本文将通过JOL分析Java对象的内存布局,包括基本使用、字节对齐、实例域重排序、继承、继承栅栏、继承对齐等内容
代码托管在https://github.com/zhongmingmao/java_object_layout
Maven依赖
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.jol</groupId>
<artifactId>jol-core</artifactId>
<version>0.8</version>
</dependency>
|
基本使用
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public class JOLSample_01_Basic {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(A.class).toPrintable());
}
public static class A {
boolean f;
}
}
|
运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| # Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
me.zhongmingmao.jol.JOLSample_01_Basic$A object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
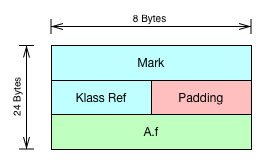
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 1 boolean A.f N/A
13 3 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 16 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 3 bytes external = 3 bytes total
|
对象布局

分析
64-bit HotSpot JVM默认开启指针压缩,Mark Word占用8 Bytes,Klass Ref占用4 Bytes,对象头总共占据了12 Bytes(如果是数组对象,对象头还会包括4 Bytes的Array Length,总共占据16 Bytes)64-bit HotSpot JVM是8 Bytes对齐,因此有3 Byte的字节填充(Padding)
字节对齐
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public class JOLSample_02_Alignment {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(A.class).toPrintable());
}
public static class A {
long f;
}
}
|
运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| # Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
me.zhongmingmao.jol.JOLSample_02_Alignment$A object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 4 (alignment/padding gap)
16 8 long A.f N/A
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 4 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 4 bytes total
|
对象布局

分析
a.f是long类型,占用8 Bytes,由于8 Bytes字节对齐的限制,无法放入12~15的位置,因此12~15只能是Paddinga.f顺延到16~23的位置
实例域重排序
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public class JOLSample_03_Packing {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(A.class).toPrintable());
}
public static class A {
boolean bo1, bo2;
byte b1, b2;
char c1, c2;
double d1, d2;
float f1, f2;
int i1, i2;
long l1, l2;
short s1, s2;
}
}
|
运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| # Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
me.zhongmingmao.jol.JOLSample_03_Packing$A object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 4 float A.f1 N/A
16 8 double A.d1 N/A
24 8 double A.d2 N/A
32 8 long A.l1 N/A
40 8 long A.l2 N/A
48 4 float A.f2 N/A
52 4 int A.i1 N/A
56 4 int A.i2 N/A
60 2 char A.c1 N/A
62 2 char A.c2 N/A
64 2 short A.s1 N/A
66 2 short A.s2 N/A
68 1 boolean A.bo1 N/A
69 1 boolean A.bo2 N/A
70 1 byte A.b1 N/A
71 1 byte A.b2 N/A
Instance size: 72 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total
|
对象布局

分析
- 「对象内存布局 - Instrumentation + sa-jdi 实例分析」也存在类似的实例
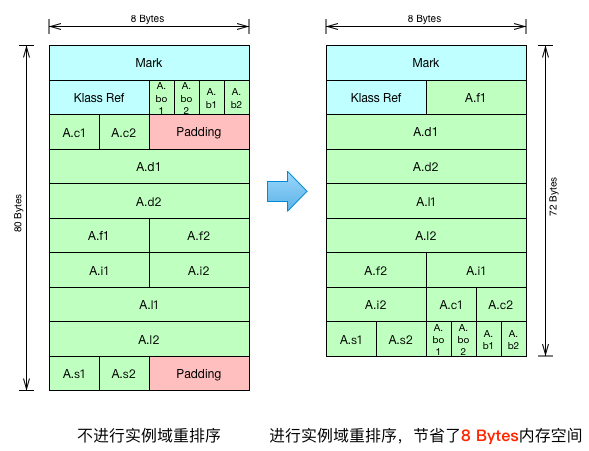
实例域重排序是为了让内存更紧凑- 重排序规则:按照
域占用空间大小来倒排,8->4->2->1,即double/long->int/float->short/char->boolean/byte->reference
- 如果间隙能容纳
占用空间更小的实例域,则将该间隙分配给该实例域,因此A.f1会排在了A.d1前面
- 由上面左右图对比可知,进行了实例域重排序后,节省了
8 Bytes的内存空间
- 由于实例域重排序,也导致了实例域在
内存中的顺序和声明的顺序往往是不一致的
继承
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public class JOLSample_04_Inheritance {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(C.class).toPrintable());
}
public static class A {
int a;
}
public static class B extends A {
int b;
}
public static class C extends B {
int c;
}
}
|
运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| # Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
me.zhongmingmao.jol.JOLSample_04_Inheritance$C object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
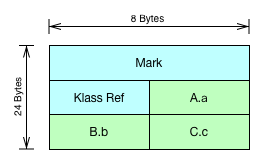
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 4 int A.a N/A
16 4 int B.b N/A
20 4 int C.c N/A
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 0 bytes external = 0 bytes total
|
对象布局

分析
- 在继承关系
C->B->A中,父类的实例域必然排在子类的实例域之前
继承栅栏
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public class JOLSample_05_InheritanceBarrier {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(C.class).toPrintable());
}
public static class A {
long a;
}
public static class B extends A {
long b;
}
public static class C extends B {
long c;
int d;
}
}
|
运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| # Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
me.zhongmingmao.jol.JOLSample_05_InheritanceBarrier$C object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
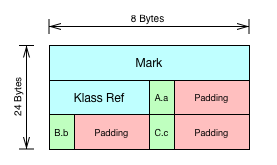
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 4 (alignment/padding gap)
16 8 long A.a N/A
24 8 long B.b N/A
32 8 long C.c N/A
40 4 int C.d N/A
44 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 48 bytes
Space losses: 4 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 8 bytes total
|
对象布局

分析
- 继承栅栏(
inheritance barrier)通俗点就是在继承关系中,分配当前类的实例域时,Hotspot JVM不会考虑在之前可能存在的内存间隙,实例域的重排序仅限于当前类,因此父类的实例域必然排在子类的实例域之前
- 因此
C.d不会被提升到12的位置
继承对齐
继承对齐只是我个人的表述,指的是在继承关系中,Hotspot JVM会通过Padding的的方式将每个类自身定义的实例域总空间填充为引用大小(4 Bytes/8 Bytes)的整数倍
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public class JOLSample_06_Gaps {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
out.println(VM.current().details());
out.println(ClassLayout.parseClass(C.class).toPrintable());
}
public static class A {
boolean a;
}
public static class B extends A {
boolean b;
}
public static class C extends B {
boolean c;
}
}
|
运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| # Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
me.zhongmingmao.jol.JOLSample_06_Gaps$C object internals:
OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 12 (object header) N/A
12 1 boolean A.a N/A
13 3 (alignment/padding gap)
16 1 boolean B.b N/A
17 3 (alignment/padding gap)
20 1 boolean C.c N/A
21 3 (loss due to the next object alignment)
Instance size: 24 bytes
Space losses: 6 bytes internal + 3 bytes external = 9 bytes total
|
对象布局

分析
64-bit Hotspot JVM默认是开启指针压缩,因为引用大小为4 Bytes- 由于
继承补全的限制,因此在B.b没有存放在13的位置,而是等A继承对齐后,存放在16的位置