size_limit: 30MB relabel_configs: # 只监控带注解的服务 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: "true" 开发环境配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'dev-services' static_configs: - targets: ['dev-app:8080'] # 开发环境使用宽松的限制 body_size_limit: 100MB sample_limit: 0 # 无限制 label_limit: 0 # 无限制 label_name_length_limit: 0 label_value_length_limit: 0 监控和告警 建议为这些限制设置告警: # 监控接近限制的目标 - alert: ScrapeNearLimits expr: prometheus_target_interval_length_seconds_count / prometheus_target_interval_length_seconds_sum > 0.9 labels: severity: warning annotations: summary: "Target {{ $labels.instance }} near scraping limits" 这些限制机制帮助保护 Prometheus 免受异常大的数据影响,确保系统的稳定性和性能。
keep_dropped_targets
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 ⏺ keep_dropped_targets 控制在内存中保留多少个被 relabeling 丢弃的目标,用于调试和监控目的。 默认行为 # 默认不保留丢弃的目标 keep_dropped_targets: 0 功能说明 为什么需要保留丢弃的目标? 1. 调试 relabeling 规则:查看哪些目标被意外丢弃 2. 配置验证:确认 relabeling 规则按预期工作 3. 服务发现问题排查:了解目标发现过程中的问题 4. 性能监控:跟踪 relabeling 的效果 内存中的信息 保留的目标包含以下信息: - 原始目标地址 - 丢弃原因 - 相关的元数据标签 - 丢弃时间 配置示例 调试配置 # 保留最近 1000 个被丢弃的目标,用于调试 - job_name: 'kubernetes-pods-debug' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod keep_dropped_targets: 1000 relabel_configs: # 只抓取特定注解的 Pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: "true" # 排除测试环境的 Pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_environment] action: drop regex: "test" 生产环境配置 # 生产环境保留少量用于监控 - job_name: 'production-services' static_configs: - targets: ['prod1:8080', 'prod2:8080'] keep_dropped_targets: 100 # 保留最近 100 个 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: "true" 大规模环境配置 # 大规模集群限制内存使用 - job_name: 'large-cluster' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints keep_dropped_targets: 500 # 适中的限制 target_limit: 5000 实际应用场景 1. 调试 relabeling 规则 - job_name: 'debug-relabeling' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod keep_dropped_targets: 1000 # 保留足够多用于调试 relabel_configs: # 复杂的过滤逻辑 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_app, __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_version] action: keep regex: "(nginx|apache);(v1\.2|v1\.3)" 2. 监控目标发现健康度 - job_name: 'monitor-discovery' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: service keep_dropped_targets: 200 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_label_monitor] action: keep regex: "enabled" 3. 多环境管理 # 开发环境 - 保留更多用于调试 - job_name: 'dev-services' static_configs: - targets: ['dev-app:8080'] keep_dropped_targets: 500 # 生产环境 - 只保留关键信息 - job_name: 'prod-services' static_configs: - targets: ['prod-app:8080'] keep_dropped_targets: 50 内存影响分析 内存使用估算 # 每个丢弃的目标大约占用 1-2KB 内存 # 1000 个目标 ≈ 1-2MB keep_dropped_targets: 1000 # 对于大规模部署要谨慎 # 10000 个目标 ≈ 10-20MB keep_dropped_targets: 10000 性能考虑 # 小规模集群 (< 100 targets) keep_dropped_targets: 500 # 中等规模集群 (100-1000 targets) keep_dropped_targets: 1000 # 大规模集群 (> 1000 targets) keep_dropped_targets: 2000 最佳实践 1. 分阶段配置 # 开发/测试阶段 - job_name: 'debug-mode' keep_dropped_targets: 2000 # 详细日志 # 宽松限制 # 生产阶段 - job_name: 'production-mode' keep_dropped_targets: 100 # 最小内存占用 # 严格限制 2. 环境差异化 # 开发环境 - job_name: 'dev' keep_dropped_targets: 1000 # 测试环境 - job_name: 'staging' keep_dropped_targets: 500 # 生产环境 - job_name: 'prod' keep_dropped_targets: 50 3. 监控丢弃率 # 通过其他指标监控丢弃情况 - job_name: 'monitor-drops' static_configs: - targets: ['prometheus:9090'] keep_dropped_targets: 200 # 定期检查 drop 情况 注意事项 1. 内存消耗:每个丢弃的目标都会占用内存 2. 数据保留:只保留最近的 N 个,旧的会被丢弃 3. 调试用途:主要用于开发和调试阶段 4. 生产环境:建议使用较小的值 调试工作流 1. 开发阶段:设置较高的值(如 1000-2000) 2. 测试阶段:调整到适中值(如 500) 3. 生产阶段:设置较低值(如 50-100) 4. 问题排查时:临时增加数值进行调试 这个功能为 Prometheus 提供了强大的调试能力,帮助理解和优化复杂的 relabeling 配置。
metric_name_validation_scheme + metric_name_escaping_scheme
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 metric_name_validation_scheme - 指标名验证方案 "utf8" (默认) - 完整 UTF-8 支持 # 支持所有 Unicode 字符 metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" 支持的字符: - 所有 UTF-8 字符 - 中文、日文、韩文等非拉丁字符 - Emoji 和特殊符号 - 数学符号 示例指标名: cpu_使用率 memory_mb response_time_ms 🚀_requests_total αβγ_metric "legacy" - 传统字符集 # 只支持传统 Prometheus 字符集 metric_name_validation_scheme: "legacy" 支持的字符: - 字母 a-z, A-Z - 数字 0-9 - 冒号 : - 下划线 _ 示例指标名: cpu_usage memory_mb http_requests_total node_cpu_seconds_total metric_name_escaping_scheme - 转义方案 "allow-utf-8" (默认) - 允许 UTF-8 # UTF-8 模式下的默认转义方案 metric_name_escaping_scheme: "allow-utf-8" metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" 特点: - 不需要转义 - 完整保留原始字符 - 推荐用于新系统 "underscores" - 下划线转义 # 将所有非法字符转为下划线 metric_name_escaping_scheme: "underscores" 转换示例: 原始: "app.requests-per-second" 转义: "app_requests_per_second" 原始: "cpu@usage" 转义: "cpu_usage" 原始: "metric:with:dots" 转义: "metric_with_dots" "dots" - 点号转义方案 # 特殊的点号和下划线转义 metric_name_escaping_scheme: "dots" 转换示例: 原始: "app.requests.per.second" 转义: "app_dot_requests_dot_per_dot_second" 原始: "app_requests" 转义: "app__requests" 原始: "app@metrics" 转义: "app_metrics" "values" - Unicode 值转义 # 使用 Unicode 值进行转义 metric_name_escaping_scheme: "values" 转换示例: 原始: "my.dotted.name" 转义: "U__my_2e_dotted_2e_name" 原始: "metric@with:special" 转义: "U__metric_40_with_3a_special" 原始: "app_requests" 转义: "U__app__requests" Unicode 码点对应: - . → _2e_ (ASCII 46) - @ → _40_ (ASCII 64) - : → _3a_ (ASCII 58) - _ → __ (双下划线) 配置组合示例 现代应用配置 # 支持 UTF-8,不转义 - job_name: 'modern-app' static_configs: - targets: ['app:8080'] metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "allow-utf-8" 兼容旧系统配置 # 传统字符集,下划线转义 - job_name: 'legacy-app' static_configs: - targets: ['legacy:8080'] metric_name_validation_scheme: "legacy" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "underscores" 混合环境配置 # 国际化应用 - job_name: 'i18n-app' static_configs: - targets: ['i18n:8080'] metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "allow-utf-8" # 传统监控系统 - job_name: 'monitoring' static_configs: - targets: ['monitor:9090'] metric_name_validation_scheme: "legacy" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "dots" 实际应用场景 1. 国际化指标 # 中文指标名 - job_name: 'chinese-app' metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "allow-utf-8" # 支持指标名如: cpu使用率, 内存占用率 2. 微服务架构 # 使用点号分隔的服务指标 - job_name: 'microservices' metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "dots" # app.requests.per.second → app_dot_requests_dot_per_dot_second 3. 第三方集成 # 处理各种特殊字符的指标 - job_name: 'external-system' metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "values" # 将所有特殊字符转为 Unicode 值 迁移策略 从 Legacy 到 UTF-8 # 阶段 1: Legacy 验证,dots 转义 metric_name_validation_scheme: "legacy" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "dots" # 阶段 2: Legacy 验证,underscores 转义 metric_name_validation_scheme: "legacy" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "underscores" # 阶段 3: UTF-8 验证,allow-utf-8 转义 metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "allow-utf-8" 兼容性配置 # 确保与旧客户端兼容 - job_name: 'compatible' metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "underscores" # 新字符支持下划线转义 最佳实践 1. 新项目 # 推荐配置:完全 UTF-8 支持 metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "allow-utf-8" 2. 多语言环境 # 国际化应用 metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "allow-utf-8" 3. 现有系统升级 # 渐进式迁移 metric_name_validation_scheme: "utf8" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "underscores" # 便于向后兼容 4. 严格环境 # 企业级标准化 metric_name_validation_scheme: "legacy" metric_name_escaping_scheme: "dots" # 确保指标名标准化 性能影响 - UTF-8 验证:性能影响最小 - 转义处理:少量性能开销 - 兼容性:建议统一使用相同方案 这些配置项为 Prometheus 提供了灵活的指标命名策略,支持国际化需求,同时保持向后兼容性。
native_histogram_bucket_limit + native_histogram_min_bucket_factor + convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 ⏺ 这三个配置项控制 Prometheus 3.0+ 中的原生直方图(Native Histograms)功能,这是对传统直方图的重大改进。 native_histogram_bucket_limit - 桶数量限制 控制单个原生直方图允许的最大桶数(包括正数和负数桶)。 默认行为 # 无限制(默认) native_histogram_bucket_limit: 0 配置示例 # 限制最多 1000 个桶 - job_name: 'high-resolution-histograms' static_configs: - targets: ['app:8080'] native_histogram_bucket_limit: 1000 # 严格限制 - job_name: 'controlled-metrics' static_configs: - targets: ['app:8080'] native_histogram_bucket_limit: 500 行为说明 - 超出限制:Prometheus 会降低直方图分辨率以符合限制 - 无法降低:如果仍然超出限制,抓取会失败 - 内存考虑:更多桶 = 更多内存使用 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor - 最小桶增长因子 控制直方图桶的密度,即相邻桶之间的最小增长比例。 Schema 对应表 # 不同 schema 的配置示例 - job_name: 'coarse-histogram' native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 16 # Schema -2 - job_name: 'medium-histogram' native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 2 # Schema 0 - job_name: 'fine-histogram' native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 1.1 # Schema 2 - job_name: 'ultra-fine-histogram' native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 1.01 # Schema 6 常用配置 高精度场景 # 需要高精度的延迟测量 - job_name: 'latency-critical' native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 1.02 # Schema 5 native_histogram_bucket_limit: 2000 一般监控 # 标准业务指标 - job_name: 'business-metrics' native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 2 # Schema 0 native_histogram_bucket_limit: 1000 低精度场景 # 粗粒度资源监控 - job_name: 'resource-usage' native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 16 # Schema -2 native_histogram_bucket_limit: 100 convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb - 经典直方图转换 控制是否将传统直方图转换为原生直方图的自定义桶格式。 启用条件 # 需要在启动时启用 native-histograms 功能 # ./prometheus --enable-feature=native-histograms 配置示例 启用转换 - job_name: 'legacy-histograms' static_configs: - targets: ['legacy-app:8080'] convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true # 将传统直方图转换为本机格式 禁用转换 - job_name: 'keep-classic' static_configs: - targets: ['classic-app:8080'] convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: false # 保持传统直方图格式 完整配置示例 高精度延迟监控 - job_name: 'latency-monitoring' static_configs: - targets: ['api-gateway:8080'] native_histogram_bucket_limit: 5000 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 1.01 # Schema 6 - 超高精度 convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true scrape_interval: 15s scrape_timeout: 10s 通用业务监控 - job_name: 'business-metrics' static_configs: - targets: ['app:8080'] native_histogram_bucket_limit: 1000 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 2 # Schema 0 - 标准精度 convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true scrape_interval: 30s 资源使用监控 - job_name: 'resource-monitoring' static_configs: - targets: ['node-exporter:9100'] native_histogram_bucket_limit: 500 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 4 # Schema -1 - 低精度 convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: false # 保持传统格式 scrape_interval: 60s 混合环境配置 # 高精度服务 - job_name: 'critical-services' static_configs: - targets: ['payment-api:8080', 'auth-service:8080'] native_histogram_bucket_limit: 2000 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 1.04 # Schema 4 convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true # 标准服务 - job_name: 'standard-services' static_configs: - targets: ['user-service:8080', 'order-service:8080'] native_histogram_bucket_limit: 1000 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 2 # Schema 0 convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true # 传统服务 - job_name: 'legacy-services' static_configs: - targets: ['legacy-app:8080'] native_histogram_bucket_limit: 0 # 无限制 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 0 # 使用默认 convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: false # 不转换 性能考虑 内存使用 # 高精度 = 更多内存 native_histogram_bucket_limit: 5000 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 1.01 # 可能需要几 MB 内存 per 指标 # 低精度 = 更少内存 native_histogram_bucket_limit: 100 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 16 # 只需要几百 KB 内存 per 指标 网络传输 # 更高精度 = 更大的网络负载 - job_name: 'network-sensitive' native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 4 # 适中的精度 native_histogram_bucket_limit: 500 # 合理的桶数 存储成本 # 根据存储预算调整 - job_name: 'cost-optimized' native_histogram_bucket_limit: 200 # 限制存储 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 8 # 较低的精度 最佳实践 1. 分层配置 # 关键业务指标 - 高精度 - job_name: 'critical-metrics' native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 1.04 native_histogram_bucket_limit: 2000 # 一般业务指标 - 标准精度 - job_name: 'standard-metrics' native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 2 native_histogram_bucket_limit: 1000 # 基础设施指标 - 低精度 - job_name: 'infra-metrics' native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 16 native_histogram_bucket_limit: 500 2. 渐进式迁移 # 阶段 1: 禁用转换 convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: false # 阶段 2: 启用转换,保守限制 convert_classic_histograms_to_nhcb: true native_histogram_bucket_limit: 500 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 4 # 阶段 3: 优化配置 native_histogram_bucket_limit: 1000 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 2 3. 监控和调优 # 定期检查直方图性能 - job_name: 'histogram-monitoring' static_configs: - targets: ['prometheus:9090'] # 监控 native_histogram 相关指标 原生直方图是 Prometheus 的重大改进,提供了更好的精度、性能和存储效率,但需要合理配置以平衡精度和资源使用。
growth factor + resulting schema AKA scale
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 正确的换算公式 根据 OpenTelemetry 的指数直方图规范: growth_factor = 2^(1/2^scale) 让我们验证: Schema 0 growth_factor = 2^(1/2^0) = 2^(1/1) = 2^1 = 2 ✓ Schema 1 growth_factor = 2^(1/2^1) = 2^(1/2) = 2^0.5 ≈ 1.414 ≈ 1.4 ✓ Schema 2 growth_factor = 2^(1/2^2) = 2^(1/4) = 2^0.25 ≈ 1.189 ≈ 1.1 ✓ Schema -1 growth_factor = 2^(1/2^-1) = 2^(2/1) = 2^2 = 4 ✓ Schema -2 growth_factor = 2^(1/2^-2) = 2^(4/1) = 2^4 = 16 ✓ 负数 Schema 的计算 对于负数 schema: Schema -1 scale = -1 growth_factor = 2^(1/2^-1) = 2^(2) = 4 Schema -2 scale = -2 growth_factor = 2^(1/2^-2) = 2^(4) = 16 Schema -3 scale = -3 growth_factor = 2^(1/2^-3) = 2^(8) = 256 Schema -4 scale = -4 growth_factor = 2^(1/2^-4) = 2^(16) = 65536 逆向计算 从 growth_factor 计算 scale scale = log₂(1) / log₂(log₂(growth_factor)) 更准确的公式: scale = -log₂(log₂(growth_factor)) 示例计算 growth_factor = 2 scale = -log₂(log₂(2)) = -log₂(1) = -0 = 0 ✓ growth_factor = 4 scale = -log₂(log₂(4)) = -log₂(2) = -1 ✓ growth_factor = 1.4 scale = -log₂(log₂(1.4)) = -log₂(0.485) ≈ -(-1.04) ≈ 1 ✓ 桶边界计算 桶边界公式 base = 2^scale bucket_boundary = base * growth_factor^bucket_index 示例:Schema 0, growth_factor = 2 base = 2^0 = 1 桶边界序列: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, ... 示例:Schema 1, growth_factor = 1.4 base = 2^1 = 2 桶边界序列: 2, 2.8, 3.92, 5.49, 7.69, ... 实际配置示例 计算特定精度需求 如果需要 growth_factor = 1.5: import math def calculate_scale_from_growth_factor(gf): return -math.log2(math.log2(gf)) scale = calculate_scale_from_growth_factor(1.5) print(f"Scale: {scale}") # Scale: 0.737 (约等于 0.7) 由于 schema 必须是整数,所以会选择最接近的 schema = 0 或 schema = 1 自定义配置 # 如果想要约 1.3 的 growth factor # 需要在 schema 1 (1.4) 和 schema 2 (1.1) 之间选择 - job_name: 'custom-precision' # 选择 schema 1: growth_factor = 1.4 (较高精度) native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 1.4 精度对比 Schema 精度递减 Schema -4: growth_factor = 65536 (极粗糙) Schema -3: growth_factor = 256 (很粗糙) Schema -2: growth_factor = 16 (粗糙) Schema -1: growth_factor = 4 (较粗糙) Schema 0: growth_factor = 2 (标准) Schema 1: growth_factor = 1.4 (较精细) Schema 2: growth_factor = 1.1 (精细) Schema 3: growth_factor = 1.09 (很精细) Schema 4: growth_factor = 1.04 (非常精细) Schema 5: growth_factor = 1.02 (极精细) Schema 6: growth_factor = 1.01 (超精细) Schema 7: growth_factor = 1.005 (极致精细) Schema 8: growth_factor = 1.002 (最精细) 选择建议 基于用例选择 # 延迟监控 - 需要高精度 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 1.04 # Schema 4 # 计数器 - 中等精度即可 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 2 # Schema 0 # 流量监控 - 低精度够用 native_histogram_min_bucket_factor: 16 # Schema -2 理解这个换算关系有助于根据具体的监控需求选择最合适的精度级别。
http_config A http_config allows configuring HTTP requests.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 ⏺ 这些配置项构成了 Prometheus 的 HTTP 客户端认证和安全设置,提供了多种方式来访问受保护的监控端点。 basic_auth - 基础认证 使用 HTTP Basic Authentication 进行身份验证。 配置方式 # 直接配置用户名密码 basic_auth: username: "prometheus" password: "secure_password" # 从文件读取(推荐,更安全) basic_auth: username_file: "/etc/prometheus/username.txt" password_file: "/etc/prometheus/password.txt" 安全最佳实践 # 生产环境推荐配置 basic_auth: username_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/username" password_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/password" 文件权限 # 设置安全的文件权限 chmod 600 /etc/prometheus/secrets/username chmod 600 /etc/prometheus/secrets/password chown prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/secrets/* authorization - 令牌认证 使用自定义的 Authorization 头进行身份验证。 Bearer Token 配置 # 直接配置令牌 authorization: type: "Bearer" credentials: "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9..." # 从文件读取令牌(推荐) authorization: type: "Bearer" credentials_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/bearer_token.txt" 自定义认证类型 # API Key 认证 authorization: type: "ApiKey" credentials: "your-api-key-here" # 自定义认证头 authorization: type: "CustomAuth" credentials: "custom_auth_token" 多种认证方案示例 # JWT Token authorization: type: "JWT" credentials_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/jwt_token" # AWS Signature (简化示例) authorization: type: "AWS4-HMAC-SHA256" credentials_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/aws_creds" oauth2 - OAuth 2.0 认证 使用 OAuth 2.0 流程进行身份验证。 完整 OAuth 2.0 配置 oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-client" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/oauth_client_secret" token_url: "https://auth.example.com/oauth2/token" scopes: ["metrics:read"] endpoint_params: audience: "prometheus" OAuth 2.0 参数详解 oauth2: # 客户端 ID client_id: "your-client-id" # 客户端密钥(可以从文件读取) client_secret: "your-client-secret" # 或者 client_secret_file: "/path/to/client_secret" # 获取令牌的端点 token_url: "https://oauth.example.com/token" # 请求的权限范围 scopes: ["read", "metrics"] # 额外的端点参数 endpoint_params: grant_type: "client_credentials" audience: "api.example.com" # TLS 配置 tls_config: insecure_skip_verify: false ca_file: "/etc/ssl/certs/ca.crt" follow_redirects - 跟随重定向 控制是否跟随 HTTP 3xx 重定向。 配置示例 # 跟随重定向(默认) follow_redirects: true # 不跟随重定向 follow_redirects: false 使用场景 # 严格的安全策略 - 不跟随重定向 - job_name: 'secure-endpoints' follow_redirects: false static_configs: - targets: ['secure-api.example.com'] # 灵活的监控 - 跟随重定向 - job_name: 'web-monitoring' follow_redirects: true static_configs: - targets: ['web.example.com'] enable_http2 - HTTP/2 支持 控制是否启用 HTTP/2 协议。 配置示例 # 启用 HTTP/2(默认) enable_http2: true # 禁用 HTTP/2 enable_http2: false 兼容性考虑 # 旧服务兼容性 - job_name: 'legacy-services' enable_http2: false static_configs: - targets: ['legacy-app:8080'] # 现代服务 - job_name: 'modern-services' enable_http2: true static_configs: - targets: ['modern-app:8080'] tls_config - TLS 配置 配置 HTTPS 连接的安全设置。 基础 TLS 配置 tls_config: # 跳过证书验证(仅测试环境) insecure_skip_verify: true # CA 证书 ca_file: "/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt" # 客户端证书(双向认证) cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/client.key" # 服务器名称验证 server_name: "secure.example.com" 完整 TLS 配置示例 tls_config: # CA 证书配置 ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/ca.crt" # 或者 ca: | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIC... -----END CERTIFICATE----- # 客户端证书 cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/client.key" # 服务器名称验证 server_name: "metrics.example.com" # 禁用不安全的协议 min_version: "TLS12" max_version: "TLS13" # 密码套件 cipher_suites: - "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA" - "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA" # 跳过验证(仅开发环境) insecure_skip_verify: false 代理配置 proxy_url - 代理服务器 # HTTP 代理 proxy_url: "http://proxy.example.com:8080" # HTTPS 代理 proxy_url: "https://secure-proxy.example.com:8080" # 带认证的代理 proxy_url: "http://user:[email protected] :8080" no_proxy - 代理排除 proxy_url: "http://proxy.example.com:8080" no_proxy: "localhost,127.0.0.1,.internal,*.local" proxy_from_environment - 环境变量代理 proxy_from_environment: true # 将使用 HTTP_PROXY, HTTPS_PROXY, NO_PROXY 环境变量 proxy_connect_header - 代理连接头 proxy_connect_header: Proxy-Authorization: ["Basic dXNlcjpwYXNz"] User-Agent: ["Prometheus/2.0"] http_headers - 自定义 HTTP 头 为每个请求添加自定义 HTTP 头。 基本配置 http_headers: # 添加请求头 User-Agent: values: ["Prometheus/2.45.0"] # 添加认证头 X-API-Key: values: ["your-api-key-here"] # 添加追踪头 X-Request-ID: values: ["prometheus-request"] 敏感信息配置 http_headers: # 使用 secrets 隐藏敏感信息 Authorization: secrets: ["bearer_token_here"] # 从文件读取 X-Custom-Auth: files: ["/etc/prometheus/secrets/custom_auth.txt"] # 组合使用 X-Multiple-Values: values: ["public_value"] secrets: ["secret_value"] 动态配置 http_headers: # 追踪头 X-Trace-ID: values: ["${env:TRACE_ID}"] # 环境标识 X-Environment: values: ["production"] # 版本信息 X-Client-Version: values: ["prometheus-2.45.0"] 完整配置示例 企业级安全配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'secure-api' static_configs: - targets: ['api.example.com:443'] # OAuth 2.0 认证 oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-client" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/oauth_secret" token_url: "https://auth.example.com/oauth2/token" scopes: ["metrics:read"] # TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/client.key" server_name: "api.example.com" min_version: "TLS12" # 自定义头 http_headers: X-Client-Name: values: ["prometheus"] X-Environment: values: ["production"] # 代理配置 proxy_url: "http://corporate-proxy:8080" no_proxy: "localhost,.internal" # HTTP 配置 follow_redirects: true enable_http2: true 简单内部服务配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'internal-service' static_configs: - targets: ['service:8080'] # 基础认证 basic_auth: username_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/username" password_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/password" # 自定义头 http_headers: X-Monitoring: values: ["prometheus"] 这些配置为 Prometheus 提供了全面的安全认证能力,能够适应各种企业级安全需求。
tls_config 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 ⏺ tls_config 是 Prometheus 中配置 TLS (Transport Layer Security) 连接的核心组件,用于保护 HTTPS 连接的安全性。 CA 证书配置 验证服务器证书 # 直接配置 CA 证书内容 tls_config: ca: | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIICljCCAX4CCQCKLyqR1MOqTzANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADCBjDELMAkGA1UEBhMC VVMxCzAJBgNVBAgMAkNBMRYwFAYDVQQHDA1TYW4gRnJhbmNpc2NvMRMwEQYDVQQK DApFeGFtcGxlIE9yZzEUMBIGA1UECwwLRXhhbXBsZSBVbml0MRcwFQYDVQQDDA5l eGFtcGxlLmNvbS90bHMwHhcNMjQwMTAxMDAwMDAwWhcNMjUwMTAxMDAwMDAwWjCB jDELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxCzAJBgNVBAgMAkNBMRYwFAYDVQQHDA1TYW4gRnJhbmNp c2NvMRMwEQYDVQQKDApFeGFtcGxlIE9yZzEUMBIGA1UECwwLRXhhbXBsZSBVbml0 MRcwFQYDVQQDDA5leGFtcGxlLmNvbS90bHMwggEiMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4IB DwAwggEKAoIBAQC... -----END CERTIFICATE----- # 从文件读取 CA 证书(推荐) tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/ca.crt" 文件组织结构 /etc/prometheus/certs/ ├── ca.crt # CA 根证书 ├── client.crt # 客户端证书 ├── client.key # 客户端私钥 └── internal-ca.crt # 内部 CA 证书 客户端证书认证 双向 TLS (mTLS) 配置 tls_config: # CA 证书 ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/ca.crt" # 客户端证书 cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/client.key" # 或者直接配置 cert: | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIICkDCCAfagAwIBAgIU... -----END CERTIFICATE----- key: | -----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- MIIEvgIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCBKgwggSkAgEAAoIBAQC... -----END PRIVATE KEY----- 多环境客户端证书 # 开发环境 - job_name: 'dev-services' tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/dev-ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/dev-client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/dev-client.key" # 生产环境 - job_name: 'prod-services' tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/prod-ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/prod-client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/prod-client.key" 服务器名称验证 防止中间人攻击 tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/ca.crt" server_name: "secure-api.example.com" # 或者使用 IP 地址 server_name: "192.168.1.100" 证书名称匹配 # 证书中的 CN 或 SAN 必须匹配 tls_config: server_name: "metrics.internal.company.com" # 证书应包含: # CN: metrics.internal.company.com # 或 SAN: DNS:metrics.internal.company.com 跳过证书验证 仅用于测试环境 # 危险:仅用于开发和测试 tls_config: insecure_skip_verify: true # 测试环境示例 - job_name: 'test-services' static_configs: - targets: ['test-app:8080'] tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/test-ca.crt" insecure_skip_verify: true # 测试证书可能无效 生产环境警告 # ❌ 生产环境不要这样做 - job_name: 'production' tls_config: insecure_skip_verify: true # 安全风险! # ✅ 生产环境正确配置 - job_name: 'production' tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/prod-ca.crt" server_name: "prod-api.example.com" insecure_skip_verify: false TLS 版本控制 版本配置 # 现代 TLS 配置 tls_config: min_version: "TLS12" # 最低 TLS 1.2 max_version: "TLS13" # 最高 TLS 1.3 # 高安全性配置 tls_config: min_version: "TLS13" # 仅允许 TLS 1.3 max_version: "TLS13" # 兼容旧系统配置 tls_config: min_version: "TLS11" # 允许 TLS 1.1+ max_version: "TLS12" # 最高 TLS 1.2 版本兼容性矩阵 # 现代系统 (推荐) tls_config: min_version: "TLS12" max_version: "TLS13" # 企业内部系统 tls_config: min_version: "TLS12" max_version: "TLS12" # 兼容遗留系统 tls_config: min_version: "TLS10" max_version: "TLS12" # 最高安全 tls_config: min_version: "TLS13" max_version: "TLS13" 完整配置示例 企业级安全配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'secure-corporate-api' static_configs: - targets: ['api.company.com:443'] # OAuth 2.0 认证 oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-corporate" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/oauth_secret" token_url: "https://auth.company.com/oauth2/token" scopes: ["metrics:read"] # OAuth 令牌端点的 TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/corporate-ca.crt" server_name: "auth.company.com" min_version: "TLS12" max_version: "TLS13" # 目标服务的 TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/corporate-ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/prometheus-client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/prometheus-client.key" server_name: "api.company.com" min_version: "TLS12" max_version: "TLS13" insecure_skip_verify: false # 自定义头 http_headers: X-Client-Name: values: ["prometheus"] X-Department: values: ["observability"] 云服务配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'cloud-provider-metrics' static_configs: - targets: ['metrics.cloud-provider.com'] tls_config: # 使用系统 CA 证书 ca_file: "/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt" server_name: "metrics.cloud-provider.com" min_version: "TLS12" max_version: "TLS13" # 客户端证书认证 cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/cloud-client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/cloud-client.key" 开发环境配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'dev-services' static_configs: - targets: ['dev-app:8080'] # 开发环境 TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/dev-ca.crt" server_name: "dev-app.local" min_version: "TLS12" insecure_skip_verify: false # 使用自签名证书 # 简单认证 basic_auth: username_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/dev_user" password_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/dev_pass" 微服务网格配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'service-mesh' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints namespaces: names: ["mesh"] # 服务网格 TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/mesh-ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/mesh-client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/mesh-client.key" server_name: "mesh-gateway.local" min_version: "TLS12" max_version: "TLS13" relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_ready] action: keep regex: true 安全最佳实践 1. 文件权限管理 # 设置安全的文件权限 sudo mkdir -p /etc/prometheus/certs sudo mkdir -p /etc/prometheus/secrets # 证书文件权限 sudo chmod 644 /etc/prometheus/certs/*.crt sudo chmod 600 /etc/prometheus/certs/*.key sudo chmod 600 /etc/prometheus/secrets/* # 所有者设置 sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/certs sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/secrets 2. 证书轮换策略 # 使用符号链接便于证书轮换 tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/current/ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/current/client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/current/client.key" 3. 监控 TLS 连接 # 监控 TLS 相关指标 - job_name: 'prometheus-self' static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:9090'] # 可以监控 prometheus_http_server_tls_errors_total 等指标 4. 环境分离 /etc/prometheus/ ├── certs/ │ ├── dev/ │ │ ├── ca.crt │ │ ├── client.crt │ │ └── client.key │ ├── staging/ │ │ ├── ca.crt │ │ ├── client.crt │ │ └── client.key │ └── prod/ │ ├── ca.crt │ ├── client.crt │ └── client.key 这些 TLS 配置为 Prometheus 提供了全面的安全传输能力,确保监控数据在传输过程中的机密性和完整性。
oauth2
OAuth 2.0 authentication using the client credentials or password grant type .
Prometheus fetches an access token from the specified endpoint
with the given client access and secret keys.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 ⏺ 这部分详细说明了 Prometheus 中的 OAuth 2.0 认证配置,支持 Client Credentials 和 Password Grant 两种授权模式。 OAuth 2.0 授权模式 1. Client Credentials Grant (客户端凭证模式) 适用于服务到服务的认证,无需用户交互。 2. Resource Owner Password Credentials Grant (密码模式) 适用于可信的第一方应用,直接使用用户名密码获取令牌。 配置参数详解 基本认证信息 # 客户端 ID - 在 OAuth 提供商处注册的应用标识 client_id: "prometheus-monitoring" # 客户端密钥 - 可以直接配置或从文件读取 client_secret: "your_client_secret_here" # 或者(推荐) client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/oauth_client_secret" 权限范围 (Scopes) # 定义请求的权限范围 scopes: - "metrics:read" - "monitoring:access" - "read:services" 令牌端点 # OAuth 令牌服务的 URL token_url: "https://auth.example.com/oauth2/token" 完整配置示例 Client Credentials 模式 - job_name: 'api-service-oauth' static_configs: - targets: ['api.example.com'] oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-client" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/oauth_client_secret" token_url: "https://auth.example.com/oauth2/token" scopes: - "metrics:read" - "monitoring:access" # TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt" insecure_skip_verify: false Password Grant 模式 - job_name: 'legacy-system-oauth' static_configs: - targets: ['legacy-api.example.com'] oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-legacy" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/legacy_client_secret" token_url: "https://auth.example.com/oauth2/token" scopes: - "read" - "access" # 密码模式的额外参数 endpoint_params: grant_type: "password" username: "[email protected] " password: "strong_service_password" 高级配置选项 端点参数配置 oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-client" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/client_secret" token_url: "https://auth.example.com/oauth2/token" scopes: ["metrics:read"] # 自定义端点参数 endpoint_params: grant_type: "client_credentials" audience: "prometheus-monitoring" resource: "https://api.example.com" custom_param: "custom_value" TLS 安全配置 oauth2: client_id: "secure-prometheus" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/client_secret" token_url: "https://secure-auth.example.com/oauth2/token" scopes: ["metrics:read"] # TLS 安全设置 tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/auth_ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/client.key" server_name: "secure-auth.example.com" min_version: "TLS12" insecure_skip_verify: false 代理配置 oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-client" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/client_secret" token_url: "https://auth.example.com/oauth2/token" scopes: ["metrics:read"] # 代理设置 proxy_url: "http://corporate-proxy:8080" no_proxy: "localhost,.internal,auth.example.com" # 代理连接头 proxy_connect_header: Proxy-Authorization: ["Basic dXNlcjpwYXNz"] 自定义 HTTP 头 oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-client" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/client_secret" token_url: "https://auth.example.com/oauth2/token" scopes: ["metrics:read"] # 自定义请求头 http_headers: User-Agent: values: ["Prometheus/2.45.0"] X-Client-Name: values: ["prometheus-monitoring"] X-Environment: values: ["production"] # 敏感头信息 X-Internal-Token: secrets: ["internal_token_value"] # 从文件读取 X-Custom-Auth: files: ["/etc/prometheus/secrets/custom_auth_header.txt"] 实际应用场景 企业环境 OAuth 2.0 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'enterprise-api' static_configs: - targets: ['api.company.com:443'] oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-monitoring-prod" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/prod_oauth_secret" token_url: "https://sso.company.com/oauth2/token" scopes: - "metrics:read" - "monitoring:full_access" endpoint_params: grant_type: "client_credentials" audience: "api.company.com" tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/corporate_ca.crt" server_name: "sso.company.com" http_headers: X-Service: values: ["prometheus"] X-Department: values: ["observability"] 云服务集成 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'cloud-provider-api' static_configs: - targets: ['api.cloud-provider.com'] oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-integration" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/cloud_oauth_secret" token_url: "https://auth.cloud-provider.com/oauth2/token" scopes: - "monitoring.read" - "metrics.access" endpoint_params: grant_type: "client_credentials" project_id: "my-project-123" proxy_from_environment: true 多环境配置 # 开发环境 - job_name: 'dev-api' static_configs: - targets: ['dev-api.example.com'] oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-dev" client_secret: "dev_secret" token_url: "https://dev-auth.example.com/oauth2/token" scopes: ["read"] # 测试环境 - job_name: 'staging-api' static_configs: - targets: ['staging-api.example.com'] oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-staging" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/staging_oauth_secret" token_url: "https://staging-auth.example.com/oauth2/token" scopes: ["metrics:read"] # 生产环境 - job_name: 'prod-api' static_configs: - targets: ['prod-api.example.com'] oauth2: client_id: "prometheus-prod" client_secret_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/prod_oauth_secret" token_url: "https://auth.example.com/oauth2/token" scopes: ["metrics:read", "monitoring:full"] tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/prod_ca.crt" 令牌管理 自动刷新机制 - Prometheus 会在令牌过期前自动刷新 - 令牌会缓存在内存中 - 失败时会自动重试 监控 OAuth 2.0 状态 可以通过 Prometheus 自身指标监控 OAuth 2.0 状态: prometheus_scrape_oauth_token_failures_total prometheus_scrape_oauth_token_cache_hits_total 安全最佳实践 1. 使用文件存储密钥:避免在配置文件中明文存储 2. 设置适当的文件权限:chmod 600 和 chown prometheus:prometheus 3. 限制权限范围:只申请必要的权限 4. 使用 TLS:确保令牌请求的安全性 5. 定期轮换密钥:定期更新客户端密钥 这种 OAuth 2.0 配置为 Prometheus 提供了现代化的认证方式,特别适合微服务和云原生环境。
docker_sd_config 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 ⏺ Docker 服务发现 (Docker SD) 是 Prometheus 用于自动发现和监控 Docker 容器的功能,通过 Docker Engine API 获取容器信息并创建监控目标。 基本概念 Docker SD 通过以下方式工作: 1. 连接到 Docker Engine API 2. 获取所有容器信息 3. 为每个容器的暴露端口创建监控目标 4. 提供丰富的元数据标签用于过滤和配置 配置选项详解 host - Docker 守护进程地址 # 本地 Docker socket docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" # 远程 Docker API docker_sd_configs: - host: "tcp://docker.example.com:2376" # TLS 加密的远程连接 docker_sd_configs: - host: "tcp://secure-docker.example.com:2376" port - 默认抓取端口 # 默认端口 80 docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" port: 80 # 自定义默认端口 docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" port: 9090 host_networking_host - 主机网络模式的主机地址 # 容器使用 host 网络模式时的默认主机 docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" host_networking_host: "localhost" # 自定义主机地址 docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" host_networking_host: "host.docker.internal" match_first_network - 多网络处理 # 只使用第一个网络(默认) docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" match_first_network: true # 监控所有网络 docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" match_first_network: false 过滤器配置 基本过滤器 docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" filters: # 只监控运行中的容器 - name: "status" values: ["running"] # 只监控特定镜像 - name: "ancestor" values: ["nginx:latest", "redis:alpine"] # 排除特定容器 - name: "name" values: ["!test-container"] 高级过滤器 docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" filters: # 只监控带特定标签的容器 - name: "label" values: ["monitoring.enabled=true"] # 只监控特定网络中的容器 - name: "network" values: ["monitoring"] # 只监控暴露特定端口的容器 - name: "expose" values: ["8080", "9090"] 复合过滤示例 docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" filters: # 运行中的 Web 服务容器 - name: "status" values: ["running"] - name: "label" values: ["app.type=web"] - name: "label" values: ["monitoring.scrape=true"] # 排除测试和开发容器 - name: "label" values: ["!env=test", "!env=dev"] 刷新间隔配置 # 快速刷新(开发环境) docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" refresh_interval: 30s # 标准刷新(生产环境) docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" refresh_interval: 60s # 慢速刷新(稳定环境) docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" refresh_interval: 5m HTTP 客户端配置 TLS 安全连接 docker_sd_configs: - host: "tcp://secure-docker.example.com:2376" refresh_interval: 30s # TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/docker-ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/docker-client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/docker-client.key" server_name: "secure-docker.example.com" insecure_skip_verify: false # 认证 basic_auth: username_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/docker_user" password_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/docker_pass" 代理配置 docker_sd_configs: - host: "tcp://remote-docker.example.com:2376" # 代理设置 proxy_url: "http://corporate-proxy:8080" no_proxy: "localhost,.internal" # 自定义头 http_headers: User-Agent: values: ["Prometheus-Docker-SD/2.0"] X-Client: values: ["prometheus"] 元数据标签使用 容器信息标签 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'docker-containers' docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" filters: - name: "status" values: ["running"] relabel_configs: # 只监控带注解的容器 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_label_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: "true" # 设置抓取端口 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_label_prometheus_io_port] action: replace target_label: __address__ regex: (.+) replacement: ${1} # 添加容器名称标签 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_name] target_label: container_name # 添加容器 ID 标签 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_id] target_label: container_id # 添加镜像信息 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_label_com_docker_compose_service] target_label: service 网络信息标签 relabel_configs: # 添加网络名称 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_network_name] target_label: network_name # 添加网络 IP - source_labels: [__meta_docker_network_ip] target_label: container_ip # 区分内外网 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_network_internal] target_label: network_type replacement: "internal" regex: "true" # 端口映射信息 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_port_private, __meta_docker_port_public] target_label: port_mapping replacement: "${1}:${2}" regex: (.+);(.+) 完整配置示例 基础 Docker 监控 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'docker-containers' docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" port: 9090 refresh_interval: 30s filters: - name: "status" values: ["running"] - name: "label" values: ["prometheus.scrape=true"] relabel_configs: # 只监控启用的容器 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_label_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: "true" # 设置抓取路径 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_label_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) replacement: ${1} # 设置抓取端口 - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_docker_container_label_prometheus_io_port] action: replace regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+) replacement: $1:$2 target_label: __address__ # 添加容器元数据 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_name] target_label: container_name - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_label_com_docker_compose_service] target_label: compose_service - source_labels: [__meta_docker_network_name] target_label: network 企业级 Docker 监控 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'production-docker' docker_sd_configs: - host: "tcp://docker-swarm.example.com:2376" port: 9090 refresh_interval: 60s match_first_network: true filters: - name: "status" values: ["running"] - name: "label" values: ["env=production"] - name: "label" values: ["monitoring.enabled=true"] # TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/docker-ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/docker-client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/docker-client.key" server_name: "docker-swarm.example.com" # 认证 basic_auth: username_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/docker_user" password_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/docker_pass" relabel_configs: # 环境和业务标签 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_label_env] target_label: environment - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_label_app] target_label: application - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_label_version] target_label: version # 服务发现标签 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_name] target_label: container_name - source_labels: [__meta_docker_network_name] target_label: network # 端口配置 - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_docker_port_private] target_label: __address__ regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+) replacement: $1:$2 # 监控配置 - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_label_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) replacement: ${1} 多环境配置 # 开发环境 - job_name: 'dev-docker' docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" refresh_interval: 30s filters: - name: "label" values: ["env=dev"] - name: "label" values: ["monitoring.scrape=true"] relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_docker_container_name] target_label: container_name # 测试环境 - job_name: 'staging-docker' docker_sd_configs: - host: "tcp://staging-docker.example.com:2376" refresh_interval: 60s filters: - name: "label" values: ["env=staging"] tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/staging-ca.crt" # 生产环境 - job_name: 'prod-docker' docker_sd_configs: - host: "tcp://prod-docker.example.com:2376" refresh_interval: 60s filters: - name: "label" values: ["env=production"] - name: "label" values: ["monitoring.enabled=true"] tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/prod-ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/prod-client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/prod-client.key" 最佳实践 1. 标签规范化 # Docker Compose 文件示例 version: '3.8' services: web-app: image: nginx:latest labels: prometheus.io/scrape: "true" prometheus.io/port: "9090" prometheus.io/path: "/metrics" app.type: "web" env: "production" monitoring.enabled: "true" 2. 性能优化 # 大规模部署的优化配置 docker_sd_configs: - host: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" refresh_interval: 2m # 降低刷新频率 match_first_network: true # 避免重复目标 filters: - name: "status" values: ["running"] - name: "label" values: ["monitoring.scrape=true"] # API 层面过滤 3. 安全考虑 # 生产环境安全配置 docker_sd_configs: - host: "tcp://secure-docker.example.com:2376" tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/docker-ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/docker-client.crt" key_file: "/etc/prometheus/certs/docker-client.key" insecure_skip_verify: false basic_auth: username_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/docker_user" password_file: "/etc/prometheus/secrets/docker_pass" Docker SD 为 Prometheus 提供了强大的容器自动发现能力,特别适合动态和容器化的环境。
file_sd_config 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 ⏺ 基于文件的服务发现 (File SD) 是 Prometheus 最灵活的服务发现机制,通过读取文件中的目标配置来实现动态监控目标管理。 基本概念 File SD 的工作原理: 1. 监控指定模式的文件变化 2. 解析 JSON 或 YAML 格式的目标配置 3. 通过文件系统 watch 机制实时检测变化 4. 立即应用格式正确的配置更改 文件格式 JSON 格式 [ { "targets": ["localhost:9090", "localhost:9091"], "labels": { "job": "prometheus", "env": "production" } }, { "targets": ["api.example.com:8080"], "labels": { "job": "api", "service": "user-service", "version": "v1.2.0" } } ] YAML 格式 - targets: - "localhost:9090" - "localhost:9091" labels: job: "prometheus" env: "production" - targets: - "api.example.com:8080" labels: job: "api" service: "user-service" version: "v1.2.0" 配置选项 files - 文件模式配置 file_sd_configs: - files: # 单个文件 - "/etc/prometheus/targets.yml" # 通配符匹配 - "/etc/prometheus/targets/*.yml" - "/etc/prometheus/targets/*.json" # 复杂路径模式 - "/etc/prometheus/discovery/*_targets.json" - "/var/lib/prometheus/sd/configs/tg_*.yml" refresh_interval - 刷新间隔 # 默认 5 分钟 file_sd_configs: - files: - "/etc/prometheus/targets/*.yml" refresh_interval: 5m # 快速刷新(开发环境) file_sd_configs: - files: - "/etc/prometheus/targets/*.yml" refresh_interval: 30s # 慢速刷新(稳定环境) file_sd_configs: - files: - "/etc/prometheus/targets/*.yml" refresh_interval: 10m 实际应用示例 基础配置 # prometheus.yml scrape_configs: - job_name: 'file-discovery' file_sd_configs: - files: - "/etc/prometheus/targets/*.yml" refresh_interval: 1m # /etc/prometheus/targets/web-services.yml - targets: - "web1.example.com:8080" - "web2.example.com:8080" labels: job: "web-services" env: "production" # /etc/prometheus/targets/databases.yml - targets: - "db1.example.com:5432" - "db2.example.com:5432" labels: job: "databases" env: "production" type: "postgresql" 动态环境配置 # /etc/prometheus/targets/dev.yml - targets: - "dev-web1:8080" - "dev-api1:9090" labels: env: "development" team: "backend" # /etc/prometheus/targets/staging.yml - targets: - "staging-web1:8080" - "staging-api1:9090" labels: env: "staging" team: "backend" # /etc/prometheus/targets/production.yml - targets: - "prod-web1:8080" - "prod-web2:8080" - "prod-api1:9090" - "prod-api2:9090" labels: env: "production" team: "backend" 复杂业务配置 # /etc/prometheus/targets/microservices.yml - targets: - "user-service:8080" - "order-service:8080" - "payment-service:8080" labels: job: "microservices" architecture: "microservices" team: "platform" # /etc/prometheus/targets/infrastructure.yml - targets: - "node-exporter:9100" - "cadvisor:8080" - "blackbox-exporter:9115" labels: job: "infrastructure" category: "system" 元数据标签使用 __meta_filepath 标签 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'file-discovery' file_sd_configs: - files: - "/etc/prometheus/targets/*.yml" relabel_configs: # 使用文件路径作为环境标识 - source_labels: [__meta_filepath] target_label: config_file regex: '.*/([^/]+)\.yml' replacement: '$1' # 从文件名提取环境信息 - source_labels: [__meta_filepath] target_label: environment regex: '.*/(dev|staging|prod)_.*\.yml' replacement: '$1' 动态标签生成 relabel_configs: # 从文件路径获取业务域 - source_labels: [__meta_filepath] target_label: domain regex: '.*/([^/]+)/targets\.yml' replacement: '$1' # 添加文件更新时间标签 - source_labels: [__meta_filepath] target_label: config_source replacement: "file_discovery" 高级用法 1. 多文件组织结构 /etc/prometheus/ ├── prometheus.yml └── targets/ ├── environments/ │ ├── dev.yml │ ├── staging.yml │ └── production.yml ├── services/ │ ├── web-services.yml │ ├── databases.yml │ └── cache.yml └── infrastructure/ ├── nodes.yml └── exporters.yml # Prometheus 配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'environments' file_sd_configs: - files: - "/etc/prometheus/targets/environments/*.yml" refresh_interval: 2m - job_name: 'services' file_sd_configs: - files: - "/etc/prometheus/targets/services/*.yml" refresh_interval: 1m - job_name: 'infrastructure' file_sd_configs: - files: - "/etc/prometheus/targets/infrastructure/*.yml" refresh_interval: 5m 2. 自动化脚本集成 #!/bin/bash # generate_targets.sh - 自动生成目标配置 # 生成数据库服务配置 cat > /etc/prometheus/targets/databases.yml << EOF - targets: $(kubectl get pods -n database -l app=postgres -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.status.podIP}:5432{","}{end}' | sed 's/,$/\n/') labels: job: "postgresql" team: "data" env: "$ENVIRONMENT" EOF # 生成 Web 服务配置 cat > /etc/prometheus/targets/web-services.yml << EOF - targets: $(kubectl get pods -n web -l app=web -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.status.podIP}:8080{","}{end}' | sed 's/,$/\n/') labels: job: "web-services" team: "frontend" env: "$ENVIRONMENT" EOF 3. 外部系统集成 #!/usr/bin/env python3 # cmdb_sync.py - 从 CMDB 同步目标配置 import json import requests import yaml def fetch_targets_from_cmdb(): """从 CMDB 获取监控目标""" response = requests.get("https://cmdb.example.com/api/prometheus/targets") return response.json() def generate_prometheus_targets(targets): """生成 Prometheus 目标配置""" prometheus_targets = [] for target in targets: prometheus_targets.append({ "targets": [target['address']], "labels": { "job": target['service'], "env": target['environment'], "team": target['team'], "version": target.get('version', 'unknown') } }) return prometheus_targets def update_target_files(): """更新目标文件""" targets = fetch_targets_from_cmdb() prometheus_targets = generate_prometheus_targets(targets) # 按环境分组写入不同文件 for env in ['dev', 'staging', 'production']: env_targets = [t for t in prometheus_targets if t['labels']['env'] == env] with open(f"/etc/prometheus/targets/{env}.yml", 'w') as f: yaml.dump(env_targets, f, default_flow_style=False) if __name__ == "__main__": update_target_files() 4. 监控配置变更 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'file-discovery' file_sd_configs: - files: - "/etc/prometheus/targets/*.yml" relabel_configs: # 添加配置文件路径标签 - source_labels: [__meta_filepath] target_label: config_file # 添加最后更新时间(通过外部脚本) - source_labels: [config_file] target_label: last_updated replacement: "unknown" # 额外监控文件变更的 job - job_name: 'config-monitoring' static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:9090'] scrape_interval: 1m 性能和安全考虑 1. 文件数量优化 # ❌ 避免过多小文件 file_sd_configs: - files: - "/etc/prometheus/targets/*_*.yml" # 可能匹配数千文件 # ✅ 使用合理的文件组织 file_sd_configs: - files: - "/etc/prometheus/targets/environments.yml" - "/etc/prometheus/targets/services.yml" - "/etc/prometheus/targets/infrastructure.yml" 2. 文件权限管理 # 设置安全的文件权限 sudo mkdir -p /etc/prometheus/targets sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/targets sudo chmod 755 /etc/prometheus/targets # 目标文件权限 sudo chmod 644 /etc/prometheus/targets/*.yml sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/targets/*.yml 3. 原子更新 #!/bin/bash # 原子更新脚本 # 生成临时文件 cat > /etc/prometheus/targets/new_targets.yml << EOF - targets: - "new-service:8080" labels: job: "new-service" EOF # 原子替换 mv /etc/prometheus/targets/new_targets.yml /etc/prometheus/targets/production.yml 最佳实践 1. 文件命名规范 # 推荐的命名模式 /environments/prod.yml /environments/staging.yml /environments/dev.yml /services/web-servers.yml /services/databases.yml /infrastructure/nodes.yml 2. 配置验证 #!/bin/bash # validate_targets.sh - 验证目标配置 for file in /etc/prometheus/targets/*.yml; do if command -v yamllint >/dev/null 2>&1; then yamllint "$file" || echo "YAML validation failed for $file" fi if command -v jq >/dev/null 2>&1; then python3 -c "import yaml, json; json.dumps(yaml.safe_load(open('$file')))" \ || echo "Content validation failed for $file" fi done File SD 提供了极大的灵活性,适合各种自定义服务发现需求,特别是在没有标准服务发现机制的环境中。
http_sd_config 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 ⏺ 基于 HTTP 的服务发现 (HTTP SD) 是 Prometheus 通过 HTTP 端点动态获取监控目标的机制,提供了灵活的远程服务发现能力。 基本工作原理 HTTP SD 的工作流程: 1. 定期向配置的 HTTP 端点发送请求 2. 期望返回 JSON 格式的目标配置列表 3. 验证响应状态码和 Content-Type 4. 解析 JSON 并更新监控目标 5. 记录失败次数到指标 prometheus_sd_http_failures_total 响应格式 标准 JSON 响应 [ { "targets": ["localhost:9090", "localhost:9091"], "labels": { "job": "prometheus", "env": "production" } }, { "targets": ["api.example.com:8080", "api.example.com:8081"], "labels": { "job": "api", "service": "user-service", "version": "v1.2.0" } } ] 复杂响应示例 [ { "targets": ["web1.prod.example.com:8080", "web2.prod.example.com:8080"], "labels": { "job": "web-services", "environment": "production", "datacenter": "us-west-2", "service": "frontend", "version": "v2.1.0" } }, { "targets": ["db1.prod.example.com:5432"], "labels": { "job": "databases", "environment": "production", "datacenter": "us-west-2", "service": "postgresql", "role": "master" } }, { "targets": ["cache1.prod.example.com:6379", "cache2.prod.example.com:6379"], "labels": { "job": "cache", "environment": "production", "datacenter": "us-west-2", "service": "redis" } } ] 基本配置 简单 HTTP SD 配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'http-discovery' http_sd_configs: - url: 'http://service-discovery.example.com/targets' refresh_interval: 60s 多端点配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'services-discovery' http_sd_configs: - url: 'http://discovery.internal/api/services' refresh_interval: 30s - url: 'http://discovery.internal/api/databases' refresh_interval: 60s - job_name: 'infrastructure-discovery' http_sd_configs: - url: 'http://config-manager.example.com/prometheus/targets' refresh_interval: 2m HTTP 客户端配置 基础认证 http_sd_configs: - url: 'http://secure-discovery.example.com/targets' refresh_interval: 60s # 基础认证 basic_auth: username: 'prometheus' password_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/discovery_password' # 或者使用令牌认证 authorization: type: 'Bearer' credentials_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/bearer_token' TLS 安全配置 http_sd_configs: - url: 'https://secure-discovery.example.com/targets' refresh_interval: 60s # TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/discovery_ca.crt' cert_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/client.crt' key_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/client.key' server_name: 'secure-discovery.example.com' insecure_skip_verify: false # 认证 basic_auth: username_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/discovery_user' password_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/discovery_pass' 代理配置 http_sd_configs: - url: 'http://external-discovery.example.com/targets' refresh_interval: 60s # 代理设置 proxy_url: 'http://corporate-proxy:8080' no_proxy: 'localhost,.internal' # 自定义头 http_headers: User-Agent: values: ['Prometheus-HTTP-SD/2.0'] X-Client-ID: values: ['prometheus-cluster-1'] X-Environment: values: ['production'] OAuth 2.0 认证 http_sd_configs: - url: 'https://api.example.com/prometheus/targets' refresh_interval: 60s # OAuth 2.0 配置 oauth2: client_id: 'prometheus-discovery' client_secret_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/oauth_secret' token_url: 'https://auth.example.com/oauth2/token' scopes: ['discovery:read'] # TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/auth_ca.crt' server_name: 'auth.example.com' # 目标端点 TLS tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/api_ca.crt' server_name: 'api.example.com' 元数据标签使用 __meta_url 标签 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'http-discovery' http_sd_configs: - url: 'http://discovery.example.com/api/services' refresh_interval: 60s relabel_configs: # 添加源 URL 标签 - source_labels: [__meta_url] target_label: discovery_url # 从 URL 提取服务类型 - source_labels: [__meta_url] target_label: service_type regex: '.*/api/([^/]+).*' replacement: '$1' # 从 URL 提取环境信息 - source_labels: [__meta_url] target_label: environment regex: '.*/(dev|staging|prod)/.*' replacement: '$1' 动态标签配置 relabel_configs: # 组合发现源标签 - source_labels: [__meta_url, job] target_label: full_job_name regex: '(.*)/api/(.+);(.+)' replacement: '$1-$2-$3' # 添加发现时间戳 - source_labels: [__meta_url] target_label: discovery_method replacement: 'http_sd' 实际应用场景 1. 微服务注册中心集成 # Prometheus 配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'microservices' http_sd_configs: - url: 'http://service-registry.example.com/prometheus/targets' refresh_interval: 30s # 认证配置 basic_auth: username_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/registry_user' password_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/registry_pass' # 自定义头 http_headers: Accept: values: ['application/json'] X-Client-Name: values: ['prometheus'] relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_url] target_label: registry_url # 服务标签处理 - source_labels: [service_name] target_label: service - source_labels: [environment] target_label: env 2. 配置管理平台集成 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'config-managed-targets' http_sd_configs: - url: 'https://config-manager.example.com/api/v1/prometheus/targets' refresh_interval: 60s # TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/config_manager_ca.crt' server_name: 'config-manager.example.com' # API 认证 authorization: type: 'APIKey' credentials_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/config_api_key' # 自定义头 http_headers: X-API-Version: values: ['v1'] X-Cluster: values: ['production'] 3. 多环境配置管理 # 开发环境 - job_name: 'dev-services' http_sd_configs: - url: 'http://discovery.dev.example.com/targets' refresh_interval: 30s basic_auth: username_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/dev_user' password_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/dev_pass' # 测试环境 - job_name: 'staging-services' http_sd_configs: - url: 'http://discovery.staging.example.com/targets' refresh_interval: 60s basic_auth: username_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/staging_user' password_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/staging_pass' # 生产环境 - job_name: 'prod-services' http_sd_configs: - url: 'https://discovery.prod.example.com/targets' refresh_interval: 60s tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/prod_ca.crt' oauth2: client_id: 'prometheus-prod' client_secret_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/prod_oauth' token_url: 'https://auth.prod.example.com/oauth2/token' 服务发现端点实现 Go 示例 package main import ( "encoding/json" "log" "net/http" ) type Target struct { Targets []string `json:"targets"` Labels map[string]string `json:"labels"` } func main() { http.HandleFunc("/targets", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { targets := []Target{ { Targets: []string{"web1:8080", "web2:8080"}, Labels: map[string]string{ "job": "web-services", "env": "production", "datacenter": "us-west-2", }, }, { Targets: []string{"db1:5432"}, Labels: map[string]string{ "job": "databases", "env": "production", "datacenter": "us-west-2", }, }, } w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json") json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(targets) }) log.Println("Service discovery server listening on :8080") http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil) } Python 示例 from flask import Flask, jsonify import redis import json app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/targets') def get_targets(): # 从 Redis 或数据库获取目标 r = redis.Redis(host='redis', port=6379, db=0) targets = [] # 获取服务注册信息 services = r.smembers('services') for service in services: instances = r.smembers(f'service:{service}:instances') for instance in instances: targets.append({ "targets": [instance], "labels": { "job": service, "env": r.hget(f'service:{service}', 'env') or 'unknown', "version": r.hget(f'service:{service}', 'version') or 'unknown' } }) return jsonify(targets) if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8080) 高级配置 1. 带重试和超时的配置 http_sd_configs: - url: 'https://unreliable-discovery.example.com/targets' refresh_interval: 60s # HTTP 客户端配置 scrape_timeout: 10s scrape_interval: 60s # TLS 配置 tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/ca.crt' # 代理配置 proxy_url: 'http://proxy:8080' # 自定义头 http_headers: Timeout: values: ['10'] Retry-Count: values: ['3'] 2. 多源聚合配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'aggregated-services' http_sd_configs: # 主要服务发现 - url: 'http://primary-discovery.example.com/targets' refresh_interval: 30s http_headers: X-Priority: values: ['primary'] # 备用服务发现 - url: 'http://backup-discovery.example.com/targets' refresh_interval: 60s http_headers: X-Priority: values: ['backup'] relabel_configs: # 添加优先级标签 - source_labels: [__meta_url] target_label: discovery_priority regex: '.*primary.*' replacement: 'high' - source_labels: [__meta_url] target_label: discovery_priority regex: '.*backup.*' replacement: 'low' 监控和调试 监控 HTTP SD 状态 # Prometheus 自身监控 - job_name: 'prometheus-self' static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:9090'] # 可以监控以下指标: # prometheus_sd_http_failures_total{url="http://discovery.example.com/targets"} # prometheus_target_interval_length_seconds_count{scrape_job="http-discovery"} 故障排查 # 手动测试服务发现端点 curl -H "Accept: application/json" \ -H "User-Agent: Prometheus/2.0" \ http://discovery.example.com/targets # 检查响应格式 curl -s http://discovery.example.com/targets | jq . # 验证 Content-Type curl -I http://discovery.example.com/targets 最佳实践 1. 端点设计 - 始终返回 HTTP 200 状态码 - 设置正确的 Content-Type: application/json - 响应时间控制在秒级 - 实现缓存机制减少后端压力 2. 错误处理 - 实现健康检查端点 - 记录请求日志 - 提供故障转移机制 - 设置合理的超时时间 3. 安全考虑 - 使用 HTTPS 传输 - 实现适当的认证和授权 - 限制访问频率 - 验证输入参数 HTTP SD 为 Prometheus 提供了强大的远程服务发现能力,特别适合云原生和微服务架构环境。
kubernetes_sd_config 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 692 693 694 695 696 697 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716 717 718 719 720 721 722 723 724 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 750 751 752 753 754 755 756 757 758 759 760 761 762 763 764 765 766 767 768 769 770 771 772 773 774 775 776 777 778 779 780 781 782 783 784 785 786 787 788 789 790 791 792 793 794 795 796 797 798 799 800 801 802 803 804 805 806 807 808 809 810 811 812 813 814 815 816 817 818 819 820 821 822 823 824 825 826 827 828 829 830 831 832 833 834 835 836 837 838 839 840 841 842 843 844 845 846 847 848 849 850 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 863 864 865 866 867 868 869 870 871 872 873 874 875 876 877 878 879 880 881 882 883 884 885 886 887 888 889 890 891 892 893 894 895 896 897 898 899 900 901 902 903 904 905 906 907 908 909 910 911 912 913 914 915 916 917 918 919 ⏺ Kubernetes 服务发现详细解释 Kubernetes 服务发现是 Prometheus 最强大的功能之一,通过与 Kubernetes API 集成自动发现和监控集群中的资源。 六种角色类型详解 1. Node Role (节点角色) 用途: 监控 Kubernetes 集群的节点 工作机制: - 为每个集群节点创建一个监控目标 - 默认地址为 Kubelet HTTP 端口 (通常为 10250) - 地址优先级: NodeInternalIP > NodeExternalIP > NodeLegacyHostIP > NodeHostName 元数据标签: __meta_kubernetes_node_name # 节点名称 __meta_kubernetes_node_provider_id # 云提供商的节点 ID __meta_kubernetes_node_label_<label> # 节点标签 __meta_kubernetes_node_labelpresent_<label> # 标签存在标记 __meta_kubernetes_node_annotation_<annotation> # 节点注解 __meta_kubernetes_node_address_<type> # 节点地址 (InternalIP, ExternalIP, etc.) 配置示例: - job_name: 'kubernetes-nodes' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node attach_metadata: node: true # 附加节点元数据 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name] target_label: node_name - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_label_kubernetes_io_arch] target_label: architecture 2. Service Role (服务角色) 用途: 监控 Kubernetes 服务,适合黑盒监控 工作机制: - 为每个服务的每个端口创建监控目标 - 地址设置为 Kubernetes DNS 名称 - 适合监控服务可用性和响应时间 元数据标签: __meta_kubernetes_namespace # 命名空间 __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_<anno> # 服务注解 __meta_kubernetes_service_cluster_ip # 集群 IP __meta_kubernetes_service_loadbalancer_ip # 负载均衡器 IP __meta_kubernetes_service_external_name # 外部名称 __meta_kubernetes_service_label_<label> # 服务标签 __meta_kubernetes_service_name # 服务名称 __meta_kubernetes_service_port_name # 端口名称 __meta_kubernetes_service_port_number # 端口号 __meta_kubernetes_service_port_protocol # 端口协议 __meta_kubernetes_service_type # 服务类型 (ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer) 配置示例: - job_name: 'kubernetes-services' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: service namespaces: names: ['default', 'monitoring'] relabel_configs: # 只监控带特定注解的服务 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: "true" # 设置服务类型标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_type] target_label: service_type 3. Pod Role (Pod 角色) 用途: 直接监控 Pod 容器,最常用和灵活的角色 工作机制: - 发现所有 Pod 并将其容器作为目标 - 为每个容器声明的端口创建目标 - 如果容器没有指定端口,创建无端口目标供手动配置 元数据标签: __meta_kubernetes_namespace # 命名空间 __meta_kubernetes_pod_name # Pod 名称 __meta_kubernetes_pod_ip # Pod IP __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_<label> # Pod 标签 __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_<annotation> # Pod 注解 __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_init # 是否为 InitContainer __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_name # 容器名称 __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_id # 容器 ID __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_image # 容器镜像 __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_name # 容器端口名称 __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_number # 容器端口号 __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_protocol # 容器端口协议 __meta_kubernetes_pod_ready # Pod 就绪状态 __meta_kubernetes_pod_phase # Pod 阶段 (Pending, Running, etc.) __meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name # Pod 所在节点 __meta_kubernetes_pod_host_ip # Pod 主机 IP __meta_kubernetes_pod_uid # Pod UID __meta_kubernetes_pod_controller_kind # 控制器类型 (Deployment, StatefulSet, etc.) __meta_kubernetes_pod_controller_name # 控制器名称 配置示例: - job_name: 'kubernetes-pods' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod namespaces: names: ['default', 'production'] attach_metadata: node: true namespace: true relabel_configs: # 只监控带特定注解的 Pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: "true" # 设置抓取端口 - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port] action: replace regex: '([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)' replacement: '$1:$2' target_label: __address__ # 设置抓取路径 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) # 添加控制器信息 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_controller_kind] target_label: controller_kind - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_controller_name] target_label: controller_name ⏺ 4. Endpoints Role (端点角色) ⚠️ 已弃用 重要提示: Endpoints API 在 Kubernetes v1.33+ 中已弃用,推荐使用 EndpointSlice 角色。 用途: 监控服务的端点,即实际运行的服务实例 工作机制: - 从服务的端点列表中发现目标 - 为每个端点地址的每个端口创建目标 - 如果端点由 Pod 支持,还会发现 Pod 的其他容器端口 5. EndpointSlice Role (端点切片角色) ✅ 推荐 用途: 现代化的端点发现,替代 Endpoints 角色 优势: - 适用于大规模集群,性能更好 - 减少 Kubernetes API 负载 - 需要 discovery.k8s.io/v1 API (Kubernetes v1.21+) 特有元数据标签: __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_name # EndpointSlice 名称 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_label_<label> # EndpointSlice 标签 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_annotation_<annotation> # EndpointSlice 注解 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_address_target_kind # 目标对象类型 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_address_target_name # 目标对象名称 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_address_type # 地址类型 (IPv4, IPv6, FQDN) __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_endpoint_conditions_ready # 端点就绪状态 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_endpoint_conditions_serving # 端点服务状态 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_endpoint_conditions_terminating # 端点终止状态 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_endpoint_topology_kubernetes_io_hostname # 节点主机名 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_endpoint_node_name # 节点名称 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_endpoint_zone # 可用区 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_port # 端口号 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_port_name # 端口名称 __meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_port_protocol # 端口协议 配置示例: - job_name: 'kubernetes-endpointslices' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpointslice namespaces: own_namespace: false names: ['default', 'production'] relabel_configs: # 只监控就绪的端点 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_endpoint_conditions_ready] action: keep regex: "true" # 添加拓扑信息 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_endpoint_zone] target_label: availability_zone - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_endpoint_node_name] target_label: node_name 6. Ingress Role (入口角色) 用途: 监控 Ingress 资源,适合黑盒监控 工作机制: - 为每个 Ingress 的每个路径创建目标 - 地址设置为 Ingress 规范中的主机名 - 需要 networking.k8s.io/v1 API (Kubernetes v1.19+) 元数据标签: __meta_kubernetes_namespace # 命名空间 __meta_kubernetes_ingress_name # Ingress 名称 __meta_kubernetes_ingress_label_<label> # Ingress 标签 __meta_kubernetes_ingress_annotation_<annotation> # Ingress 注解 __meta_kubernetes_ingress_class_name # Ingress 类名 __meta_kubernetes_ingress_scheme # 协议方案 (http/https) __meta_kubernetes_ingress_path # 路径 配置示例: - job_name: 'kubernetes-ingress' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: ingress namespaces: names: ['ingress-nginx', 'default'] relabel_configs: # 设置地址为 Ingress 主机名 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_ingress_scheme, __meta_kubernetes_ingress_path] action: replace target_label: __address__ regex: (.+);(.+) replacement: $1 separator: ';' # 添加路径标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_ingress_path] target_label: ingress_path # 添加 Ingress 类标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_ingress_class_name] target_label: ingress_class ⏺ 配置选项详解 基础连接配置 api_server - API 服务器地址 # 空值表示在集群内运行,自动发现 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod # api_server: 留空使用集群内配置 # 外部集群配置 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod api_server: 'https://kubernetes.example.com:6443' kubeconfig_file - Kubeconfig 文件 # 使用外部 kubeconfig kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod kubeconfig_file: '/etc/prometheus/kubeconfig' # 注意:api_server 和 kubeconfig_file 互斥 命名空间配置 namespaces - 命名空间发现 # 监控所有命名空间 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod namespaces: own_namespace: false # 不限制当前命名空间 # 只监控指定命名空间 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod namespaces: own_namespace: false names: - 'default' - 'monitoring' - 'production' - 'staging' # 只监控当前命名空间 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod namespaces: own_namespace: true 选择器配置 selectors - 标签和字段选择器 # Pod 角色选择器 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod selectors: - role: pod label: 'app=nginx' # 标签选择器 field: 'status.phase=Running' # 字段选择器 # Service 角色选择器 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: service selectors: - role: service label: 'monitoring.enabled=true' # 只监控启用监控的服务 # Node 角色选择器 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node selectors: - role: node label: 'node-type=worker' # 只监控工作节点 # Endpoints 角色支持多类型选择器 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints selectors: - role: service label: 'service-type=monitoring' - role: pod label: 'monitor=true' 元数据附加配置 attach_metadata - 附加元数据 # 附加节点和命名空间元数据 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod attach_metadata: node: true # 附加节点元数据(需要节点访问权限) namespace: true # 附加命名空间元数据(需要命名空间访问权限) # 只附加命名空间元数据 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: service attach_metadata: namespace: true node: false HTTP 客户端配置 认证配置 # 基础认证 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod basic_auth: username_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/k8s_user' password_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/k8s_pass' # 令牌认证 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod authorization: type: 'Bearer' credentials_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/k8s_token' # TLS 配置 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/k8s_ca.crt' cert_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/client.crt' key_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/client.key' server_name: 'kubernetes.example.com' insecure_skip_verify: false 代理配置 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod proxy_url: 'http://corporate-proxy:8080' no_proxy: 'localhost,.cluster.local,.svc' proxy_from_environment: true ⏺ 完整配置示例 1. 生产环境 Pod 监控 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'kubernetes-pods-production' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod namespaces: names: ['production', 'monitoring'] attach_metadata: node: true namespace: true # 性能优化:使用选择器减少不必要的资源 selectors: - role: pod label: 'prometheus.io/scrape=true' relabel_configs: # 只监控带特定注解的 Pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: "true" # 设置抓取端口 - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port] action: replace regex: '([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)' replacement: '$1:$2' target_label: __address__ # 设置抓取路径 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) # 添加环境和服务标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: environment replacement: 'production' - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_app] target_label: service - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_version] target_label: version # 添加控制器信息 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_controller_kind] target_label: controller_kind - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_controller_name] target_label: controller_name # 添加节点信息 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name] target_label: node_name # 删除不需要的标签 - action: labeldrop regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_.+ 2. 多环境服务发现配置 scrape_configs: # 开发环境 - 使用 Endpoints(小规模) - job_name: 'kubernetes-dev-services' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints namespaces: names: ['development'] selectors: - role: service label: 'env=dev' label: 'monitoring.enabled=true' relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_ready] action: keep regex: "true" - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: environment replacement: 'development' # 生产环境 - 使用 EndpointSlice(大规模) - job_name: 'kubernetes-prod-services' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpointslice namespaces: names: ['production'] selectors: - role: endpointslice label: 'env=prod' label: 'monitoring.enabled=true' attach_metadata: node: true namespace: true relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_endpoint_conditions_ready] action: keep regex: "true" - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpointslice_endpoint_zone] target_label: availability_zone - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: environment replacement: 'production' 3. Ingress 黑盒监控配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'kubernetes-ingress-blackbox' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: ingress namespaces: names: ['ingress-nginx', 'default', 'production'] selectors: - role: ingress label: 'monitoring.blackbox=true' relabel_configs: # 设置监控地址 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_ingress_scheme] action: replace target_label: __param_target regex: (https?) replacement: ${1}://__address__ # 设置 Ingress 路径 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_ingress_path] action: replace target_label: __param_module regex: (.+) replacement: http_2xx # 添加主机名标签 - source_labels: [__address__] target_label: instance # 添加路径标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_ingress_path] target_label: ingress_path # 添加命名空间标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: namespace # 设置抓取地址为 Blackbox Exporter - source_labels: [] target_label: __address__ replacement: 'blackbox-exporter:9115' 4. 节点和基础设施监控 scrape_configs: # 节点监控 - job_name: 'kubernetes-nodes' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node attach_metadata: node: true relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name] target_label: node_name - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_label_kubernetes_io_instance_type] target_label: instance_type - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_label_topology_kubernetes_io_zone] target_label: availability_zone # 设置抓取端口 - source_labels: [__address__] target_label: __address__ regex: '(.+):10250' replacement: '$1:9100' # 假设运行 node-exporter # 节点网络监控 - job_name: 'kubernetes-nodes-network' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node selectors: - role: node label: 'network-monitoring=true' relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] target_label: __address__ regex: '(.+):10250' replacement: '$1:9101' # 假设网络监控端口 最佳实践 1. 性能优化 选择器优化 # ❌ 避免无选择器的大规模发现 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod # 这会监控所有 Pod,性能开销大 # ✅ 使用精确的选择器 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod selectors: - role: pod label: 'prometheus.io/scrape=true' field: 'status.phase=Running' 使用 EndpointSlice # ✅ 大规模集群使用 EndpointSlice kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpointslice # 而不是 endpoints # ✅ 小规模集群可以使用 Endpoints kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints # 节点 < 100 2. 标签管理 标准化注解 # Pod 注解标准 apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: annotations: prometheus.io/scrape: "true" prometheus.io/port: "8080" prometheus.io/path: "/metrics" prometheus.io/scheme: "http" labels: app: "my-app" version: "v1.2.0" env: "production" team: "backend" 标签清理 relabel_configs: # 保留有用的标签 - action: labelkeep regex: '(job|instance|namespace|service|version|team|env)' # 删除敏感或冗余标签 - action: labeldrop regex: '__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_.+' 3. 安全配置 RBAC 权限最小化 # ServiceAccount 配置 apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: prometheus namespace: monitoring --- # 最小权限的 RBAC apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: prometheus rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["nodes", "services", "endpoints", "pods", "namespaces"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"] - apiGroups: ["discovery.k8s.io"] resources: ["endpointslices"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"] TLS 配置 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/ca.crt' cert_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/client.crt' key_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/client.key' server_name: 'kubernetes.default.svc' insecure_skip_verify: false 4. 监控配置健康状态 # 监控 Kubernetes SD 自身状态 - job_name: 'prometheus-self' static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:9090'] scrape_interval: 30s # 关键指标监控 # prometheus_sd_kubernetes_events_total # prometheus_target_interval_length_seconds_count # prometheus_sd_discovered_targets ⏺ 性能考虑和优化建议 1. 规模化建议 集群规模对应的策略 # 小型集群 (< 100 节点, < 1000 Pod) - 使用 Endpoints 角色 - 可以使用较少的选择器 - 刷新间隔可以较短 (30s) # 中型集群 (100-500 节点, 1000-5000 Pod) - 使用 EndpointSlice 角色 - 使用精确的选择器 - 适中的刷新间隔 (60s) # 大型集群 (> 500 节点, > 5000 Pod) - 必须使用 EndpointSlice 角色 - 严格的选择器过滤 - 较长的刷新间隔 (2-5m) - 考虑分命名空间监控 选择器性能影响 # ⚠️ 每个选择器组合会创建独立的 LIST/WATCH # ❌ 性能差:过多选择器组合 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod selectors: - role: pod label: 'env=prod' field: 'status.phase=Running' - role: pod label: 'env=staging' field: 'status.phase=Running' # ... 更多的选择器组合 # ✅ 性能好:使用单个配置配合 relabeling kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod selectors: - role: pod field: 'status.phase=Running' relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_env] action: keep regex: '(prod|staging)' 2. 内存和 CPU 优化 减少发现的资源数量 # ✅ 使用注解过滤 metadata: annotations: prometheus.io/scrape: "true" # 只监控需要监控的 # ✅ 使用标签过滤 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod selectors: - role: pod label: 'monitoring.enabled=true' # ✅ 限制命名空间 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod namespaces: names: ['production', 'monitoring'] # 不监控所有命名空间 标签数量优化 relabel_configs: # ✅ 删除不需要的元数据标签 - action: labeldrop regex: '__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_.+' - action: labeldrop regex: '__meta_kubernetes_pod_labelpresent_.+' # ✅ 只保留必要的标签 - action: labelkeep regex: '(job|instance|service|namespace|version|env|team)' 3. 网络和 API 负载优化 刷新间隔配置 # ✅ 根据集群规模调整刷新间隔 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpointslice # 小型集群 refresh_interval: 30s - role: pod # 大型集群 refresh_interval: 5m - role: service # 服务变化较少 refresh_interval: 10m 分层监控策略 # ✅ 不同频率的监控配置 scrape_configs: # 高频:关键服务 - job_name: 'critical-services' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpointslice selectors: - role: endpointslice label: 'priority=critical' scrape_interval: 15s refresh_interval: 30s # 中频:业务服务 - job_name: 'business-services' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpointslice selectors: - role: endpointslice label: 'priority=normal' scrape_interval: 30s refresh_interval: 60s # 低频:基础设施 - job_name: 'infrastructure' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node scrape_interval: 60s refresh_interval: 5m 4. 故障排查和监控 关键监控指标 # 监控 Prometheus 自身的 Kubernetes SD 状态 # prometheus_sd_kubernetes_events_total - Kubernetes 事件总数 # prometheus_sd_discovered_targets - 发现的目标数量 # prometheus_target_interval_length_seconds - 抓取间隔 # prometheus_config_last_reload_successful - 配置重载是否成功 常见问题和解决方案 # 问题 1: 发现的目标过多 # 解决方案:使用更精确的选择器 kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod selectors: - role: pod label: 'prometheus.io/scrape=true' field: 'status.phase=Running' # 问题 2: API 服务器负载过高 # 解决方案:减少刷新频率,使用 EndpointSlice kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpointslice # 而不是 pod refresh_interval: 5m # 增加刷新间隔 # 问题 3: 内存使用过高 # 解决方案:清理不必要的标签 relabel_configs: - action: labeldrop regex: '__meta_.*' - action: labelkeep regex: '(job|instance|service|namespace)' 5. 高级优化技巧 并行发现配置 # ✅ 分离不同角色的配置以实现并行处理 scrape_configs: # 节点监控(变化频率低) - job_name: 'kubernetes-nodes' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node refresh_interval: 10m # 服务监控(变化频率中等) - job_name: 'kubernetes-services' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: service refresh_interval: 2m # Pod 监控(变化频率高) - job_name: 'kubernetes-pods' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod selectors: - role: pod label: 'monitoring.enabled=true' refresh_interval: 1m 智能重试机制 # ✅ 配置适当的超时和重试 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'kubernetes-pods' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod refresh_interval: 1m scrape_timeout: 10s scrape_interval: 30s # 对失败的抓取进行重试 metric_relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__name__] action: keep regex: 'up' ⏺ 总结 Kubernetes 服务发现是 Prometheus 的核心功能,提供了六种不同的角色来适应各种监控需求: 角色选择指南 1. Pod Role - 最灵活,直接监控容器 2. EndpointSlice Role - 现代化端点监控,适合大规模集群 3. Service Role - 服务级别监控,适合黑盒测试 4. Node Role - 节点基础设施监控 5. Ingress Role - 入口流量监控 6. Endpoints Role - 已弃用,使用 EndpointSlice 替代 关键优化原则 1. 使用精确选择器 - 减少不必要的资源发现 2. EndpointSlice 优先 - 大规模集群必须使用 3. 合理刷新间隔 - 平衡实时性和性能 4. 标签管理 - 清理不需要的元数据标签 5. 分离监控配置 - 不同角色使用不同的刷新频率 生产环境建议 1. RBAC 最小权限 - 只授予必要的 API 访问权限 2. TLS 安全通信 - 保护与 Kubernetes API 的连接 3. 故障转移机制 - 监控服务发现健康状态 4. 分层监控策略 - 根据服务重要性设置不同监控频率 通过合理配置和优化,Kubernetes 服务发现可以为大规模云原生环境提供高效、可靠的监控目标自动发现能力。
static_config 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 ⏺ static_config 是 Prometheus 中最基础的静态目标配置方式,用于明确指定要监控的目标列表和通用标签。 基本结构 static_configs: - targets: ['host1:9090', 'host2:9090'] labels: job: 'my-job' env: 'production' 详细配置 targets - 目标列表 指定要监控的服务端点列表: # 单个目标 static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:9090'] # 多个目标 static_configs: - targets: - 'localhost:9090' - 'localhost:8080' - 'localhost:9091' # 带协议的目标 static_configs: - targets: - 'http://prometheus.example.com:9090' - 'https://secure-metrics.example.com:443' # 不同端口的服务 static_configs: - targets: - 'web-server1:8080' - 'web-server2:8080' - 'api-server:9090' - 'database-exporter:9100' labels - 通用标签 为所有目标添加相同的标签: static_configs: - targets: ['web1:8080', 'web2:8080', 'web3:8080'] labels: job: 'web-servers' environment: 'production' team: 'frontend' service_type: 'http' 实际应用示例 1. 基础服务监控 scrape_configs: # Prometheus 自身监控 - job_name: 'prometheus' static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:9090'] labels: job: 'prometheus' component: 'server' # Node Exporter 监控 - job_name: 'node-exporter' static_configs: - targets: - 'server1:9100' - 'server2:9100' - 'server3:9100' labels: job: 'node-exporter' environment: 'production' team: 'infrastructure' 2. 多环境配置 scrape_configs: # 开发环境 - job_name: 'dev-services' static_configs: - targets: - 'dev-web1:8080' - 'dev-api1:9090' labels: job: 'dev-services' environment: 'development' team: 'backend' # 测试环境 - job_name: 'staging-services' static_configs: - targets: - 'staging-web1:8080' - 'staging-api1:9090' labels: job: 'staging-services' environment: 'staging' team: 'backend' # 生产环境 - job_name: 'prod-services' static_configs: - targets: - 'prod-web1:8080' - 'prod-web2:8080' - 'prod-api1:9090' - 'prod-api2:9090' labels: job: 'prod-services' environment: 'production' team: 'backend' 3. 不同服务类型 scrape_configs: # Web 服务监控 - job_name: 'web-services' static_configs: - targets: - 'nginx1:9113' # Nginx Exporter - 'nginx2:9113' - 'apache1:9117' # Apache Exporter - 'apache2:9117' labels: job: 'web-services' service_type: 'web-server' # 数据库监控 - job_name: 'databases' static_configs: - targets: - 'postgres1:9187' # PostgreSQL Exporter - 'postgres2:9187' - 'mysql1:9104' # MySQL Exporter - 'redis1:9121' # Redis Exporter labels: job: 'databases' service_type: 'database' # 中间件监控 - job_name: 'middleware' static_configs: - targets: - 'kafka1:9308' # Kafka Exporter - 'rabbitmq1:9419' # RabbitMQ Exporter - 'elasticsearch1:9114' # Elasticsearch Exporter labels: job: 'middleware' service_type: 'message-queue' 4. 外部服务监控 scrape_configs: # 外部 API 监控 - job_name: 'external-apis' static_configs: - targets: - 'api.github.com:443' - 'api.stripe.com:443' - 'api.twilio.com:443' labels: job: 'external-apis' monitoring_type: 'blackbox' environment: 'production' # CDN 监控 - job_name: 'cdn-monitoring' static_configs: - targets: - 'cdn.jsdelivr.net:443' - 'cdnjs.cloudflare.com:443' - 'unpkg.com:443' labels: job: 'cdn-monitoring' monitoring_type: 'availability' 5. 本地开发环境 scrape_configs: # 本地开发服务 - job_name: 'local-dev' static_configs: - targets: - 'localhost:8080' # 本地 Web 应用 - 'localhost:9090' # 本地 Prometheus - 'localhost:3000' # 本地前端应用 labels: job: 'local-development' environment: 'local' developer: 'john.doe' # Docker 容器监控 - job_name: 'docker-containers' static_configs: - targets: - 'host.docker.internal:9323' # Docker Exporter - 'cadvisor:8080' # cAdvisor labels: job: 'docker-infrastructure' environment: 'local' 高级用法 1. 组合多个静态配置 scrape_configs: # 主要应用服务 - job_name: 'primary-apps' static_configs: - targets: ['app1:8080', 'app2:8080'] labels: job: 'primary-apps' priority: 'high' - targets: ['app3:8080', 'app4:8080'] labels: job: 'primary-apps' priority: 'medium' # 辅助服务 - job_name: 'auxiliary-services' static_configs: - targets: ['cache1:6379', 'cache2:6379'] labels: job: 'auxiliary-services' service_type: 'cache' - targets: ['queue1:5672', 'queue2:5672'] labels: job: 'auxiliary-services' service_type: 'queue' 2. 使用文件包含模式 # 主配置文件 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'core-services' file: '/etc/prometheus/targets/core-services.yml' - job_name: 'external-services' file: '/etc/prometheus/targets/external-services.yml' # /etc/prometheus/targets/core-services.yml static_configs: - targets: - 'api-server:9090' - 'web-server:8080' labels: job: 'core-services' environment: 'production' 3. 配置模板化 # 使用不同环境的模板 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'app-services' static_configs: - targets: - 'app-{{ .Environment }}-1:8080' - 'app-{{ .Environment }}-2:8080' labels: job: 'app-services' environment: '{{ .Environment }}' team: '{{ .Team }}' 最佳实践 1. 命名规范 # ✅ 清晰的 job 名称 - job_name: 'nginx-exporter' - job_name: 'postgresql-metrics' - job_name: 'application-services' # ✅ 有意义的标签 labels: job: 'web-servers' environment: 'production' datacenter: 'us-west-2' team: 'frontend' version: 'v1.2.0' 2. 环境分离 # ✅ 按环境分组 - job_name: 'production-web' static_configs: - targets: ['prod-web1:8080', 'prod-web2:8080'] labels: environment: 'production' tier: 'frontend' - job_name: 'staging-web' static_configs: - targets: ['staging-web1:8080'] labels: environment: 'staging' tier: 'frontend' 3. 服务分类 # ✅ 按服务类型分类 - job_name: 'infrastructure' static_configs: - targets: ['node1:9100', 'node2:9100'] labels: category: 'infrastructure' service: 'node-exporter' - job_name: 'application' static_configs: - targets: ['app1:8080', 'app2:8080'] labels: category: 'application' service: 'web-api' 与其他服务发现的对比 | 特性 | static_config | file_sd | kubernetes_sd | |-------|---------------|---------|---------------| | 配置复杂度 | 简单 | 中等 | 复杂 | | 动态性 | 静态 | 半动态 | 完全动态 | | 维护成本 | 低 | 中等 | 高 | | 适用场景 | 固定目标 | 变化较少 | 容器化环境 | | 性能开销 | 最低 | 低 | 较高 | static_config 是最简单直接的目标配置方式,适合固定的、变化较少的监控目标,特别适合传统的服务器环境和小规模部署。
relabel_config 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 ⏺ relabel_config 是 Prometheus 中最强大的功能之一,允许在抓取目标前动态重写目标的标签集。它是实现灵活监控配置的核心工具。 基本概念 Relabeling 的工作原理: 1. 按配置顺序应用多个 relabeling 步骤 2. 每个步骤处理目标的标签集 3. 基于匹配规则执行相应动作 4. 最终决定目标是否被抓取以及如何被抓取 初始标签集 系统默认标签 # 初始可用的标签 __address__ # 目标地址 host:port __scheme__ # HTTP/HTTPS 协议 __metrics_path__ # 指标路径 __param_<name> # URL 参数 __scrape_interval__ # 抓取间隔 __scrape_timeout__ # 抓取超时 job # job 名称 __meta_* # 服务发现元数据(根据机制不同) 标签处理流程 初始标签 → Relabeling 步骤 1 → Relabeling 步骤 2 → ... → 最终标签 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 目标发现 标签重写 标签过滤 决定抓取 配置参数详解 source_labels - 源标签列表 # 单个标签 source_labels: [__address__] # 多个标签 source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name, __meta_kubernetes_pod_namespace] # 使用默认(所有标签) # source_labels 不指定时使用所有标签 separator - 标签分隔符 # 默认分号分隔 separator: ';' # label1;label2;label3 # 自定义分隔符 separator: ',' # label1,label2,label3 separator: '|' # label1|label2|label3 separator: '_' # label1_label2_label3 target_label - 目标标签 # 设置新标签 target_label: instance target_label: service_name target_label: environment # 临时标签(用于后续处理) target_label: __tmp_port target_label: __tmp_service regex - 正则表达式 # 匹配任意内容(默认) regex: '(.*)' # 匹配特定端口 regex: ':(\d+)$' # 匹配命名空间 regex: '^([a-z]+)-(.+)$' # 复杂匹配 regex: '([^:]+)(?::(\d+))?.*;prometheus.io/port=(\d+)' replacement - 替换字符串 # 使用捕获组 replacement: '$1' # 第一个捕获组 replacement: '$1:$2' # 多个捕获组组合 replacement: 'service-$1' # 添加前缀 replacement: '$1-metrics' # 添加后缀 # 默认值 replacement: '$1' # 默认使用第一个捕获组 modulus - 模数运算 # 哈希分片 modulus: 3 # 分成 3 组 modulus: 10 # 分成 10 组 modulus: 100 # 分成 100 组 Relabel Actions 详解 1. replace - 替换(默认) # 基础替换 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] target_label: instance regex: '([^:]+):.*' replacement: '$1' # 端口替换 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port] regex: '([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)' replacement: '$1:$2' target_label: __address__ # 路径替换 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path] target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: '(.+)' replacement: '$1' 2. lowercase / uppercase - 大小写转换 # 转小写 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: service_name action: lowercase # 转大写 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [environment] target_label: ENVIRONMENT action: uppercase 3. keep - 保留匹配的目标 # 只保留特定注解的 Pod relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: 'true' # 只保留特定命名空间 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] action: keep regex: '(production|staging)' # 只保留运行中的 Pod relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_phase] action: keep regex: 'Running' 4. drop - 丢弃匹配的目标 # 排除测试环境 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_environment] action: drop regex: 'test' # 排除特定端口 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] action: drop regex: '.*:9091' # 排除 9091 端口 # 排除失败的 Pod relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_ready] action: drop regex: 'false' 5. hashmod - 哈希分片 # 分片到不同 Prometheus 实例 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] target_label: __tmp_hash modulus: 3 action: hashmod - source_labels: [__tmp_hash] regex: '^0$' action: keep # 负载均衡分片 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name] target_label: shard modulus: 5 action: hashmod 6. labelmap - 标签映射 # 复制所有 Kubernetes 标签 relabel_configs: - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+) replacement: k8s_label_$1 # 复制所有注解 relabel_configs: - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_(.+) replacement: k8s_annotation_$1 # 服务标签映射 relabel_configs: - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+) replacement: service_label_$1 7. labeldrop / labelkeep - 标签过滤 # 删除元数据标签 relabel_configs: - action: labeldrop regex: __meta_kubernetes_.* # 只保留必要标签 relabel_configs: - action: labelkeep regex: '(job|instance|service|namespace|version)' # 删除临时标签 relabel_configs: - action: labeldrop regex: __tmp_.* 实际应用示例 1. Kubernetes Pod 监控 relabel_configs: # 只监控带特定注解的 Pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: 'true' # 设置抓取端口 - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port] action: replace regex: '([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)' replacement: '$1:$2' target_label: __address__ # 设置抓取路径 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) # 添加服务标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_app] target_label: service # 添加版本标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_version] target_label: version # 添加环境标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: environment # 添加控制器信息 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_controller_name] target_label: controller # 清理元数据标签 - action: labeldrop regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_.+ 2. 多环境服务发现 relabel_configs: # 从命名空间提取环境 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: environment regex: '(.+)-(.+)' replacement: '$1' # 从服务名提取应用名 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: application regex: '(.+)-(.+)' replacement: '$1' # 只监控生产环境 - source_labels: [environment] action: keep regex: 'production' # 设置实例名 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_address_target_name] target_label: instance 3. 高级过滤和转换 relabel_configs: # 组合多个标签进行过滤 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_environment, __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_team] separator: '-' action: keep regex: 'production-backend' # 动态设置抓取间隔 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_priority] target_label: __scrape_interval__ regex: 'high' replacement: '15s' - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_priority] target_label: __scrape_interval__ regex: 'low' replacement: '2m' # 设置自定义超时 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_timeout] target_label: __scrape_timeout__ regex: '(\d+)s' replacement: '${1}s' 4. 复杂标签操作 relabel_configs: # 步骤 1: 提取服务类型 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: __tmp_service_type regex: '(.+)-(.+)' replacement: '$1' # 步骤 2: 提取服务名 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: service_name regex: '(.+)-(.+)' replacement: '$2' # 步骤 3: 根据服务类型设置不同配置 - source_labels: [__tmp_service_type] target_label: job_type regex: 'web' replacement: 'web-service' - source_labels: [__tmp_service_type] target_label: job_type regex: 'api' replacement: 'api-service' # 步骤 4: 清理临时标签 - action: labeldrop regex: __tmp_.* 性能优化建议 1. 过滤顺序优化 # ✅ 先过滤减少处理量 relabel_configs: # 先过滤 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: 'true' # 再处理 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_app] target_label: service # ❌ 先处理再过滤(性能差) relabel_configs: # 先处理所有 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_app] target_label: service # 最后过滤 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: 'true' 2. 标签数量控制 # ✅ 主动清理不需要的标签 relabel_configs: - action: labeldrop regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_.+ - action: labeldrop regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_labelpresent_.+ # ✅ 只保留必要的标签 relabel_configs: - action: labelkeep regex: '(job|instance|service|namespace|version|team)' 3. 正则表达式优化 # ✅ 使用精确的正则表达式 regex: 'true' regex: '^production$' regex: ':(\d+)$' # ❌ 避免过于宽泛的正则表达式 regex: '.*' regex: '.+' 最佳实践 1. 临时标签使用 # 使用 __tmp 前缀进行中间处理 relabel_configs: # 步骤 1: 提取端口到临时标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port] target_label: __tmp_port regex: '(\d+)' # 步骤 2: 组合地址和端口 - source_labels: [__address__, __tmp_port] target_label: __address__ regex: '([^:]+).*;(\d+)' replacement: '$1:$2' # 步骤 3: 清理临时标签 - action: labeldrop regex: __tmp_.* 2. 错误处理 # 处理缺失标签的情况 relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_version] target_label: version regex: '(.+)' replacement: '${1}' # 如果标签不存在,使用默认值 replacement: 'unknown' # 或者使用多个步骤 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_version] target_label: version regex: '(.+)' replacement: '$1' - source_labels: [version] target_label: version regex: '^$' replacement: 'unknown' Relabeling 是 Prometheus 监控配置的核心技能,掌握它能让你构建出强大而灵活的监控系统。
metric_relabel_configs 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 ⏺ Metric Relabeling 是 Prometheus 在指标数据摄入前的最后一步处理机制,它与 Target Relabeling 使用相同的配置格式,但作用于不同的对象。 基本概念对比 Target Relabeling vs Metric Relabeling | 方面 | Target Relabeling | Metric Relabeling | |-----------|-------------------|------------------------| | 作用对象 | 监控目标 (targets) | 指标样本 (samples) | | 执行时机 | 抓取前 | 摄入前 | | 影响 | 决定是否抓取 | 决定是否存储 | | 配置位置 | relabel_configs | metric_relabel_configs | | 适用指标 | N/A | 所有抓取的指标 | | 对 up 指标影响 | ✅ | ❌ | 处理流程 目标发现 → Target Relabeling → 指标抓取 → Metric Relabeling → 数据摄入 → 存储 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 所有目标 过滤目标 抓取指标 过滤指标 存储到 时序数据库 和重写标签 和重写标签 主要用途 1. 删除高成本指标 # 删除不需要的指标以节省存储 metric_relabel_configs: # 删除 Go 运行时指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: 'go_.*' # 删除进程指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: 'process_.*' # 删除 Prometheus 自身指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: 'prometheus_.*' # 删除 HTTP 请求指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: 'http_.*' # 删除高基数的标签组合 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: '.*_bucket.*|.*_count.*|.*_sum.*' 2. 指标重命名和标准化 # 重命名指标以符合命名规范 metric_relabel_configs: # 统一前缀 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: 'custom_(.+)' replacement: 'app_$1' target_label: __name__ # 删除前缀 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: 'application_(.+)' replacement: '$1' target_label: __name__ # 标准化命名 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: '(.*)_metrics_(.+)' replacement: '${1}_${2}' target_label: __name__ 3. 标签过滤和清理 # 删除特定标签组合 metric_relabel_configs: # 删除高基数标签 - action: labeldrop regex: 'user_id|session_id|request_id' # 删除调试标签 - action: labeldrop regex: 'debug_.*|trace_.*' # 只保留核心标签 - action: labelkeep regex: '(job|instance|service|method|status|environment)' # 删除空值标签 - source_labels: [environment] regex: '^$' target_label: environment replacement: 'unknown' 4. 数据聚合和降采样 # 聚合指标减少存储 metric_relabel_configs: # 只保留特定标签组合 - source_labels: [__name__, method, status_code] regex: 'http_requests_total;(GET|POST);(200|400|500)' action: keep # 移除细粒度标签 - source_labels: [pod, container] action: labeldrop # 降采样直方图 - source_labels: [__name__, le] regex: 'request_duration_seconds_bucket;.*' action: replace target_label: le replacement: '+Inf' # 只保留总数 # 删除详细 bucket - source_labels: [le] regex: '^[0-9.]+$' # 匹配数字 bucket action: drop 完整配置示例 1. Web 应用监控优化 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'web-application' static_configs: - targets: ['app:8080'] metric_relabel_configs: # 删除 Go 运行时指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: 'go_.*|process_.*' # 删除调试指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: 'debug_.*|trace_.*' # 重命名自定义指标 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: 'app_(.+)' replacement: 'webapp_$1' target_label: __name__ # 标准化 HTTP 指标 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: 'http_server_requests_(.+)' replacement: 'http_requests_$1' target_label: __name__ # 删除高基数标签 - action: labeldrop regex: 'user_id|session_id|request_id' # 添加环境标签 - target_label: environment replacement: 'production' # 只保留核心标签 - action: labelkeep regex: '(job|instance|__name__|service|method|status|environment)' 2. 数据库监控优化 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'postgresql-exporter' static_configs: - targets: ['postgres-exporter:9187'] metric_relabel_configs: # 只保留重要的数据库指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: keep regex: '(pg_stat_database_.*|pg_stat_bgwriter_.*|pg_settings_.*|up)' # 删除连接详情(高基数) - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: 'pg_stat_activity_.*' # 简化数据库标签 - source_labels: [datname] target_label: database regex: '(.+)' replacement: '$1' # 删除用户信息 - action: labeldrop regex: 'usename|application_name' # 标准化指标名称 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: 'pg_stat_database_(.+)' replacement: 'postgres_db_$1' target_label: __name__ 3. 微服务环境优化 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'microservices' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod relabel_configs: # 只监控带注解的 Pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: 'true' metric_relabel_configs: # 根据服务类型过滤指标 - source_labels: [service] regex: 'web' action: keep target_label: __name__ regex: '(http_.*|request_.*|response_.*)' - source_labels: [service] regex: 'api' action: keep target_label: __name__ regex: '(api_.*|business_.*|database_.*)' # 删除中间件指标(单独监控) - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: '(redis_|mysql_|kafka_)' # 统一服务标签命名 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_app] target_label: service regex: '(.+)' replacement: '$1' # 添加基础设施标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name] target_label: node # 删除 Kubernetes 元数据 - action: labeldrop regex: '__meta_kubernetes_.*' # 限制直方图桶数量 - source_labels: [le] regex: '(0.1|0.5|1|2.5|5|10|\+Inf)' action: keep 4. 成本控制配置 scrape_configs: - job_name: 'cost-optimized' static_configs: - targets: ['app:8080'] metric_relabel_configs: # 严格限制指标数量 - source_labels: [__name__] action: keep regex: '(up|http_requests_total|http_request_duration_seconds|cpu_usage|memory_usage)' # 删除所有直方图桶,只保留摘要 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: '.*_bucket$' # 限制标签数量 - action: labelkeep regex: '(job|instance|__name__|method|status)' # 删除高基数标签值 - source_labels: [endpoint] regex: '/api/v[0-9]+/users/[0-9]+.*' target_label: endpoint replacement: '/api/v{version}/users/{id}' # 聚合相似指标 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: '(.*)_duration_seconds_(count|sum|bucket)' target_label: __name__ replacement: 'request_duration_seconds_$1' 高级用法 1. 条件性标签处理 metric_relabel_configs: # 根据环境决定保留哪些指标 - source_labels: [environment] regex: 'production' action: keep target_label: __name__ regex: '(business_.*|security_.*|performance_.*)' - source_labels: [environment] regex: 'development' action: keep target_label: __name__ regex: '.*' # 开发环境保留所有指标 2. 动态标签替换 metric_relabel_configs: # 根据标签值动态设置新标签 - source_labels: [status_code] regex: '([1-5][0-9][0-9])' target_label: status_class replacement: '$1xx' replacement: '${1}xx' # 根据服务类型设置监控级别 - source_labels: [service_type] regex: 'critical' target_label: monitoring_level replacement: 'high' - source_labels: [service_type] regex: 'normal' target_label: monitoring_level replacement: 'medium' 3. 标签值规范化 metric_relabel_configs: # 统一环境标签值 - source_labels: [environment] regex: '(prod|production)' target_label: environment replacement: 'production' - source_labels: [environment] regex: '(dev|development)' target_label: environment replacement: 'development' # 统一版本标签格式 - source_labels: [version] regex: 'v?([0-9]+\.[0-9]+\.[0-9]+).*' target_label: version replacement: '$1' 性能优化建议 1. 处理顺序优化 # ✅ 先删除不需要的指标,再处理标签 metric_relabel_configs: # 步骤 1: 删除不需要的指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: 'debug_.*|trace_.*' # 步骤 2: 处理标签 - source_labels: [service] target_label: service_name # 步骤 3: 标签清理 - action: labeldrop regex: 'temp_.*' 2. 正则表达式优化 # ✅ 使用精确的正则表达式 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: '^go_.*' # 只匹配以 go_ 开头的指标 # ✅ 使用锚点 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: 'http_requests_total$' # 精确匹配 # ❌ 避免过于宽泛的匹配 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: '.*' # 匹配所有指标 监控和调试 1. 监控 Metric Relabeling 效果 # 监控指标摄入情况 # prometheus_tsdb_head_samples_appended_total # prometheus_tsdb_head_series_created_total # prometheus_config_last_reload_successful 2. 调试配置 # 临时保留原始指标名用于调试 metric_relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__name__] target_label: original_metric_name regex: '(.+)' # 执行过滤... - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: 'debug_.*' # 生产环境删除调试标签 - action: labeldrop regex: 'original_metric_name' 最佳实践 1. 成本控制 - 在大规模部署中积极使用 metric relabeling 控制存储成本 - 定期审查和优化指标保留策略 - 根据业务价值调整指标保留优先级 2. 标签管理 - 限制标签数量和基数 - 标准化标签命名规范 - 定期清理不再需要的标签 3. 性能考虑 - 将最有效的过滤规则放在前面 - 使用精确的正则表达式 - 避免复杂的标签操作链 Metric Relabeling 是控制 Prometheus 存储成本和优化性能的重要工具,合理使用可以显著提高监控系统的效率。
alert_relabel_configs 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 ⏺ Alert Relabeling 是 Prometheus 在告警发送到 Alertmanager 之前对告警进行处理的机制,它与 Target Relabeling 和 Metric Relabeling 使用相同的配置格式,但作用于告警对象。 基本概念 处理流程 告警规则触发 → 告警生成 → 外部标签添加 → Alert Relabeling → 发送到 Alertmanager ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 规则评估 创建告警对象 添加集群标签 重写告警标签 路由和通知 作用对象 - 告警对象 (alerts),而不是目标或指标 - 在告警发送到 Alertmanager 之前执行 - 在外部标签添加之后执行 主要用途 1. HA Prometheus 标签标准化 确保高可用的 Prometheus 服务器发送相同的告警: # Prometheus A 配置 global: external_labels: cluster: 'production' region: 'us-west-2' prometheus_replica: 'A' alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 移除副本标签,确保告警一致 - action: labeldrop regex: 'prometheus_replica' # Prometheus B 配置 global: external_labels: cluster: 'production' region: 'us-west-2' prometheus_replica: 'B' alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 移除副本标签,确保告警一致 - action: labeldrop regex: 'prometheus_replica' 2. 告警标签增强 为告警添加额外的上下文信息: alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 添加集群信息 - source_labels: [cluster] target_label: datacenter regex: 'prod-(.+)' replacement: 'dc-$1' # 添加服务团队信息 - source_labels: [service] target_label: team regex: '(web|api|database)' replacement: '${1}-team' # 添加优先级 - source_labels: [severity] target_label: priority regex: 'critical' replacement: 'P1' - source_labels: [severity] target_label: priority regex: 'warning' replacement: 'P2' 3. 告警过滤和清理 删除不需要的告警或标签: alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 删除测试环境的告警 - source_labels: [environment] action: drop regex: 'test' # 删除调试告警 - source_labels: [alertname] action: drop regex: 'Debug.*|Test.*' # 清理临时标签 - action: labeldrop regex: 'temp_.*|debug_.*' # 只保留核心标签 - action: labelkeep regex: '(alertname|instance|job|severity|service|team)' 完整配置示例 1. 企业级 HA 配置 # Prometheus 配置 global: external_labels: cluster: 'production' datacenter: 'us-west-2' prometheus_id: 'prometheus-01' role: 'primary' alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 标准化告警标签,移除实例标识 - action: labeldrop regex: 'prometheus_id|role' # 添加路由信息 - source_labels: [service] target_label: alert_routing_key regex: 'payment-.*' replacement: 'finance-team' - source_labels: [service] target_label: alert_routing_key regex: 'user-.*' replacement: 'user-team' # 添加环境信息 - source_labels: [cluster] target_label: environment regex: 'production' replacement: 'prod' # 添加 SLA 信息 - source_labels: [severity] target_label: sla_impact regex: 'critical' replacement: 'sla_breach' - source_labels: [severity] target_label: sla_impact regex: 'warning' replacement: 'sla_warning' alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: - 'alertmanager-01:9093' - 'alertmanager-02:9093' 2. 多环境告警标准化 alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 统一环境标签 - source_labels: [environment] target_label: env regex: '(prod|production)' replacement: 'production' - source_labels: [environment] target_label: env regex: '(staging|stage)' replacement: 'staging' - source_labels: [environment] target_label: env regex: '(dev|development)' replacement: 'development' # 添加通知渠道 - source_labels: [env, severity] target_label: channel regex: 'production;critical' replacement: 'urgent' - source_labels: [env, severity] target_label: channel regex: 'production;warning' replacement: 'production' - source_labels: [env, severity] target_label: channel regex: 'staging;critical' replacement: 'staging-alerts' # 添加服务分类 - source_labels: [service] target_label: service_category regex: '(web|api)-.*' replacement: 'frontend' - source_labels: [service] target_label: service_category regex: '(database|cache|queue)-.*' replacement: 'backend' # 清理冗余标签 - action: labeldrop regex: 'temporary_.*|debug_.*' 3. 动态告警路由 alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 基于服务类型的动态路由 - source_labels: [service] target_label: routing_group regex: 'payment-.*' replacement: 'financial-services' - source_labels: [service] target_label: routing_group regex: 'user-.*|auth-.*' replacement: 'user-services' - source_labels: [service] target_label: routing_group regex: 'inventory-.*|order-.*' replacement: 'ecommerce' # 基于严重性的优先级设置 - source_labels: [severity] target_label: notification_priority regex: 'critical' replacement: 'high' - source_labels: [severity] target_label: notification_priority regex: 'warning' replacement: 'medium' - source_labels: [severity] target_label: notification_priority regex: 'info' replacement: 'low' # 添加时间窗口标签 - source_labels: [] target_label: business_hours replacement: 'false' # 可以通过其他方式动态设置 # 清理系统标签 - action: labeldrop regex: '__tmp_.*' 4. 合规性标签处理 alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 添加合规性标签 - source_labels: [service] target_label: compliance_category regex: '.*(payment|billing|financial).*' replacement: 'pci-dss' - source_labels: [service] target_label: compliance_category regex: '.*(user|profile|personal).*' replacement: 'gdpr' - source_labels: [service] target_label: compliance_category regex: '.*(health|medical).*' replacement: 'hipaa' # 添加数据分类 - source_labels: [compliance_category] target_label: data_classification regex: 'pci-dss' replacement: 'confidential' - source_labels: [compliance_category] target_label: data_classification regex: 'gdpr' replacement: 'personal' # 添加保留期要求 - source_labels: [data_classification] target_label: retention_days regex: 'confidential' replacement: '2555' # 7 years - source_labels: [data_classification] target_label: retention_days regex: 'personal' replacement: '1825' # 5 years # 删除敏感信息标签 - action: labeldrop regex: '.*password.*|.*secret.*|.*token.*' 高级配置示例 1. 基于时间的告警处理 alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 工作时间 vs 非工作时间处理 - source_labels: [] target_label: business_hours replacement: 'true' # 实际实现需要配合时间模板或外部标签 # 根据工作时间调整通知 - source_labels: [business_hours, severity] target_label: notification_method regex: 'true;critical' replacement: 'immediate' - source_labels: [business_hours, severity] target_label: notification_method regex: 'false;critical' replacement: 'urgent' # 添加时区信息 - source_labels: [datacenter] target_label: timezone regex: 'us-west-2' replacement: 'PST' - source_labels: [datacenter] target_label: timezone regex: 'us-east-1' replacement: 'EST' 2. 条件性告警增强 alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 基于服务类型的条件处理 - source_labels: [service, severity] regex: 'database-.*;critical' target_label: escalation_team replacement: 'database-oncall' - source_labels: [service, severity] regex: 'web-.*;critical' target_label: escalation_team replacement: 'frontend-oncall' # 添加自动修复标签 - source_labels: [alertname] target_label: auto_recovery regex: 'HighCPUUsage|HighMemoryUsage' replacement: 'enabled' - source_labels: [alertname] target_label: auto_recovery regex: 'DiskSpaceLow' replacement: 'manual' # 添加影响范围标签 - source_labels: [instance, service] target_label: impact_scope regex: '.*-master.*;.*' replacement: 'cluster-wide' - source_labels: [instance, service] target_label: impact_scope regex: '.*-worker.*;.*' replacement: 'service-specific' 最佳实践 1. HA 环境配置 # ✅ 确保 HA 配置的一致性 global: external_labels: cluster: 'production' region: 'us-west-2' # 不要添加实例唯一的标签 alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 移除任何可能造成差异的标签 - action: labeldrop regex: 'prometheus_replica|instance_id' # 添加统一的集群标识 - target_label: alert_source replacement: 'prometheus-ha-cluster' 2. 标签命名规范 # ✅ 使用一致的标签命名 alert_relabel_configs: - source_labels: [severity] target_label: alert_severity regex: '(.+)' - source_labels: [service] target_label: affected_service regex: '(.+)' - source_labels: [team] target_label: responsible_team regex: '(.+)' 3. 渐进式配置 # ✅ 分阶段应用 relabeling alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 阶段 1: 过滤不需要的告警 - source_labels: [environment] action: drop regex: 'test|debug' # 阶段 2: 标准化核心标签 - source_labels: [severity] target_label: urgency regex: '(.+)' # 阶段 3: 添加增强信息 - source_labels: [service] target_label: service_owner regex: '(.+)' replacement: '$1-team' # 阶段 4: 清理不需要的标签 - action: labeldrop regex: 'temp_.*|debug_.*' 调试和监控 1. 监控告警处理 # 监控 Alert Relabeling 的效果 # prometheus_notifications_total # prometheus_notifications_queue_capacity # prometheus_notifications_dropped_total 2. 调试配置 # 临时保留原始标签用于调试 alerting: alert_relabel_configs: # 保留原始告警名 - source_labels: [alertname] target_label: original_alertname regex: '(.+)' # 执行标签处理... # 生产环境移除调试标签 - action: labeldrop regex: 'original_alertname' 与其他 Relabeling 的区别 | 特性 | Target Relabeling | Metric Relabeling | Alert Relabeling | |---------|-------------------|------------------------|-----------------------| | 作用对象 | 监控目标 | 指标样本 | 告警对象 | | 执行时机 | 抓取前 | 摄入前 | 发送前 | | 影响 | 是否抓取 | 是否存储 | 如何路由 | | 配置位置 | relabel_configs | metric_relabel_configs | alert_relabel_configs | | 对 up 指标 | ✅ 影响 | ❌ 不影响 | ❌ 不影响 | Alert Relabeling 是确保告警一致性和正确路由的重要工具,特别是在 HA 环境和多集群部署中至关重要。
alertmanager_config 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 ⏺ alertmanager_config 是 Prometheus 配置中用于指定 Alertmanager 实例和通信参数的部分。它支持静态配置和动态服务发现,提供了丰富的配置选项来适应不同的部署架构。 基本概念 Alertmanager 配置的主要功能: - 指定要发送告警的 Alertmanager 实例 - 配置通信协议和认证方式 - 支持多种服务发现机制 - 提供 relabeling 功能进行目标选择和路径修改 基础配置参数 连接参数 alerting: alertmanagers: # 基础配置 - timeout: 10s # 连接超时时间 api_version: v2 # Alertmanager API 版本 path_prefix: / # HTTP 路径前缀 scheme: http # 协议方案 (http/https) 静态配置示例 alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: - 'alertmanager-01:9093' - 'alertmanager-02:9093' timeout: 15s api_version: v2 scheme: http # 带路径前缀的配置 - static_configs: - targets: - 'alertmanager.internal:9093' path_prefix: '/alertmanager' scheme: https 认证配置 1. 基础认证 alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ['alertmanager:9093'] basic_auth: username: 'prometheus' password_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/alertmanager_password' scheme: https 2. 令牌认证 alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ['alertmanager:9093'] authorization: type: 'Bearer' credentials_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/bearer_token' scheme: https 3. AWS SigV4 认证 alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ['alertmanager.amazonaws.com'] sigv4: region: 'us-west-2' access_key: 'AKIA...' secret_key_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/aws_secret' # 或者使用角色 role_arn: 'arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/PrometheusAlertManager' profile: 'default' scheme: https 4. OAuth 2.0 认证 alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ['alertmanager.example.com'] oauth2: client_id: 'prometheus' client_secret_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/oauth_secret' token_url: 'https://auth.example.com/oauth2/token' scopes: ['alertmanager:write'] scheme: https TLS 配置 HTTPS 连接配置 alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ['secure-alertmanager:9093'] scheme: https tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/ca.crt' cert_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/client.crt' key_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/client.key' server_name: 'secure-alertmanager' insecure_skip_verify: false min_version: 'TLS12' 服务发现配置 1. Kubernetes 服务发现 alerting: alertmanagers: - kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: service namespaces: names: ['monitoring'] selectors: - role: service label: 'app=alertmanager' relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: __alerts_path__ regex: 'alertmanager-(.+)' replacement: '/api/v1/alerts' - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_ready] action: keep regex: 'true' 2. DNS 服务发现 alerting: alertmanagers: - dns_sd_configs: - names: - 'alertmanager.service.consul' - 'alertmanager-internal.service.consul' type: 'SRV' port: 9093 refresh_interval: 30s 3. 文件服务发现 alerting: alertmanagers: - file_sd_configs: - files: - '/etc/prometheus/alertmanager_targets/*.yml' refresh_interval: 60s # /etc/prometheus/alertmanager_targets/production.yml - targets: - 'alertmanager-prod-01:9093' - 'alertmanager-prod-02:9093' labels: environment: 'production' cluster: 'us-west-2' 4. HTTP 服务发现 alerting: alertmanagers: - http_sd_configs: - url: 'http://config-manager.example.com/alertmanager/targets' refresh_interval: 60s basic_auth: username_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/config_user' password_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/config_pass' 完整配置示例 1. 生产环境 HA 配置 alerting: alertmanagers: # 主要 Alertmanager 集群 - kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints namespaces: names: ['monitoring'] selectors: - role: endpoints label: 'app=alertmanager' label: 'role=primary' relabel_configs: # 选择就绪的端点 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_ready] action: keep regex: 'true' # 设置正确的告警路径 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name] target_label: __alerts_path__ regex: 'web' replacement: '/api/v1/alerts' - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name] target_label: __alerts_path__ regex: 'api' replacement: '/api/v1/alerts' # 添加集群标识 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: cluster regex: 'monitoring' replacement: 'production' timeout: 15s api_version: v2 scheme: http # 备用 Alertmanager - static_configs: - targets: - 'backup-alertmanager-01:9093' - 'backup-alertmanager-02:9093' labels: role: 'backup' environment: 'production' timeout: 10s api_version: v2 scheme: https tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/backup_ca.crt' 2. 多环境配置 alerting: alertmanagers: # 开发环境 - static_configs: - targets: ['alertmanager-dev:9093'] timeout: 5s api_version: v2 labels: environment: 'development' priority: 'low' # 测试环境 - file_sd_configs: - files: - '/etc/prometheus/alertmanagers/staging.yml' refresh_interval: 30s timeout: 10s api_version: v2 labels: environment: 'staging' priority: 'medium' # 生产环境 - kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: service namespaces: names: ['monitoring', 'production'] selectors: - role: service label: 'monitoring=alertmanager' label: 'environment=production' relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: alertmanager_cluster regex: 'alertmanager-(.+)' replacement: '$1' timeout: 15s api_version: v2 labels: environment: 'production' priority: 'high' 3. 混合云配置 alerting: alertmanagers: # 本地集群 - kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints namespaces: names: ['monitoring'] relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_label_cloud] action: keep regex: 'local' timeout: 10s scheme: http # AWS 集群 - ec2_sd_configs: - region: 'us-west-2' port: 9093 filters: - name: 'tag:Monitoring' values: ['alertmanager'] - name: 'instance-state-name' values: ['running'] relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_ec2_tag_Environment] target_label: environment - source_labels: [__meta_ec2_private_ip] target_label: __address__ regex: '(.+)' replacement: '$1:9093' timeout: 15s sigv4: region: 'us-west-2' profile: 'prometheus' scheme: https # Azure 集群 - azure_sd_configs: - port: 9093 subscription_id: '12345678-90ab-cdef-1234-567890abcdef' resource_group: 'monitoring-rg' filters: - name: 'tag:monitoring' values: ['alertmanager'] relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_azure_location] target_label: region timeout: 15s scheme: https Relabel 配置 1. 选择特定 Alertmanager alerting: alertmanagers: - kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints namespaces: names: ['monitoring'] relabel_configs: # 只选择 Alertmanager 服务 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] action: keep regex: 'alertmanager.*' # 排除测试实例 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_environment] action: drop regex: 'test' # 设置告警路径 - target_label: __alerts_path__ replacement: '/api/v1/alerts' 2. 动态路径配置 alerting: alertmanagers: - kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints relabel_configs: # 根据服务名设置不同的 API 路径 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: __alerts_path__ regex: 'alertmanager-v1' replacement: '/api/v1/alerts' - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: __alerts_path__ regex: 'alertmanager-v2' replacement: '/api/v2/alerts' # 默认路径 - source_labels: [] target_label: __alerts_path__ regex: '.*' replacement: '/api/v2/alerts' 3. 负载均衡配置 alerting: alertmanagers: - kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints relabel_configs: # 添加权重标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_address_target_name] target_label: weight regex: 'alertmanager-01' replacement: '2' - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_address_target_name] target_label: weight regex: 'alertmanager-02' replacement: '1' # 添加区域标签 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_topology_kubernetes_io_zone] target_label: zone 高级配置 1. 代理配置 alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ['alertmanager.external.com:9093'] proxy_url: 'http://corporate-proxy:8080' no_proxy: 'localhost,.internal' proxy_from_environment: true scheme: https 2. 自定义 HTTP 头 alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ['alertmanager:9093'] http_headers: User-Agent: values: ['Prometheus/2.0'] X-Cluster-ID: values: ['prod-cluster-01'] X-Environment: values: ['production'] 3. 多版本 API 支持 alerting: alertmanagers: # Alertmanager v1 - static_configs: - targets: ['alertmanager-v1:9093'] api_version: v1 path_prefix: '/api/v1' relabel_configs: - target_label: __alerts_path__ replacement: '/alerts' # Alertmanager v2 - static_configs: - targets: ['alertmanager-v2:9093'] api_version: v2 relabel_configs: - target_label: __alerts_path__ replacement: '/api/v2/alerts' 最佳实践 1. HA 配置 # ✅ 配置多个 Alertmanager 实例 alerting: alertmanagers: - kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints namespaces: names: ['monitoring'] relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] action: keep regex: 'alertmanager' # 至少配置 2-3 个实例 2. 超时配置 # ✅ 根据网络环境调整超时 alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ['alertmanager:9093'] timeout: 15s # 生产环境使用较长超时 api_version: v2 3. 安全配置 # ✅ 生产环境使用 HTTPS 和认证 alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ['alertmanager:9093'] scheme: https tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/ca.crt' insecure_skip_verify: false basic_auth: username_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/username' password_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/password' 监控和调试 1. 监控连接状态 # 监控指标 # prometheus_notifications_alertmanagers_discovered # prometheus_notifications_queue_length # prometheus_notifications_dropped_total # prometheus_notifications_errors_total 2. 调试配置 # 添加调试标签 alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ['alertmanager:9093'] relabel_configs: - target_label: debug_prometheus_instance replacement: '${POD_NAME}' Alertmanager 配置提供了灵活的告警路由能力,支持各种部署架构和认证方式,确保告警能够可靠地传递到正确的处理系统。
remote_write 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 ⏺ remote_write 是 Prometheus 的一个强大功能,允许将采集的指标数据实时发送到远程存储系统。这是实现长期数据存储、数 据聚合和多集群监控的核心组件。 基本概念 Remote Write 的工作流程: 指标采集 → External Labels → Write Relabeling → 队列处理 → 发送到远程存储 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 抓取指标 添加集群标签 过滤和重写 缓冲和批处理 持久化存储 核心配置参数 1. 基础连接配置 remote_write: - url: 'https://remote-storage.example.com/api/v1/write' name: 'production-storage' remote_timeout: 30s protobuf_message: 'io.prometheus.write.v2.Request' 2. 协议版本选择 # Remote Write 1.0 (传统) remote_write: - url: 'https://legacy-storage.example.com/api/v1/write' protobuf_message: 'prometheus.WriteRequest' send_native_histograms: false # Remote Write 2.0 (推荐) remote_write: - url: 'https://modern-storage.example.com/api/v2/write' protobuf_message: 'io.prometheus.write.v2.Request' send_native_histograms: true # 总是启用 Write Relabeling 配置 1. 基础过滤 remote_write: - url: 'https://storage.example.com/api/v1/write' write_relabel_configs: # 只发送特定指标的样本 - source_labels: [__name__] action: keep regex: '(cpu_.*|memory_.*|disk_.*|network_.*)' # 删除调试指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: 'debug_.*|test_.*' # 只发送生产环境的指标 - source_labels: [environment] action: keep regex: 'production' 2. 高级过滤和转换 remote_write: - url: 'https://storage.example.com/api/v1/write' write_relabel_configs: # 根据服务类型过滤 - source_labels: [service] action: keep regex: '(web|api|database|cache)' # 重命名指标 - source_labels: [__name__] regex: 'custom_(.+)' replacement: 'app_$1' target_label: __name__ # 添加存储标签 - target_label: storage_backend replacement: 's3-hot' # 删除高基数标签 - action: labeldrop regex: 'user_id|session_id|request_id' # 聚合数据减少存储量 - source_labels: [__name__] action: drop regex: '.*_bucket$' # 删除直方图桶 认证配置 1. 基础认证 remote_write: - url: 'https://storage.example.com/api/v1/write' basic_auth: username: 'prometheus' password_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/storage_password' http_config: tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/storage_ca.crt' insecure_skip_verify: false 2. 令牌认证 remote_write: - url: 'https://storage.example.com/api/v1/write' authorization: type: 'Bearer' credentials_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/storage_token' headers: X-Prometheus-Cluster: 'production-cluster-01' 3. AWS SigV4 认证 remote_write: - url: 'https://aps-workspaces.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/workspaces/ws-1234567890/api/v1/remote_write' sigv4: region: 'us-west-2' role_arn: 'arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/PrometheusRemoteWrite' queue_config: max_shards: 10 capacity: 5000 4. Azure AD 认证 remote_write: - url: 'https://azure-monitor.azure.com/api/v1/write' azuread: managed_identity: client_id: 'your-client-id' cloud: 'AzurePublic' headers: X-Azure-Monitoring-Resource: '/subscriptions/subscription-id/resourceGroups/rg-name/providers/microsoft.monitor/accounts/account-name' 队列配置优化 1. 基础队列配置 remote_write: - url: 'https://storage.example.com/api/v1/write' queue_config: capacity: 10000 # 每个分片的缓冲区大小 max_shards: 20 # 最大并发数 min_shards: 1 # 最小并发数 max_samples_per_send: 2000 # 每批发送的最大样本数 batch_send_deadline: 5s # 批发送截止时间 min_backoff: 30ms # 初始重试延迟 max_backoff: 5s # 最大重试延迟 2. 高性能配置 remote_write: - url: 'https://high-throughput-storage.example.com/api/v1/write' queue_config: capacity: 50000 # 大缓冲区 max_shards: 50 # 高并发 min_shards: 5 # 保持最小并发 max_samples_per_send: 5000 # 大批发送 batch_send_deadline: 10s # 较长批处理时间 min_backoff: 10ms # 快速重试 max_backoff: 2s # 较短最大延迟 retry_on_http_429: true # 启用 429 重试 3. 低延迟配置 remote_write: - url: 'https://low-latency-storage.example.com/api/v1/write' queue_config: capacity: 2000 # 小缓冲区 max_shards: 5 # 低并发 min_shards: 1 max_samples_per_send: 500 # 小批次 batch_send_deadline: 1s # 快速发送 min_backoff: 10ms max_backoff: 1s 完整配置示例 1. 生产环境多存储配置 remote_write: # 主存储 - 高可用长期存储 - name: 'primary-storage' url: 'https://primary-storage.example.com/api/v1/write' protobuf_message: 'io.prometheus.write.v2.Request' send_native_histograms: true send_exemplars: true remote_timeout: 30s write_relabel_configs: # 发送所有业务指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: keep regex: '(business_.*|app_.*|service_.*)' # 添加存储层标识 - target_label: storage_tier replacement: 'primary' # 删除调试数据 - action: labeldrop regex: 'debug_.*' queue_config: capacity: 25000 max_shards: 30 max_samples_per_send: 3000 batch_send_deadline: 5s http_config: tls_config: ca_file: '/etc/prometheus/certs/primary_ca.crt' basic_auth: username_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/primary_user' password_file: '/etc/prometheus/secrets/primary_pass' # 备用存储 - 成本优化 - name: 'backup-storage' url: 'https://backup-storage.example.com/api/v1/write' protobuf_message: 'prometheus.WriteRequest' send_native_histograms: false send_exemplars: false remote_timeout: 60s write_relabel_configs: # 只发送核心基础设施指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: keep regex: '(node_.*|process_.*|up)' # 添加存储层标识 - target_label: storage_tier replacement: 'backup' # 聚合数据减少量 - action: labeldrop regex: '.*_bucket' queue_config: capacity: 10000 max_shards: 10 max_samples_per_send: 1000 batch_send_deadline: 10s min_backoff: 100ms max_backoff: 10s # 实时分析存储 - 低延迟 - name: 'realtime-analytics' url: 'https://analytics.example.com/api/v2/write' protobuf_message: 'io.prometheus.write.v2.Request' send_native_histograms: true send_exemplars: true remote_timeout: 10s write_relabel_configs: # 只发送实时分析需要的指标 - source_labels: [__name__] action: keep regex: '(request_.*|response_.*|throughput_.*)' # 添加分析标签 - target_label: analytics_type replacement: 'realtime' # 确保时间精度 - source_labels: [] target_label: precision replacement: 'millisecond' queue_config: capacity: 5000 max_shards: 5 max_samples_per_send: 500 batch_send_deadline: 1s min_backoff: 5ms max_backoff: 500ms 2. 云原生配置 remote_write: # AWS Prometheus 服务 - name: 'aws-aps' url: 'https://aps-workspaces.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/workspaces/ws-1234567890/api/v1/remote_write' sigv4: region: 'us-west-2' protobuf_message: 'io.prometheus.write.v2.Request' write_relabel_configs: # 添加 AWS 特定标签 - target_label: cloud_provider replacement: 'aws' - target_label: region replacement: 'us-west-2' queue_config: capacity: 15000 max_shards: 20 retry_on_http_429: true # Azure Monitor - name: 'azure-monitor' url: 'https://eastus.monitoring.azure.com/subscriptions/sub-id/resourceGroups/rg-name/providers/Microsoft.Mo nitor/accounts/account-name/api/v1/write' azuread: managed_identity: client_id: 'managed-identity-client-id' write_relabel_configs: - target_label: cloud_provider replacement: 'azure' - target_label: region replacement: 'eastus' headers: X-Azure-Monitoring-Resource: '/subscriptions/sub-id/resourceGroups/rg-name/providers/microsoft.monitor/accounts/account-name' 3. 成本优化配置 remote_write: - name: 'cost-optimized-storage' url: 'https://cheap-storage.example.com/api/v1/write' protobuf_message: 'prometheus.WriteRequest' # 使用旧协议节省成本 send_native_histograms: false # 禁用原生直方图 send_exemplars: false # 禁用 exemplar write_relabel_configs: # 严格限制指标数量 - source_labels: [__name__] action: keep regex: '(up|cpu_usage|memory_usage|disk_usage|network_bytes)' # 删除高基数标签 - action: labeldrop regex: 'pod|container|endpoint' # 聚合数据 - action: labeldrop regex: '.*_bucket|.*_quantile' # 添加成本标签 - target_label: storage_class replacement: 'economy' queue_config: capacity: 5000 # 较小缓冲区 max_shards: 5 # 低并发 max_samples_per_send: 1000 # 中等批次 batch_send_deadline: 10s # 较长等待时间 sample_age_limit: 5m # 丢弃旧样本 元数据配置 1. 基础元数据配置 remote_write: - url: 'https://storage.example.com/api/v1/write' protobuf_message: 'prometheus.WriteRequest' metadata_config: send: true send_interval: 1m max_samples_per_send: 500 2. 高频元数据更新 remote_write: - url: 'https://storage.example.com/api/v1/write' metadata_config: send: true send_interval: 30s # 高频更新 max_samples_per_send: 200 高级功能 1. DNS 轮询 remote_write: - url: 'https://storage-cluster.example.com/api/v1/write' round_robin_dns: true queue_config: max_shards: 10 2. 自定义 HTTP 头 remote_write: - url: 'https://storage.example.com/api/v1/write' headers: X-Prometheus-Cluster: 'production' X-Prometheus-Version: '2.45.0' X-Data-Retention: '90d' X-Cost-Center: 'engineering' 3. 代理配置 remote_write: - url: 'https://external-storage.example.com/api/v1/write' http_config: proxy_url: 'http://corporate-proxy:8080' no_proxy: 'localhost,.internal' proxy_connect_header: Proxy-Authorization: ['Basic dXNlcjpwYXNz'] 性能监控 关键指标 # 监控 Remote Write 性能的指标 # prometheus_remote_storage_samples_total # prometheus_remote_storage_samples_failed_total # prometheus_remote_storage_samples_pending # prometheus_remote_storage_samples_retry_failed_total # prometheus_remote_storage_highest_timestamp_in_seconds # prometheus_remote_storage_queue_highest_sent_timestamp_seconds 告警规则示例 # Remote Write 告警规则 groups: - name: remote-write rules: # 样本积压告警 - alert: RemoteWriteBacklog expr: prometheus_remote_storage_samples_pending > 10000 for: 5m labels: severity: warning annotations: summary: "Remote write backlog is high" description: "{{ $value }} samples are pending to be sent to remote storage" # 发送失败率告警 - alert: RemoteWriteHighFailureRate expr: rate(prometheus_remote_storage_samples_failed_total[5m]) / rate(prometheus_remote_storage_samples_total[5m]) > 0.05 for: 2m labels: severity: critical annotations: summary: "Remote write failure rate is high" description: "Remote write failure rate is {{ $value | humanizePercentage }}" # 队列延迟告警 - alert: RemoteWriteQueueDelay expr: time() - prometheus_remote_storage_queue_highest_sent_timestamp_seconds > 60 for: 3m labels: severity: warning annotations: summary: "Remote write queue delay is high" description: "Samples are waiting {{ $value }} seconds to be sent" 最佳实践 1. 配置优化 - 使用 io.prometheus.write.v2.Request 协议提高效率 - 根据存储能力调整队列配置 - 使用 write_relabelings 控制发送的数据量 2. 成本控制 - 过滤不必要的指标 - 聚合高基数数据 - 选择合适的存储层级 3. 可靠性 - 配置多个远程存储端点 - 设置适当的重试策略 - 监控发送状态和失败率 Remote Write 是构建现代监控系统的关键组件,合理配置可以实现高可用、可扩展的长期数据存储解决方案。
remote_read 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 ⏺ 这是一个 Prometheus 的 remote_read 配置段,用于设置从远程存储系统读取监控数据的配置。让我详细解释每个部分: 基本配置 url: 远程读取 API 的端点 URL(必需参数) name: 远程读取配置的名称(可选) - 必须在所有远程读取配置中唯一 - 用于指标和日志记录,帮助用户区分不同的远程读取配置 选择器配置 required_matchers: 必需的标签匹配器(可选) - 查询远程端点时,选择器中必须包含这些标签匹配条件 - 示例: required_matchers: cluster: production region: us-west 连接配置 remote_timeout: 请求超时时间(可选) - 默认值为 1 分钟 - 控制向远程端点发送请求的等待时间 headers: 自定义 HTTP 头(可选) - 随每个远程读取请求一起发送 - 注意:Prometheus 自身设置的头信息不能被覆盖 - 示例: headers: Authorization: "Bearer token123" X-Custom-Header: "value" 数据读取策略 read_recent: 是否读取近期数据(可选) - 默认值为 false - 设置为 true 时,即使本地存储有完整的时间范围数据,也会查询远程端点 filter_external_labels: 是否使用外部标签作为选择器(可选) - 默认值为 true - 使用 Prometheus 的外部标签来过滤远程读取请求 HTTP 客户端配置 <http_config>: HTTP 客户端配置 - 包括身份验证方法(如基本认证、授权) - 代理配置 - TLS 选项 - 自定义 HTTP 头等 典型使用场景 1. 长期存储: 将历史数据存储在远程系统,Prometheus 只保留近期数据 2. 数据联合: 从多个 Prometheus 实例或存储系统聚合数据 3. 高可用性: 当本地存储不可用时,从远程备份读取数据 这个配置是 Prometheus 联邦查询和长期存储解决方案的重要组成部分。
tsdb 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 ⏺ 这是 Prometheus TSDB(时序数据库)的配置部分,专门用于配置乱序样本处理的时间窗口设置。让我详细解释: 核心配置 out_of_order_time_window: 乱序时间窗口(可选参数) - 默认值:0s(不接受乱序样本) - 类型:时间间隔(duration) 乱序样本处理机制 基本概念 - 正常顺序: 样本按时间戳递增顺序到达 - 乱序样本: 时间戳比当前 TSDB 最大时间更早的样本 - 越界样本: 时间戳超出合理范围的样本 处理逻辑 当设置时间窗口 > 0 时: 1. 可接受的条件: 样本时间戳 >= TSDB.MaxTime - out_of_order_time_window 2. 样本分类: - (a) 可摄取样本: - 正常顺序的样本 - 在乱序时间窗口内的乱序/越界样本 - (b) 过旧样本: - 不在顺序内且在乱序时间窗口之外的样本 错误处理变化 - 窗口 = 0 时:错误分为 "out-of-order" 和 "out-of-bounds" - 窗口 > 0 时:错误合并为单一的 "too-old" 错误 对实验性 Agent 的影响 当 out_of_order_time_window > 0 时: - Agent WAL 允许接受乱序样本 - 判断条件:相对于同一序列最后追加样本的时间戳 - 时间窗口:指定的配置时间窗口内 实际使用场景 1. 网络延迟和重排序 # 允许 5 分钟内的乱序样本 out_of_order_time_window: 5m 2. 多源数据聚合 # 当从多个时间不同步的源收集数据时 out_of_order_time_window: 10m 3. 批量传输延迟 # 处理批量传输可能导致的数据延迟 out_of_order_time_window: 30m 性能考虑 优点: - 提高数据完整性,减少因网络延迟导致的数据丢失 - 增强系统对时钟不同步的容忍度 缺点: - 增加内存使用,需要维护更大的时间窗口 - 可能影响查询性能,因为需要处理更多的数据状态 - 延迟数据可见性,因为数据可能需要等待才能被处理 这个配置主要用于处理分布式环境中因网络延迟、时钟不同步等因素导致的监控数据乱序到达问题。
exemplars 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 ⏺ 这是 Prometheus 中关于 Exemplar 存储 的配置,Exemplar 是一种用于存储具体样本数据的实验性功能。让我详细解释: 功能概述 Exemplar:存储具体的、有代表性的监控样本数据,通常用于性能分析和问题诊断 - 实验性功能:仍处于实验阶段 - 启用方式:需要通过 --enable-feature=exemplar-storage 启动参数开启 核心配置 max_exemplars: Exemplar 循环缓冲区的最大大小 - 类型:整数 - 默认值:100,000 - 运行时可调整:可在运行时重新配置大小 工作机制 循环缓冲区 - 存储方式:使用循环缓冲区存储所有序列的 Exemplar - 内存管理:当缓冲区满时,最旧的 Exemplar 会被新数据覆盖 - 全局限制:适用于所有时序序列的总和 实际用途 1. 错误追踪: # 存储导致错误的 HTTP 请求详情 exemplar: trace_id: "abc123" timestamp: "2024-01-01T12:00:00Z" value: 500 labels: error: "database_timeout" 2. 性能分析: # 存储慢查询的具体信息 exemplar: query: "SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 12345" timestamp: "2024-01-01T12:00:00Z" value: 2.5 # 秒 配置示例 # prometheus.yml tsdb: max_exemplars: 50000 # 减少内存使用 # 启动命令 ./prometheus --enable-feature=exemplar-storage 内存考虑 计算方式: - 每个 Exemplar 大约占用 100-200 字节 - 100,000 个 Exemplar ≈ 10-20 MB 内存 配置建议: - 高负载环境:200,000-500,000 - 一般环境:50,000-100,000 - 资源受限:10,000-50,000 查询方式 PromQL 中使用: # 获取 Exemplar http_request_duration_seconds{exemplar="true"} 注意:Exemplar 主要与像 Grafana 这样的可视化工具配合使用,提供深入的数据分析能力。 这个功能特别适合需要从宏观监控指标深入到具体样本场景的性能优化和故障排查。
tracing_config 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 ⏺ 这是 Prometheus 的分布式追踪导出配置,用于将追踪数据发送到支持 OTLP (OpenTelemetry Protocol) 协议的后端服务。 基本概念 实验性功能:当前仍为实验性,未来可能发生变化 协议支持:使用 OTLP 协议导出追踪数据 核心配置选项 1. 客户端类型 client_type: 导出追踪的客户端类型 - 可选值:'http' 或 'grpc' - 默认值:'grpc' - 选择考虑: - http:更好的兼容性和调试 - grpc:更好的性能和流式处理 2. 服务端点 endpoint: 追踪接收端点的地址 - 格式:<host>:<port> - 示例: endpoint: "jaeger-collector:4317" # gRPC endpoint: "jaeger-collector:4318" # HTTP 3. 采样策略 sampling_fraction: 追踪采样概率 - 类型:浮点数,范围 0 到 1 - 默认值:0(不采样) - 配置示例: sampling_fraction: 0.1 # 10% 采样率 sampling_fraction: 0.5 # 50% 采样率 sampling_fraction: 1.0 # 100% 采样率(所有请求) 4. 安全配置 insecure: 是否使用不安全连接 - 默认值:false(使用安全连接) - 用途:在开发或测试环境可能设为 true 5. 自定义头信息 headers: HTTP/gRPC 请求的自定义头信息 headers: Authorization: "Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIs..." X-Environment: "production" X-Service-Name: "prometheus" 6. 数据压缩 compression: 数据压缩类型 - 支持类型:gzip - 用途:减少网络传输开销 compression: "gzip" 7. 超时设置 timeout: 每批导出的最大等待时间 - 默认值:10s - 场景:网络慢或后端处理慢时可适当增加 8. TLS 配置 tls_config: TLS 安全连接配置 tls_config: cert_file: "/path/to/cert.pem" key_file: "/path/to/key.pem" ca_file: "/path/to/ca.pem" insecure_skip_verify: false 完整配置示例 Jaeger 集成 tracing_config: client_type: "grpc" endpoint: "jaeger-collector:4317" sampling_fraction: 0.1 insecure: false compression: "gzip" timeout: "30s" headers: X-Service: "prometheus-server" Tempo 集成 tracing_config: client_type: "http" endpoint: "grafana-tempo:4318" sampling_fraction: 0.05 insecure: false timeout: "15s" tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/ssl/certs/ca.pem" 典型使用场景 1. 性能监控 - 监控 Prometheus 查询的执行时间 - 识别慢查询和性能瓶颈 2. 故障诊断 - 追踪请求的完整执行路径 - 识别分布式系统中的问题根因 3. 运维优化 - 了解系统间的调用关系 - 优化资源使用和请求路由 启用功能 需要在启动参数中启用: prometheus --enable-feature=tracing 这个配置为 Prometheus 提供了现代分布式系统中的可观测性能力,使其能够融入现有的微服务追踪体系。