Spark - Overview
MapReduce概述 MapReduce 通过简单的 Map 和 Reduce 的抽象提供了一个编程模型 可以在一个由上百台机器组成的集群上并发处理大量的数据集,而把计算细节隐藏起来 各种各样的复杂数据处理都可以分解为 Map 和 Reduce 的基本元素 复杂的数据处理可以分解成由多个 Job(包含一个 Mapper 和一个 Reducer)组成的 DAG 然后,将每个 Mapper 和 Reducer 放到 Hadoop 集群上执行,得到最终结果 不足 高昂的维护成本 时间性能不达标 MapReduce 模型的抽象层次低 大量的底层逻辑需要开发者手工完成 - 用汇编语言开发游戏 只提供 Map 和 Reduce 操作 很多现实的数据处理场景并不适合用这个模型来描述 实现复杂的操作需要技巧,让整个工程变得庞大且难以维护 维护一个多任务协调的状态机成本很高,且扩展性很差 在 Hadoop 中,每个 Job 的计算结果都会存储在 HDFS 文件存储系统中 每一步计算都要进行硬盘的读取和写入,大大增加了系统的延迟 MapReduce 对于迭代算法的处理性能很差,而且非常耗资源 因...
Big Data - Kappa
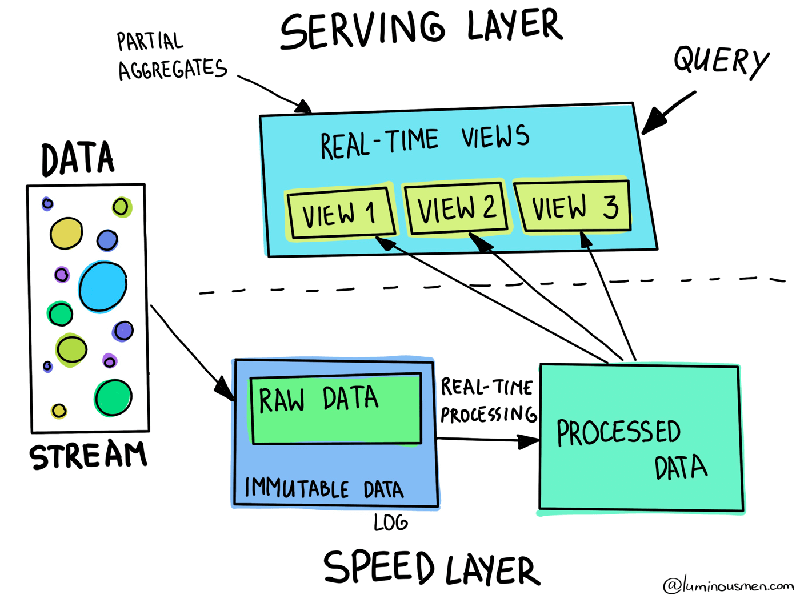
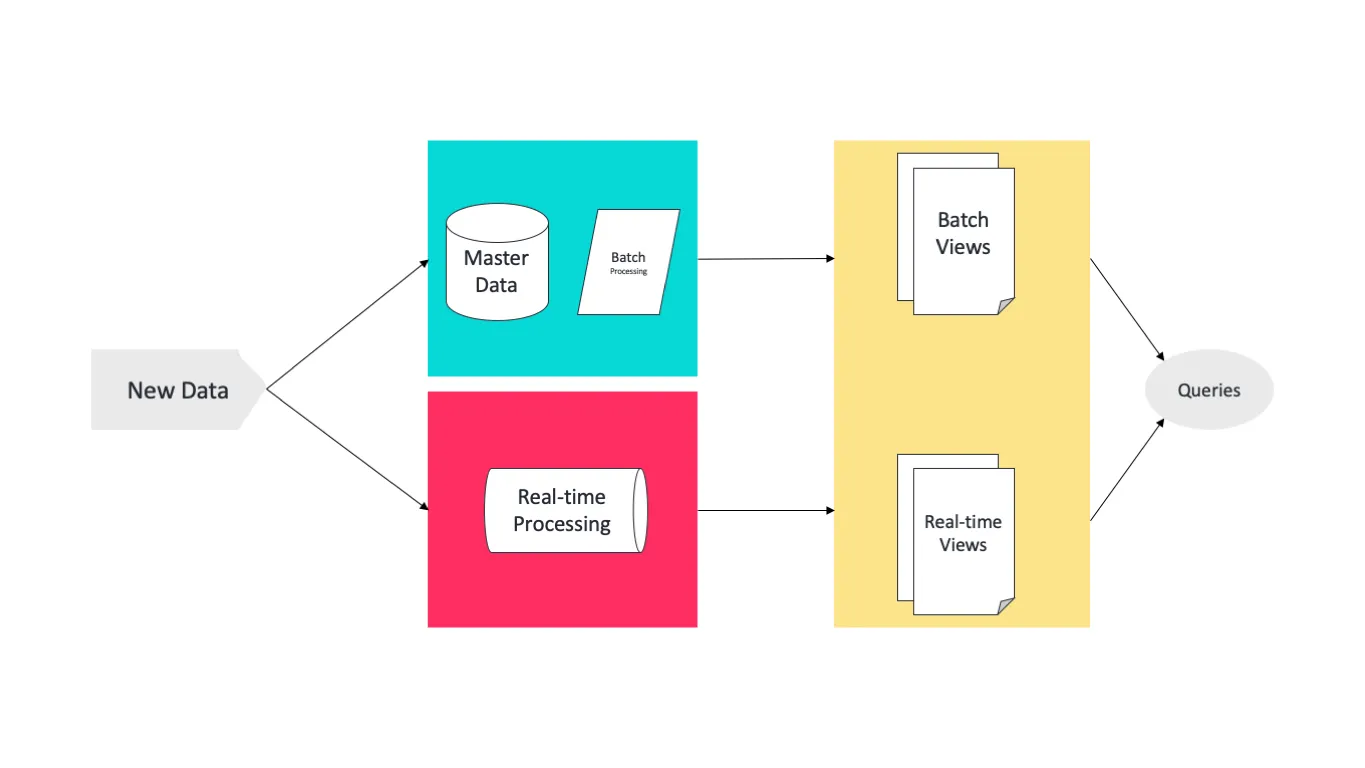
Lambda概述 Lambda 架构结合了批处理和流处理的架构思想 将进入系统的大规模数据同时送入两套架构层中,即 Batch Layer 和 Speed Layer 同时产生两套数据结果并存入 Serving Layer 中 优点 Batch Layer 有很好的容错性,同时由于保存着所有的历史记录,使得产生的数据具有很好的准确性 Speed Layer 可以及时处理流入的数据,具有低延迟性 最终 Serving Layer 将两套数据结合,并生成一个完整的数据视图提供给用户 Lambda 架构也具有很好的灵活性,可以将不同开源组件嵌入到该架构中 不足 使用 Lambda 架构,需要维护两个复杂的分布式系统,并保证它们逻辑上产生相同的结果输出到 Serving Layer 在分布式框架中进行编程是非常复杂的,尤其需要对不同的框架进行专门的优化 – 高昂的维护成本 维护 Lambda 架构的复杂性 – 同时维护两套系统架构 方向 - 改进其中一层的架构,让其具有另一层架构的特性 Kappa架构 Apache Kafka 具有永久保存数据日志的功能,基于该特性,可以让 Speed Laye...
Big Data - Lambda
Architecture Batch Layer Batch Layer 存储管理主数据集(不可变数据集)和预先批处理好计算好的视图 Batch Layer 使用可处理大量数据的分布式处理系统预先计算结果 通过处理所有的已有历史数据来实现数据的准确性 基于完整的数据集来重新计算,能够修复任何错误,然后更新现有的数据视图 输出通常存储在只读数据库中,更新则完全取代现有的预先计算好的视图 Speed Layer Speed Layer 会实时处理新来的大数据 Speed Layer 通过提供最新数据的实时视图来最小化延迟 Speed Layer 生成的数据视图可能不如 Batch Layer 最终生成的视图那么准确和完整 在收到数据后立即可用,而当同样的数据被 Batch Layer 处理完成后,在 Speed Layer 的数据可以被替换掉 本质上,Speed Layer 弥补了 Batch Layer 所导致的数据视图滞后 Serving Layer 所有在 Batch Layer 和 Speed Layer 处理完的结果都输出存储在 Serving Layer 中 Serving La...
Big Data - CAP
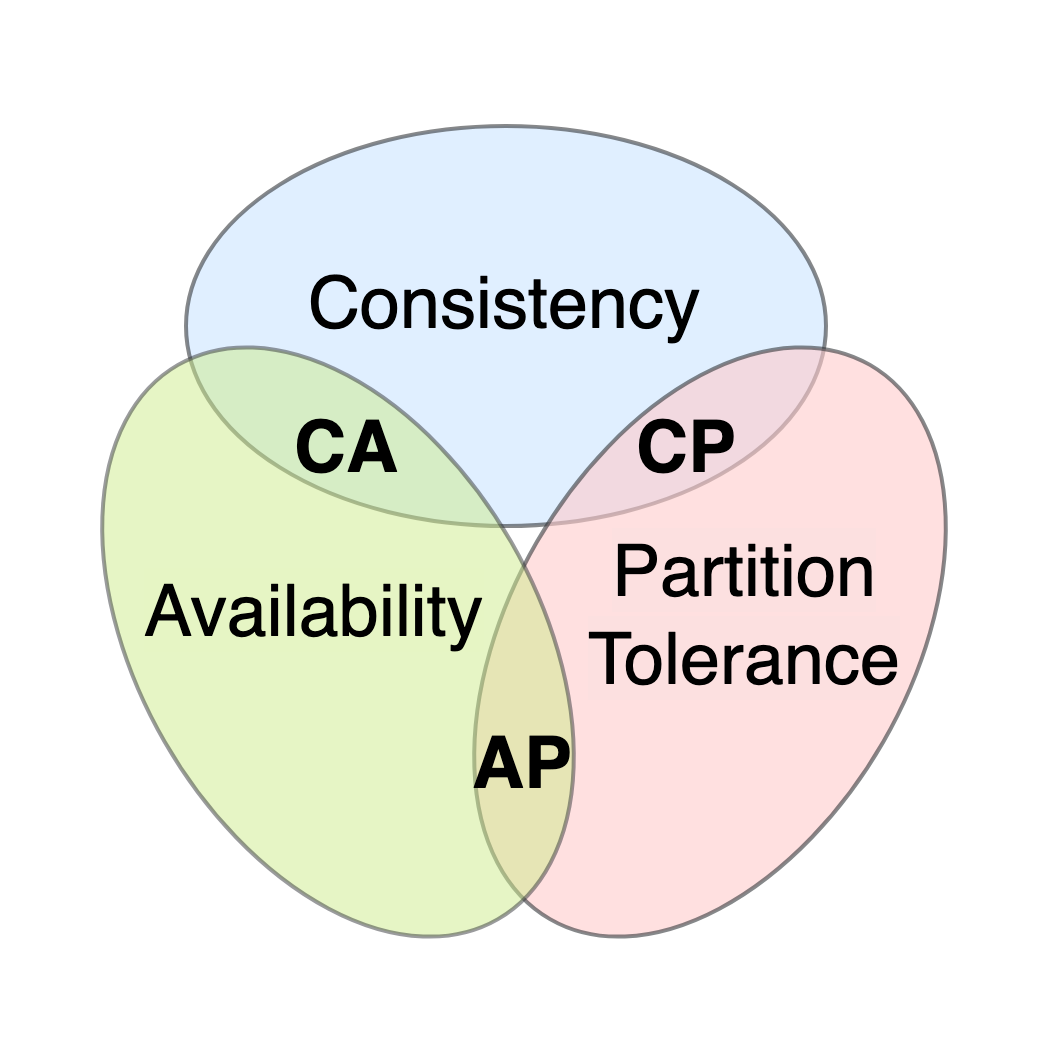
CAP 在任意的分布式系统中,最多只能同时满足两个:Consistency、Availability、Partition-tolerance Consistency Consistency 指的是 Linearizability Consistency 在 Linearizability Consistency 的保证下,所有分布式环境下的操作都像在单机上一样 所有节点的状态一直是一致的 Availability 在分布式系统中,任意非故障的节点都必须对客户的请求产生响应 当系统满足 Availability 时,除非所有节点全部崩溃,不然都能返回消息 - Netflix Eureka Partition Tolerance 在一个分布式系统中,如果出现了一些故障,可能会使得部分节点之间无法连通 由于故障节点无法连通,造成整个网络会被分成几块区域 从而使数据分散在这些无法连通的区域中的情况,从而发生了分区错误 如上图,如果需要的数据只在 Sever A 中,当出现分区错误时,无法获取到数据 如果能分区容错,既即便出现这种情况,分布式系统也能容忍,并能返回消息 Partition...
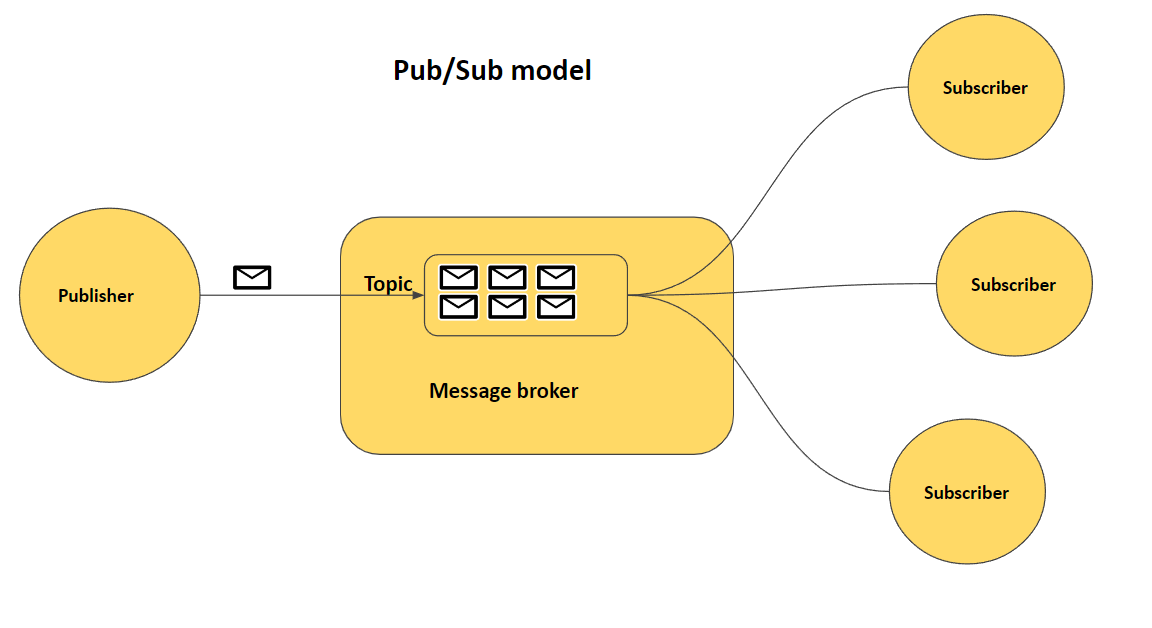
Big Data - Pub + Sub
ConceptMessage 在分布式架构中,各个组件(数据库、浏览器、服务端)需要相互沟通 各个组件依靠通过发送消息相互通信 消息可以是任意格式 Message Queue 消息队列在发布订阅模式中起到一个持久化缓冲(Durable Buffer)的作用 消息的发送方可以发送任意消息到消息队列 消息队列在接收到消息后将消息保存好 直到消息的接收方确认已经从队列消费该消息,才会将该消息从消息队列中删除 某些消息队列支持自定义消息的保留时间 - Apache Kafka Pub-Sub概述 消息的发送方可以将消息异步地发送给一个系统中的不同组件,而无需知道接收方是谁 发送方被称为 Publisher,而接收方被称为 Subscriber 可以有任意多个 Publisher,也可以有任意多个 Subscriber 优点 松耦合 高伸缩性 - 消息队列可以作为独立的数据存储中心而存在 组件通信更简洁 缺点 无法保证 Publisher 发布的消息一定会送达 Subscriber Apache Kafka 消息的发送方被称为 Producer,而消息的接收方被称为 Con...
Big Data - Workflow
Workflow 将多种不同的处理模块连接在一起,最后得出一个 DAG,称为一个 Workflow System 在 Workflow System 中,有对应的设计模式 Copier Pattern 将单个数据处理模块中的数据,完整地复制到两个或更多的数据处理模块中,然后再由不同的数据处理模块进行处理 适用场景 - 需要对同一个数据集采取多种不同的数据处理转换 - 多个数据处理模块可以并行处理 Filter Pattern 过滤掉不符合特定条件的数据 在数据集通过 Filter 后,数据集会缩减到只剩下符合条件的数据 适用场景 - 需要针对一个数据集中某些特定的数据采取数据处理 Splitter Pattern 将数据集中的数据分类为不同的类别来进行分别处理 分离模式不会过滤任何数据,只是将原来的数据集分组 同样的数据,可以被划分到不同的数据处理模块 Joiner Pattern 将多个不同的数据集转换集中在一起,成为一个总数据集 然后将总数据集放在一个工作流中进行处理
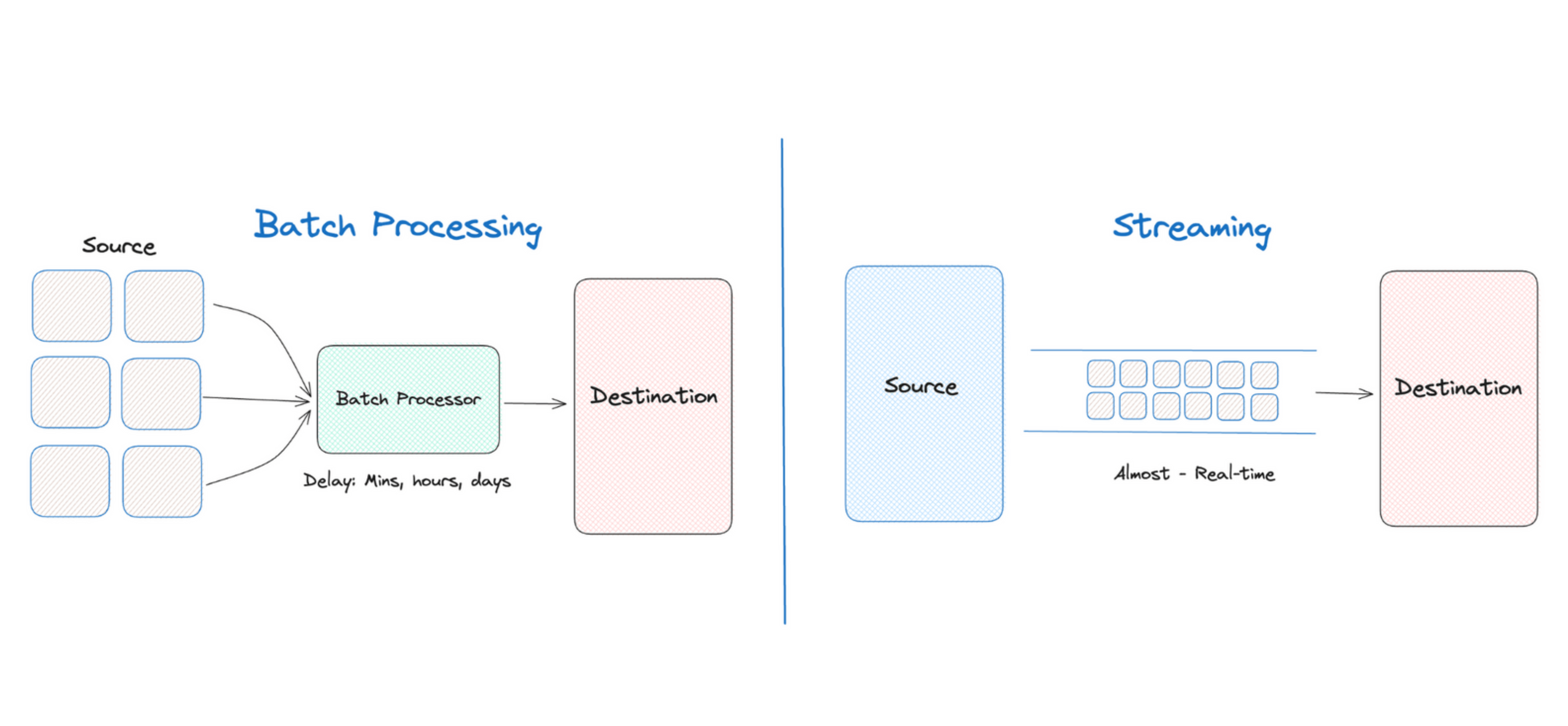
Big Data - Batch + Stream
ConceptUnbounded vs Bounded 有界数据是无界数据的一个子集 无界数据是一种不断增长,是无限的数据集,无法判定何时停止发送 - Streaming Data 有界数据是一种有限的数据集 Event Time vs Precessing Time Time Domain Desc 事件时间 - Event Time 一个数据实际产生的时间点 处理时间 - Precessing Time 处理数据的系统架构实际接收到这个数据的时间点 Batching 数据的批处理 - 一系列相关联的任务按顺序(或并行)一个接一个地执行 批处理的输入是在一段时间内已经收集保存好的数据 每次批处理所产生的输出可以作为下一次批处理的输入 - Pipeline 绝大部分情况下,批处理的输入输出都是有界数据,更多关心的数据的事件时间 批处理任务一般会以定时任务的形态存在 应用场景 - 日志分析、计费应用、数据仓库 开源项目 - Apache Hadoop、Apache Spark 缺点 - 高延迟性 Streaming 数据的流处理 - 系统需要接收并处理一系列连续不断变化的数据...
Big Data - Distributed System
SLA Service-Level Agreement - 系统服务提供者对客户的一个服务承诺 Availabilty 可用性指的是系统服务能正常运行所占的时间百分比 对许多系统来说,99.99% 可以被认为高可用性 - 中断时间≈ 50 分钟/年 Accuracy 是否允许某些数据不准确或者丢失,如果允许发生,用户可以接受的概率 不同系统平台会用不同的指标去定义准确性,常用的是 Error Rate $$错误率=\frac{导致系统产生内部错误的有效请求数}{期间的有效请求总数}$$ Case 以分钟为单位,每个月的 Error Rate 超过 5% 的时间少于 0.1% 以 5 分钟为单位,Error Rate 不会超过 0.1% 评估系统准确性 性能测试 查看系统日志 Capacity 系统容量通常指的是系统能够支持的预期负载量是多少,一般会以每秒的请求数为单位来表示 QPS - Queries Per Second RPS - Requests Per Second 定义 Capacity 的方式 - Throttling / Perf...
RAG - Qdrant
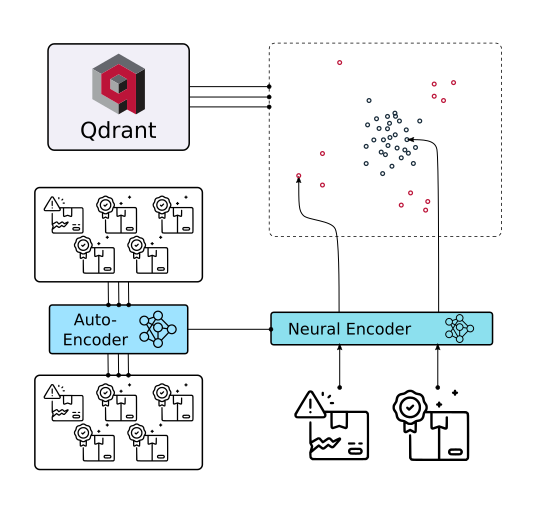
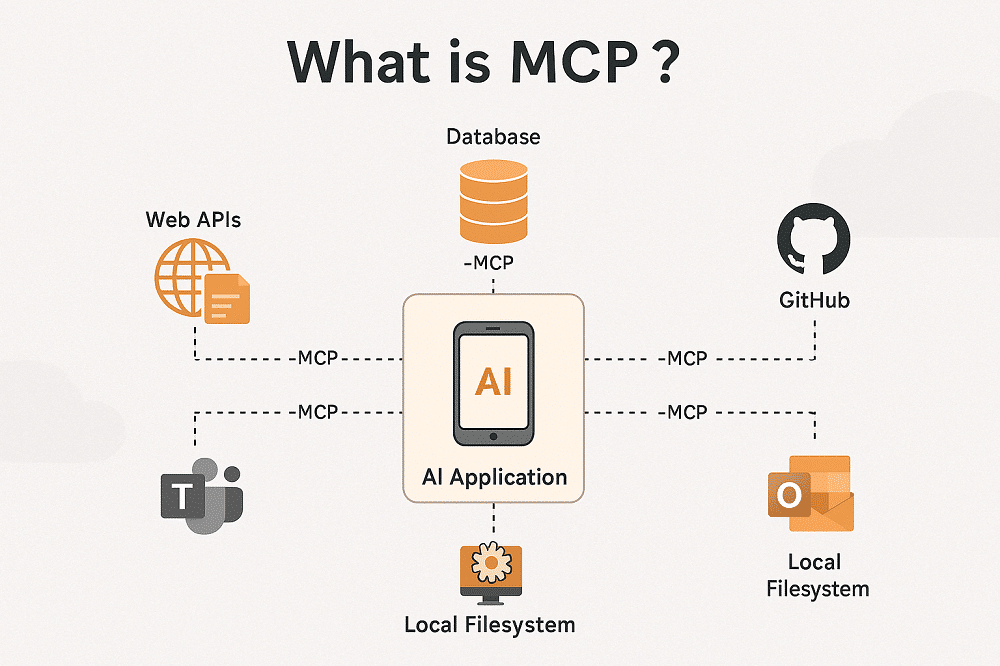
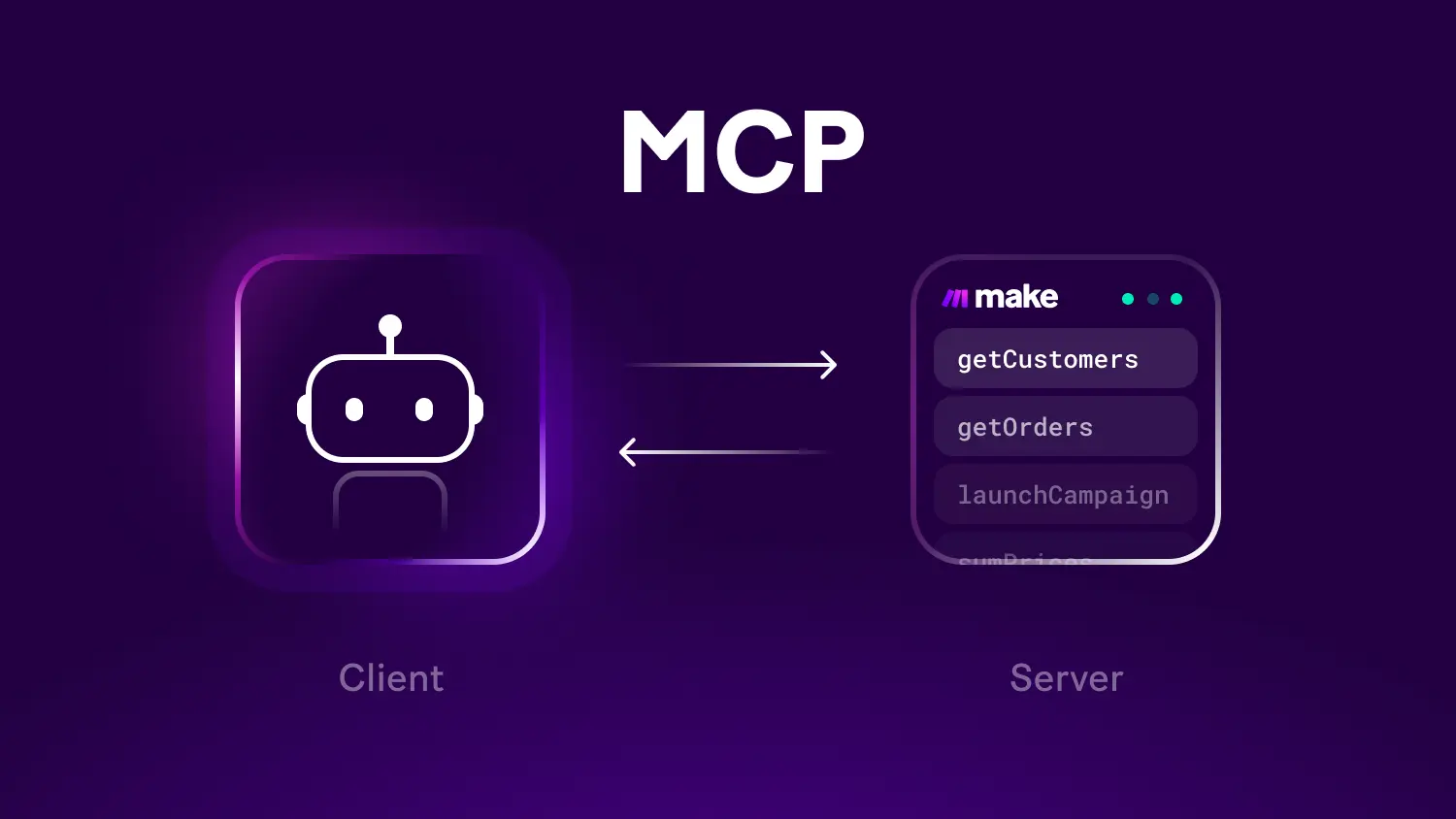
Features Getting StartedIntroduction Vector databases are a relatively new way for interacting with abstract data representations derived from opaque machine learning models such as deep learning architectures. These representations are often called vectors or embeddings and they are a compressed version of the data used to train a machine learning model to accomplish a task like sentiment analysis, speech recognition, object detection, and many others. What is Qdrant? Qdrant “is a vector similarity s...
Python - Debug + Profile
pdb pdb 是 Python 自带的调试库,为 Python 程序提供交互式的源代码调试功能,是命令行版本的 IDE 断点调试器 Instruction Desc p print n next - step over l list - show source code context s step into r stop out - 继续执行,直到当前函数完成后返回 `b [ ([filename:]lineno function) [, condition] ]` c continue - 一直执行程序,直到遇到下一个断点 step into - --Call-- + --Return-- cProfile 瓶颈在于 fib 函数 Item Desc ncalls 相应代码/函数被调用的次数 tottime 相应代码/函数总共执行所需的时间(不包括它调用其它代码/函数的执行时间) tottime percall tottime / ncalls cumtime ...